| [1] 霍振业,谢伯雅,裴建明,等.犬缺血心肌心导纳环与心电图的对照观察[J].海南医学,2002,13(1):34.
[2] Ma X,Zhang K,Li H,et al.Extracts from Astragalus membranaceus limit myocardial cell death and improve cardiac function in a rat model of myocardial ischemia.J Ethnopharmacol.2013;149(3):720-728.
[3] 沙非,温晓斐,卜丽红,等.99锝m N-2-巯基吡啶-N-氧化物与99锝m-甲氧基异丁基异腈对犬急性心肌梗死模型的对照研究[J].中华放射学杂志,2011,45(4):392-398.
[4] 王维亭,徐向伟,赵专友,等.清醒比格犬心肌梗死超急性期缺血模型研究[J].现代药物与临床,2010,25(1):35-40.
[5] Lim KS,Cha MJ,Kim JK,et al.Protective effects of protein transduction domain-metallothionein fusion proteins against hypoxia- and oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in an ischemia/reperfusion rat model.J Control Release.2013;169(3):306-312.
[6] 李峰杰,李贻奎.心肌梗死动物模型研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2013,29(1):5-10.
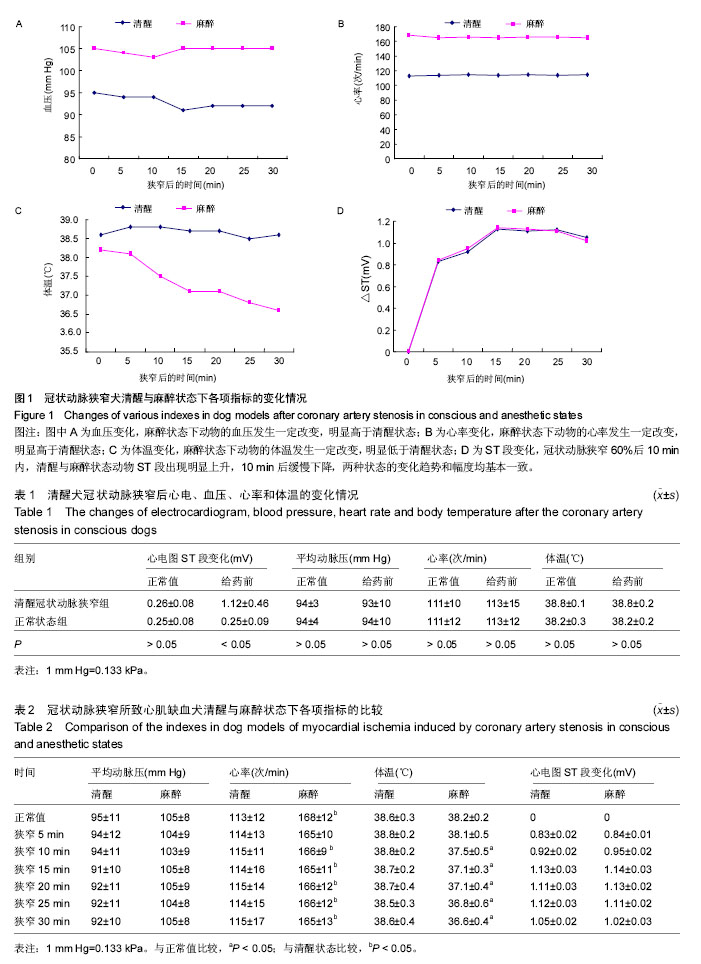
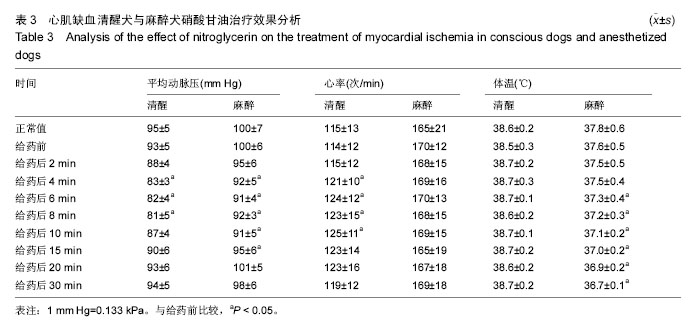
[7] 徐向伟,王维亭,赵专友,等.狭窄冠脉致犬心肌缺血模型在清醒与麻醉状态下的比较[J].药物评价研究,2010,33(1): 46-50.
[8] 金红峰,沈法荣,凌锋,等.应用聚乙烯泡沫封堵法建立Beagle犬心肌梗死模型[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2009, 25(8):1660-1661,1664.
[9] 李可,刘卫金,邹利光,等.闭胸式冠状动脉插管法建立犬急性心肌缺血模型[J].第三军医大学学报,2007,29(16): 1630-1631.
[10] Won YW,Kim JK,Cha MJ,et al.Prolongation and enhancement of the anti-apoptotic effects of PTD-Hsp27 fusion proteins using an injectable thermo-reversible gel in a rat myocardial infarction model.J Controll Release.2010;144(2):181-189.
[11] Formiga FR,Pelacho B,Garbayo E,et al.Sustained release of VEGF through PLGA microparticles improves vasculogenesis and tissue remodeling in an acute myocardial ischemia-reperfusion model.J Controll Release.2010;147(1):30-37.
[12] 刘超,赵文增,罗鸿,等.犬急性心肌梗死模型的改进[J].重庆医学,2006,35(9):823-825.
