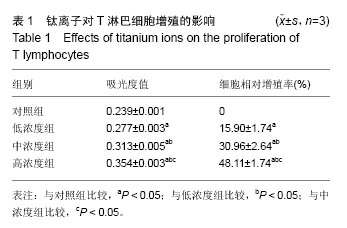
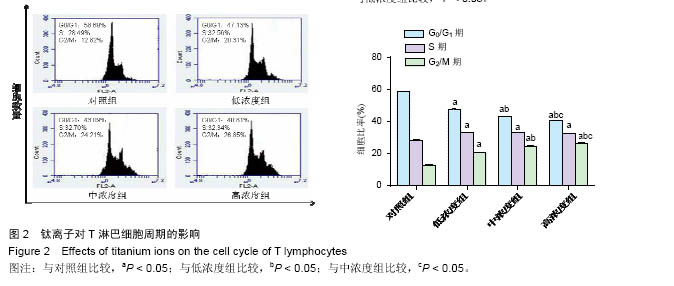
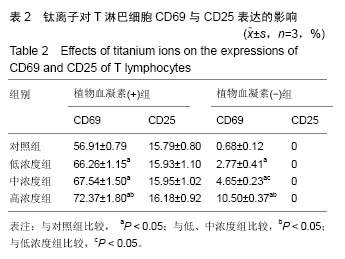
| [1]Branemark PI.Osseointegration and its experimental background.J Prosthet Dent.1983;50(3):399-410.[2]Astrand P,Nord PG,Branemark PI.Titanium implants and onlay bone graft to the atrophic edentulous maxilla: a 3-year longitudinal study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1996;25(1):25-29.[3]王方辉,张姗姗,舒静媛,等.纯钛种植体表面改性对骨结合的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(52): 8491-8497.[4]Rodrigues DC,Valderrama P,Wilson TG,et al.Titanium Corrosion Mechanisms in the Oral Environment: A Retrieval Study.Materials.2013;6(11):5258-5274.[5]Reclaru L,Meyer JM.Study of corrosion between a titanium implant and dental alloys.J Dent. 1994;22(3): 159-168.[6]黄伟城,吴泽键,陈伟生.钛种植体基台和不同合金的体外耐腐蚀性能[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(30):4784- 4789.[7]Martin SF.Tlymphocyte-mediated immune responses to chemical haptens and metal ions: implications for allergic and autoimmune disease.Int Arch Allergy Immunol.2004;134(3):186-198.[8]Goutam M,Giriyapura C,Mishra SK,et al.Titanium allergy: a literature review. Indian J Dermatol. 2014; 59(6):630.[9]Siddiqi A,Payne AG,De Silva RK,et al.Titanium allergy: could it affect dental implant integration?Clin Oral Implants Res.2011;22(7):673-680.[10]Wooley PH,Schwarz EM.Aseptic loosening.Gene Therapy.2004;11(4):402-407.[11]Wachi T,Shuto T,Shinohara Y,et al.Release of titanium ions from an implant surface and their effect on cytokine production related to alveolar bone resorption. Toxicology.2015;327:1-9.[12]Schliephake H,Reiss G,Urban R,et al.Metal release from titanium fixtures during placement in the mandible: an experimental study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1993;8(5):502-511.[13]Lorenzo J,Horowitz M,Choi Y.Osteoimmunology: interactions of the bone and immune system.Endocr Rev.2008;29(4):403-440.[14]Takayanagi H.Inflammatory bone destruction and osteoimmunology.J Periodontal Res. 2005;40(4): 287-293.[15]Caetano-Lopes J,Canhao H,Fonseca JE. Osteoimmunology--the hidden immune regulation of bone.Autoimmun Rev.2009;8(3):250-255.[16]Arron JR, Choi Y.Bone versus immune system. Nature. 2000;408:535-536.[17]Takayanagi H.Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol.2007;7(4):292-304.[18]王林红,樊立洁,谷志远.钛离子诱导骨吸收的现象及机制[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2009,36(4):441-443,447.[19]赵文杰,戴闽,张斌,等.钛金属离子介导骨溶解机制中的炎症反应-STAT信号通路[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(4): 492-496.[20]Mine Y,Makihira S, ikawa H,et al.Impact of titanium ions on osteoblast-, osteoclast- and gingival epithelial-like cells.J Prosthodont Res.2010;54(1):1-6.[21]庞振华,陈东晖,李秋莹,等.钛离子对 Jurkat T 细胞增殖及分泌骨改建相关因子的影响[J].广东医学, 2015, 36(22):3442-3445.[22]Funato A,Yamada M,Ogawa T.Success rate, healing time, and implant stability of photofunctionalized dental implants.