| [1] Graham TE, Yang Q, Bluher M, et al. Retinol-binding Protein 4 and Insulin Resistance in Lean, Obese, and Diabetic Subjects. N Engl J Med. 2006;354(24): 2552-2563.
[2] Yang Q, Graham TE, Mody N. Serum Retinol Binding Protein 4 Contributes to Insulin Resistance in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Nature. 2005;436(21): 356-362.
[3] 阮丹杰,王伟. 炎性因子与胰岛素抵抗的研究进展[J]. 医学综述,2009,15(4):508-511.
[4] Rauchenzauner M,Laimer M,Wiedmann M, et al.The novel insulin resistance parameters RBP4 and GLP-1 IN patients treated with valproic acid:just a sidestep? Epilepsy RES. 2013;104(3):285-288.
[5] 汤孙寅焱,毕艳.SREBP-1c 对骨骼肌 IRS-1表达调控的影响[A]. 2011CDS 论文汇编,2013.
[6] Xia M,Liu Y,Guo H,et al. Retinol binding protein 4 stimulates hepatic sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 and increases lipogenesis through the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator 1beta-dependent pathway. Hepatology. 2013;58(2):564-575.
[7] 窦梅.胰岛素抵抗主要原因及机制的研究进展[J].国外医学:卫生学分册,2009,36(3):174-178.
[8] 余芳,薛耀明,李晨钟,等.血清 IL-6、hs-CRP与妊娠期糖尿病胰岛素抵抗的关系[J].南方医科大学学报, 2007, 27(6):799-801.
[9] 翟骁,时佳子,叶周恒,等. 胰岛素抵抗与免疫细胞关联性研究[J]. 现代免疫学,2013,33(6):515-517.
[10] 薛宏峰.支气管哮喘患儿治疗前后血清GM-CSF、IL-8和IL-6联检的临床意义[J].放射免疫学杂志, 2006, 19(6): 485-486.
[11] Ploug T, Stallknecht BM, Pedersen O, et al. Effect of Endurance Training on Glucose Transport Capacity and Glucose Transporter Expression in Rat Skeletal Muscle. Am J Phys Endocrinol Metab.1990; 259(6): E778-E786.
[12] Mather K. Surrogate Measures of Insulin Resistance: of Rats, Mice, and Men. Am J Phys Endocrinol Metab. 2009;296(2): E398-E399.
[13] 谢铁男,岳瑛,扈聪.多囊卵巢综合征胰岛素抵抗患者 Gly972Arg 多态性与子宫内膜胰岛素受体底物1表达的关系[J].中国免疫学杂志,2012,28(3):226-230.
[14] Lim S, Choi SH, Jeong IK, et al. Insulin-sensitizing Effects of Exercise on Adiponectin and Retinol-binding Protein-4 Concentrations in Young and Middle-aged Women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(6): 2263-2268.
[15] 刘茜,刘向国,武松.肺气肿肺气虚证模型大鼠脾脏指数、胸腺指数变化的实验研究[J].甘肃中医学院学报, 2006, 23(1):20-22.
[16] Fernández- Real JM, Broch M, Vendrell J, et al. Interleukin- 6 Gene Polymorphism and Lipid Abnormalities in Healthy Subjects. J Clin Endo Meta. 2000;85: 334-339.
[17] Goyenechea E, Parra MD, Martinez Hernandez JA. Role of IL-6 and Its-174G→C Polymorphism in Weight Management and in the Metabolic Comorbidities Associated with Obesity. An Sist Sanit Navar. 2005;28: 357-366.
[18] Das UN. Anti-Inflammatory Nature of Exercise. Nutrition. 2004;20(3): 323-326.
[19] 秦志琳.RBP4、Leptin与2型糖尿病及炎症的相关研究[D].广西医科大学硕士论文,2007.
[20] 钟振民.火针“火郁发之”疗法对带状疱疹急性期患者CD4、CD8、IL-6的影响[D].广州中医药大学硕士论文, 2012.
[21] Das UN. Is Obesity an Inflammatory Molecule? Nut. 2001;17(5):409-413.