[13] Nduhirabandi F,Du Toit EF,Blackhurst D,et al.Chronic melatonin consumption prevents obesity-related metabolic abnormalities and protects the heart against myocardial ischemia and reperfusion injury in a prediabetic model of diet-induced obesity.J Pineal Res.2011;50(2):171-182.
[14] 刘建勋,马晓斌,李连达,等.地奥心血康对麻醉犬及清醒兔急性心肌梗死的影响[C].//心脑病药物临床评价专家谈, 1998:7-10.
[15] 刘素蕊,赵春生,王更银,等.冠脉结扎和介入两种方法制备犬心肌梗死模型的比较[J].中国比较医学杂志, 2011, 21(12):38-41.
[16] 宋立君,卢成志,李超,等.去肾交感神经术对心肌梗死后犬心脏氧化应激和交感神经重构的影响[J].天津医药, 2015, 43(8):864-866,867.
[17] 吴胜东,葛建军,周正春,等.犬心肌梗死模型的制备及评价[J].武警医学,2007,18(1):22-25.
[18] 崔新明,王秋静,谷欣权,等.心痛贴对急性心肌梗死犬氧化应激、心肌代谢和超微结构的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2010,30(13):1813-1814.
[19] 郭琰,郝伟,李峰杰,等.Beagle犬与杂种犬急性心肌梗死模型的比较[J].中国中药杂志,2013,38(12):2001-2004.
[20] Liehn EA,Kanzler I,Konschalla S,et al. Compartmentalized protective and detrimental effects of endogenous macrophage migration-inhibitory factor mediated by CXCR2 in a mouse model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33(9):2180-2186.
[21] 任平,黄熙,张莉,等.麻醉犬心房内注射复方川芎汤后血清中川芎嗪药时曲线双峰与血流动力学效应的关系[J].第四军医大学学报,2000,21(7):S157-S160.
[22] Popovsky J.Gradual occlusion of mesenteric vessels with ameroid clamp.Arch Surg. 1966;92(2):202-205.
[23] Wynsen JC,Kenny D,Brooks HL,et al. Regional myocardial function after repetitive brief episodes of ischemia: effect of altering the duration of the reperfusion period.Am Heart J.1991;121(5): 1331-1338.
[24] Lee BH,Kim WH,Choi MJ,et al.Chronic heart failure model in rabbits based on the concept of the Bifurcation/Trifurcation coronary artery branching pattern. Artif Organs.2002;26(4):360-365.
[25] 张晓娟,智光,陆兆龄,等.超声指导下制备犬急性心肌缺血与心肌梗死模型[J].武警医学,2009,20(5):417-420.
[26] 徐霞,陈斌.实时心肌声学造影诊断犬冠状动脉狭窄的实验研究[J].中国医师进修杂志,2011,34(z1):96-97.
[27] Zhao M,He X,Bi XY,et al.Vagal stimulation triggers peripheral vascular protection through the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in a rat model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion.Basic Res Cardiol.2013;108(3): 345.
[28] 连祺周.高位硬膜外阻滞对麻醉犬和清醒大鼠急性心肌缺血的保护作用及临床应用[D].哈尔滨医科大学,1999.
[29] Matyal R,Sakamuri S,Wang A,et al.Local infiltration of neuropeptide y as a potential therapeutic agent against apoptosis and fibrosis in a swine model of hypercholesterolemia and chronic myocardial ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol.2013;718(1-3):261-270.
[30] 周晓东,刘翠华,朱妙章,等.犬不同冠脉狭窄部位和心肌缺血范围对左室收缩功能的影响[J].心脏杂志,2000,12(6): 440-442.
[31] Gelsomino S,Luca F,Renzulli A,et al.Increased coronary blood flow and cardiac contractile efficiency with intraaortic balloon counterpulsation in a porcine model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury. ASAIO J.2011;57(5):375-381.
[32] Song Y,Huang Z,Xu J,et al.Multimodal SPION-CREKA peptide based agents for molecular imaging of microthrombus in a rat myocardial ischemia- reperfusion model.Biomaterials. 2014;35(9): 2961-2970.
[33] Marsano A,Maidhof R,Luo J,et al.The effect of controlled expression of VEGF by transduced myoblasts in a cardiac patch on vascularization in a mouse model of myocardial infarction. Biomaterials. 2013;34(2):393-401.
[34] 王秋静,路航,吕文伟,等.心痛贴对麻醉犬冠状动脉循环及心肌氧代谢的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版), 2005, 31(5):696-698.
[35] 蒋文燕,易勇.戊巴比妥钠麻醉持续时间对犬血压、体温、呼吸和心电的影响[J].四川生理科学杂志,2008,30(1): 15-17.
[36] Zhao Q,Sun C, Xu X, et al.Early use of granulocyte colony stimulating factor improves survival in a rabbit model of chronic myocardial ischemia.J Cardiol. 2013; 61(1/2):87-94.
[37] Matyal R,Chu L,Mahmood F,et al.Neuropeptide Y improves myocardial perfusion and function in a swine model of hypercholesterolemia and chronic myocardial ischemia.J Mol Cell Cardiol.2012;53(6):891-898.
[38] 李伟,付萍,陈颖丽,等.三羊益心康胶囊对麻醉犬血流动力学和心肌耗氧量的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志, 2008, 14(12):55-60.
[39] 李莲静,李七一,朱萱萱,等.冠心平对麻醉犬冠脉结扎致心肌缺血的保护作用[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2011,20(34):4337-4338,4460.
[40] 何晓雷,刘玉丽,张岩,等.清醒犬慢性充血性心力衰竭模型的血流动力学特征[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2009, 34(6): 487-491. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)