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28(5): 1261-1271.[23]Ettl T,Gerlach T,Schusselbauer T,et al.Bone resorption and complications in alveolar distraction osteogenesis.Clin Oral Investig.2010;14(5):481-489.[24]Messer RL,Tackas G,Mickalonis J,et al.Corrosion of machined titanium dental implants under inflammatory conditions.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2009; 88(2):474-481.[25]陈灼庚,唐礼.种植体钛离子释放对骨及骨周免疫的影响[J].广东牙病防治,2015,23(1):51-54.[26]Chan E,Cadosch D,Gautschi OP,et al.Influence of metal ions on human lymphocytes and the generation of titanium-specific T-lymphocytes.J Appl Biomater Biomech.2011;9(2):137-143.[27]Suska F,Esposito M,Gretzer C,et al.IL-1alpha, IL-1beta and TNF-alpha secretion during in vivo/ex vivo cellular interactions with titanium and copper. Biomaterials. 2003;24(3):461-468.[28]Cadosch D,Sutanto M,Chan E,et al.Titanium uptake, induction of RANK-L expression, and enhanced proliferation of human T-lymphocytes.J Orthop Res. 2010;28(3):341-347.[29]Abraham RT,Weiss A.Jurkat T cells and development of the T-cell receptor signalling paradigm.Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4(4):301-308.[30]Fujii T,Yamada S,Watanabe Y,et al.Induction of choline acetyltransferase mRNA in human mononuclear leukocytes stimulated by phytohemagglutinin, a T-cell activator. J Neuroimmunol.1998;82(1):101-107.[31]Fu Y,Zhang Y,Chang X,et al.Systemic immune effects of titanium dioxide nanoparticles after repeated intratracheal instillation in rat.Int J Mol Sci.2014;15(4): 6961-6973.[32]Alenzi FQ.Links between apoptosis, proliferation and the cell cycle. Br J Biomed Sci.2004;61(2):99-102.[33]Berridge M.Cell Cycle and Proliferation.Cell Signalling Biology.2014;2014(1):1-45.[34]Sancho D,Gomez M,Sanchez-Madrid F.CD69 is an immunoregulatory molecule induced following activation. Trends Immunol.2005;26(3):136-140.[35]Lindsey WB,Lowdell MW,Marti GE,et al.CD69 expression as an index of T-cell function: assay standardization, validation and use in monitoring immune recovery. Cytotherapy.2007;9(2):123-132.[36]Sang X,Fei M,Sheng L,et al.Immunomodulatory effects in the spleen-injured mice following exposure to titanium dioxide nanoparticles.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(10):3562-3572.[37]Thornton AM,Shevach EM.CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production. J Exp Med.1998;188(2):287-296.[38]Gonzalez-Garcia A,Merida I,Martinez AC,et al. Intermediate affinity interleukin-2 receptor mediates survival via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem.1997;272(15):10220-10226.[39]Cachinho SC,Pu F,Hunt JA.Cytokine secretion from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells cultured in vitro with metal particles.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013; 101(4):1201-1209.[40]Li TF,Santavirta S,Waris V,et al.No lymphokines in T-cells around loosened hip prostheses.Acta Orthop Scand.2001;72(3):241-247. |
.jpg)

.jpg)