[22] Mohamedali V, Goodrick S, Rawesh A, et al. Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Releases Interleukin-6, But Not Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha, in Vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(12):4196-4200.
[23] Vozarova B, Weyer C, Hanson K, et al. Circulating Interleukin-6 In Relation to Adiposity, Insulin Action, and Insulin Secretion. Obesity Res. 2001;9(7): 414-417.
[24] Cui J, Bai Y, Li M, et al. Effects of different intensity exercise on blood glucose, adolescent obesity rats insulin sensitivity and RBP4. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu. 2014;43(4): 535-540.
[25] Goktas W. Visfatin and RBP4 gene expression levels in different adipose tissues and insulin resistance. BMC Proc. 2012;6(Suppl 3):17.
[26] Cheng J, Song ZY, Pu L, et al. Retinol binding protein 4 affects the adipogenesis of porcine preadipocytes through insulin signaling pathways. Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;91:236-243.
[27] Mehran AE, Templeman NM, Brigidi GS, et al. Hyperinsulinemia drives diet-induced obesity independently of brain insulin production. Cell Metab. 2012;16:723-737.
[28] Wu YH, Shi DM, Niu HQ, et al. Association among retinol-binding protein 4, small dense LDL cholesterol and oxidized LDL levels in dyslipidemia subjects. Clin. Biochem. 2012;45:619-622.
[29] Jialal I, Adams-Huet B, Duong F, et al. Relationship between retinol-binding protein-4/adiponectin and leptin/adiponectin ratios with insulin resistance and inflammation. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2014;12(4): 227-230.
[30] Hu H, Xu M, Qi R, et al. Sitagliptin downregulates retinol-binding protein 4 and upregulates glucose transporter type 4 expression in a type 2 diabetes mellitus rat model. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(10): 17902-17911.
[31] Lin CJ, Chu NF, Hung YJ, et al. Genetic variants of retinol-binding protein 4 in adolescents are associated with liver function and inflammatory markers but not with obesity and insulin resistance. J Genet. 2015; 94(3):503-507. |
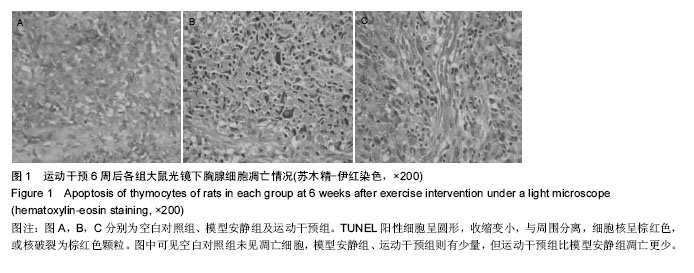
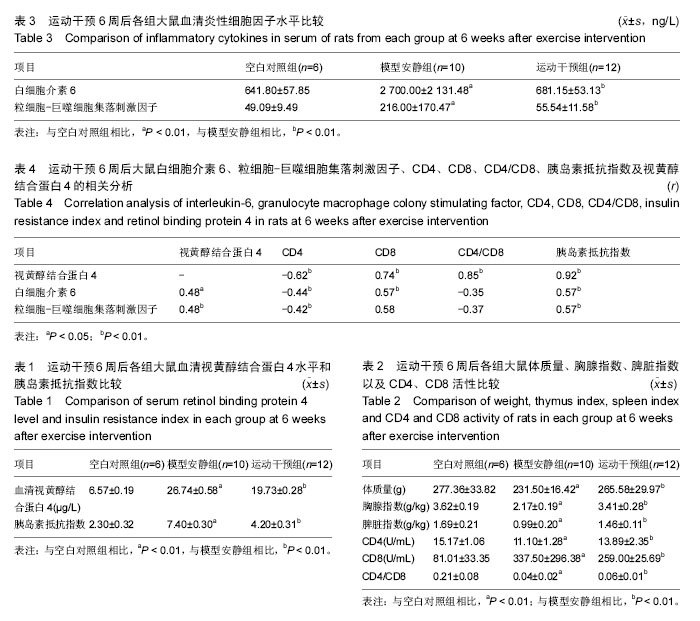
.jpg)
.jpg)