中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (35): 5688-5694.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2928
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
右美托咪定对七氟醚吸入麻醉诱导行颅脑手术围术期脑保护作用的影响:随机对照试验
刘勇攀,龚小芳
十堰市太和医院麻醉科,湖北省十堰市 442000
Effects of dexmedetomidine on perioperative brain protection in patients undergoing craniocerebral surgery under inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane: a randomized controlled study
Liu Yongpan, Gong Xiaofang
Department of Anesthesiology, Taihe Hospital, Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
右美托咪定:是高选择性α2-肾上腺素受体激动剂,通过作用于中枢神经系统和外周神经系统的α2受体产生相应的药理作用。右美托咪定还有抗焦虑、降低应激反应、稳定血流动力学、镇痛、抑制唾液腺分泌、抗寒战和利尿等作用。此外,右美托咪定与其他镇静镇痛药物联合使用时具有良好的协同效应,能显著减少其他镇静镇痛药物的使用量。
七氟醚:诱导迅速,刺激性小,血流动力学稳定,是临床广泛应用的吸入麻醉药之一。
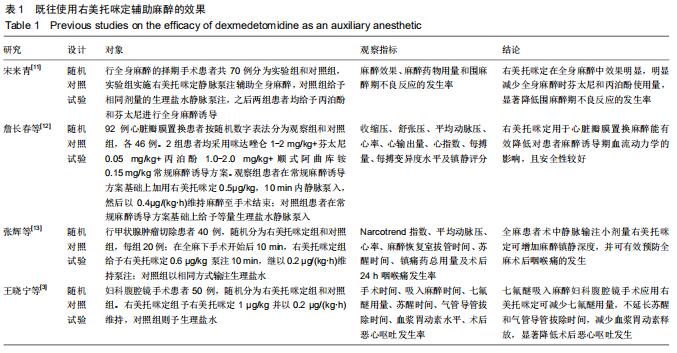
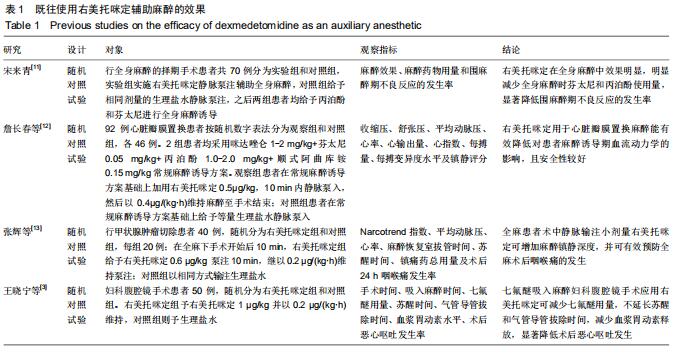
背景:颅脑手术中常使用的吸入麻醉剂是七氟醚,其具有起效速度快、循环稳定性好,且安全性高、不良反应少等优势,但是其还存在血压和心率异常以及躁动、疼痛等不良反应,因而需要一种辅助麻醉剂帮助改善不良反应。右美托咪定作为一种高效高选择性α2-肾上腺素受体激动剂,具有抗焦虑、催眠、镇痛、镇静及解交感作用,既往研究显示其可减轻七氟醚麻醉诱导后患者的躁动程度,减少围术期患者血流动力学波动,但尚缺乏在颅脑手术中进行验证。
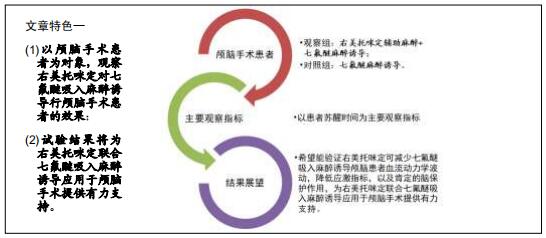
目的:观察右美托咪定对七氟醚吸入麻醉诱导行颅脑手术患者的效果。
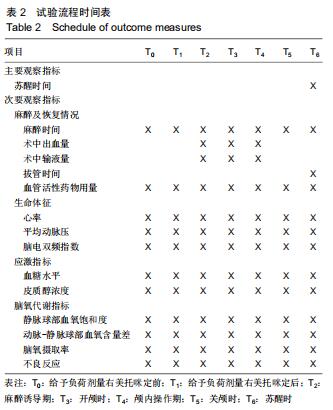
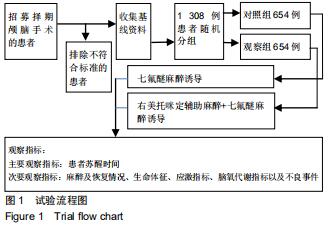
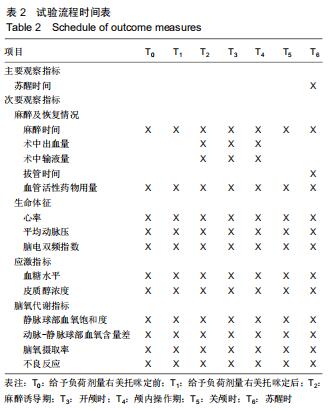
方法:此次前瞻性、单中心、随机对照试验将在中国十堰市太和医院进行,拟纳入1 308例患者,以随机数字表法分为观察组和对照组,各654例。2组均以七氟醚行麻醉诱导下进行颅脑手术。观察组麻醉诱导前15 min予负荷剂量右美托咪定1 μg/kg静脉泵注10 min,继之以0.3 μg/(kg•h)持续泵注,手术前0.5 h停药;对照组以相同方式、同等速率输注同等剂量0.9%氯化钠注射液。试验于2015-12-08经十堰市太和医院伦理审查委员会批准(批准号2015GJJ-087)。参与者对试验方案和过程均知情同意,并签署知情同意书。试验已于2020-03-02在中国临床试验注册中心进行注册(注册号:ChiCTR2000030459),注册方案版本号1.0。
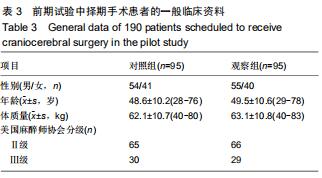
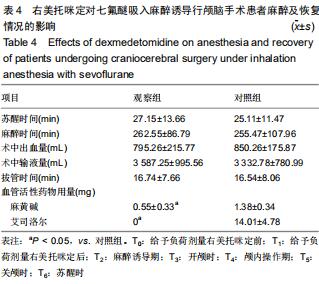
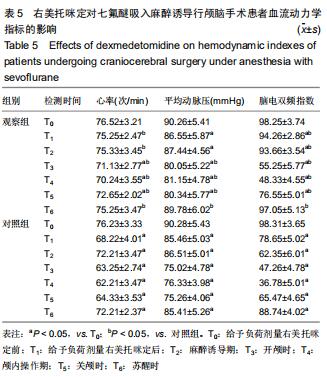
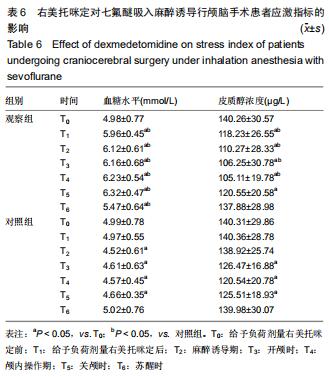
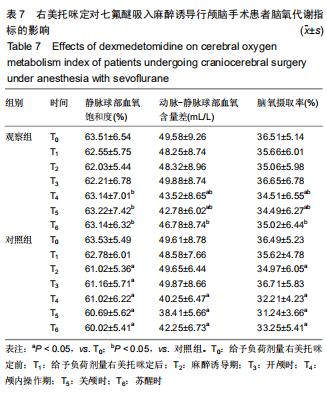
结果与结论:①试验的主要观察指标为患者苏醒时间;②试验的次要观察指标为麻醉与恢复情况以及给予负荷剂量右美托咪定前、给予负荷剂量右美托咪定后、麻醉诱导期、开颅时、颅内操作期、关颅时、苏醒时的生命体征、应激指标、脑氧代谢指标以及不良事件;③2016年3月至2017年2月进行了190例的小样本前期试验,患者随机分为对照组和观察组,各95例,分别接受七氟醚麻醉诱导以及右美托咪定辅助麻醉+七氟醚麻醉诱导,结果显示2组麻醉时间、术中出血量、术中输液量、苏醒时间、拔管时间接近(P > 0.05),但与对照组相比,观察组血管活性药物麻黄碱以及艾司洛尔的用量较低(P < 0.05),给予负荷剂量右美托咪定后、麻醉诱导期、开颅时、颅内操作期、关颅时以及苏醒时心率与脑电双频指数较高(P < 0.05),开颅时、颅内操作期、关颅时与苏醒时平均动脉压较高(P < 0.05),给予负荷剂量右美托咪定后、麻醉诱导期、开颅时、颅内操作期、关颅时以及苏醒时血糖水平较高(P < 0.05),给予负荷剂量右美托咪定后、麻醉诱导期与开颅时皮质醇浓度较低(P < 0.05),颅内操作期、关颅时以及苏醒时静脉球部血氧饱和度、动脉-静脉球部血氧含量差以及脑氧摄取率较高(P < 0.05)。试验旨在验证右美托咪定可减少七氟醚吸入麻醉诱导颅脑患者血流动力学波动,降低应激指标,以及肯定的脑保护作用,这将为右美托咪定联合七氟醚吸入麻醉诱导应用于颅脑手术提供有力支持。
ORCID: 0000-0002-2524-9449(刘勇攀)中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: