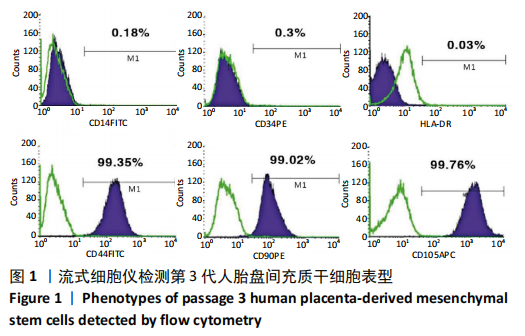
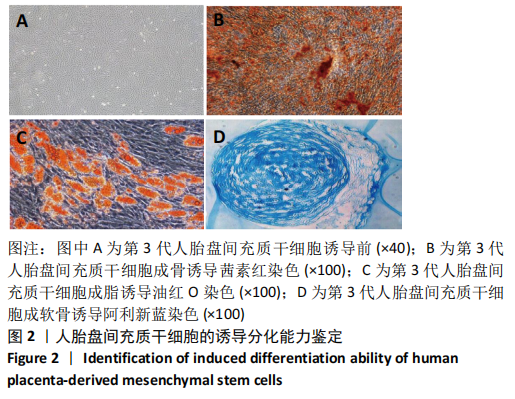
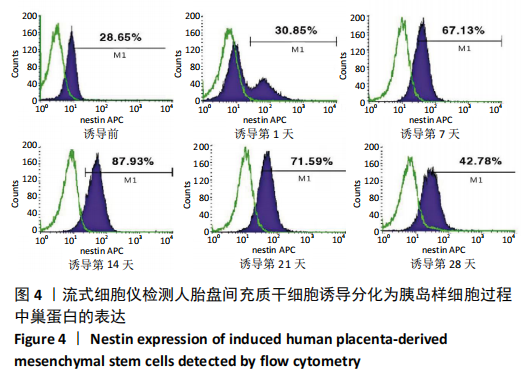
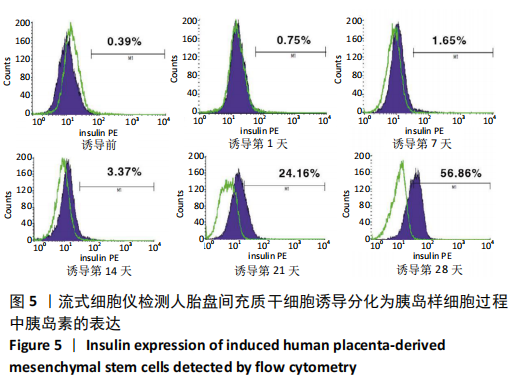
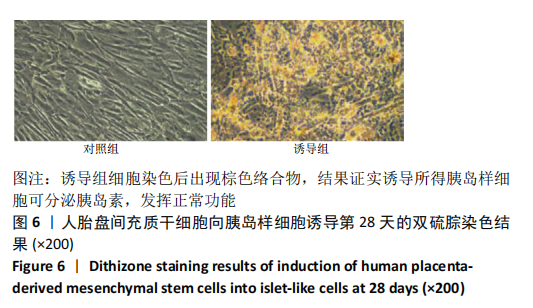
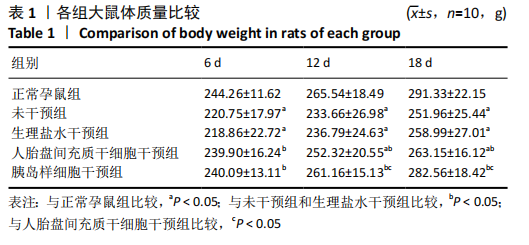
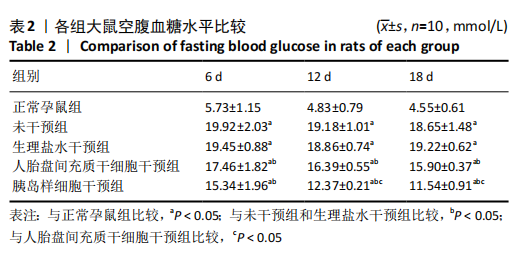
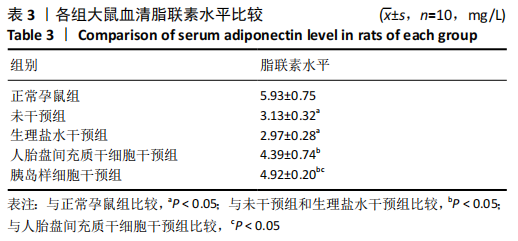
[1] DENNEY JM, QUINN KH. Gestational Diabetes: Underpinning Principles, Surveillance, and Management. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2018; 45(2):299-314.
[2] 李艺,段丽娜,陈静,等.孕前体重指数与妊娠期糖尿病发生风险及妊娠结局的相关性研究[J].现代预防医学,2019,46(2):262-264, 273.
[3] WANG Y, LUO BR. The association of body composition with the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus in Chinese pregnant women: A case-control study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(42):e17576.
[4] LANE W, BAILEY TS, GERETY G. Insulin Analogues and Hypoglycemia in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes-Reply. JAMA. 2017;318(18):1828-1829.
[5] 吴珊珊,顾俊菲,张永明.干细胞治疗1型糖尿病的研究进展[J].医学综述,2020,26(13):2647-2653.
[6] DANNE T, HEINEMANN L, BOLINDER J. New Insulins, Biosimilars, and Insulin Therapy. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2018;20(S1):S55-S70.
[7] QI Y, MA J, LI S, et al. Applicability of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):274.
[8] SORIA-JUAN B, ESCACENA N, CAPILLA-GONZÁLEZ V, et al. Cost-Effective, Safe, and Personalized Cell Therapy for Critical Limb Ischemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1151.
[9] CAPLAN AI. Mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res. 1991;9(5):641-650.
[10] NITKIN CR, BONFIELD TL. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Pediatric Disease: Perspectives on Success and Potential Improvements. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(2):539-565.
[11] PELLEGRINI S, PIEMONTI L, SORDI V. Pluripotent stem cell replacement approaches to treat type 1 diabetes. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2018;43:20-26.
[12] 牛婷,李爱斌,曹景云,等.胎盘间充质干细胞的应用研究[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2015,19(32):5236-5242.
[13] 项杰,张劼.间充质干细胞治疗糖尿病足:问题与更好的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(1):146-151.
[14] LENG ZK, GAO ZC, HE XJ, et al. Cultivation, screening, identification and transplantation of Muse cell from human umbilical cord-derived for spinal cord injury in rats. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019;32(4):327-334.
[15] XU M, LIU G, JIA Y, et al. Transplantation of human placenta mesenchymal stem cells reduces the level of inflammatory factors in lung tissues of mice with acute lung injury. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018;34(2):105-109.
[16] 黄启林,杨屹,罗晨,等.胎盘间充质干细胞移植对大鼠重症急性胰腺炎的保护作用[J].第三军医大学学报,2020,42(7):646-655.
[17] 马晨,李晓国,徐明均,等.人胎盘间充质干细胞的扩增与鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(33):5293-5299.
[18] LI XY, WU SY, LEUNG PS. Human Fetal Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote the Proliferation and Differentiation of Pancreatic Progenitor Cells and the Engraftment Function of Islet-Like Cell Clusters. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(17):4083.
[19] 于健,周燕,黎萍,等.妊娠糖尿病大鼠视黄醇结合蛋白4水平的变化及与胰岛素抵抗的关系[J].山西医药杂志,2013,42(6):606-608.
[20] 林峰,吴洁,王晓,等.黄连素改善妊娠期糖尿病大鼠胰岛素抵抗及其机制研究[J].中华全科医学,2019,17(10):1647-1651.
[21] RETNAKARAN R, YE C, CONNELLY PW, et al. Serum apoA1 (Apolipoprotein A-1), Insulin Resistance, and the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Human Pregnancy-Brief Report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019;39(10):2192-2197.
[22] BOHÁČOVÁ P, HOLÁŇ V. Mesenchymal stem cells and type 1 diabetes treatment. Vnitr Lek. 2018;64(7-8):725-728.
[23] LIAU LL, MAKPOL S, AZURAH AGN, et al. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote recovery of injured HepG2 cell line and show sign of early hepatogenic differentiation. Cytotechnology. 2018;70(4):1221-1233.
[24] MITANCHEZ D, YZYDORCZYK C, SIDDEEK B, et al. The offspring of the diabetic mother--short- and long-term implications. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 2015;29(2):256-269.
[25] SNEDDON JB, TANG Q, STOCK P, et al. Stem Cell Therapies for Treating Diabetes: Progress and Remaining Challenges. Cell Stem Cell. 2018; 22(6):810-823.
[26] BERNAL A, ARRANZ L. Nestin-expressing progenitor cells: function, identity and therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(12): 2177-2195.
[27] NAKAHARA F, BORGER DK, WEI Q, et al. Engineering a haematopoietic stem cell niche by revitalizing mesenchymal stromal cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2019;21(5):560-567.
[28] 谢幸,孔北华,段涛.妇产科学[M].9版.北京:人民卫生出版社, 2018:105-109.
[29] SHEN Y, JIA Y, LI Y, et al. Genetic determinants of gestational diabetes mellitus: a case-control study in two independent populations. Acta Diabetol. 2020;57(7):843-852.
[30] NGUYEN-NGO C, SALOMON C, QUAK S, et al. Nobiletin exerts anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects in an in vitro human model and in vivo murine model of gestational diabetes. Clin Sci (Lond). 2020; 134(6):571-592.
[31] ZHANG H, WANG Q, HE S, et al. Ambient air pollution and gestational diabetes mellitus: A review of evidence from biological mechanisms to population epidemiology. Sci Total Environ. 2020;719:137349.
[32] DE GENNARO G, PALLA G, BATTINI L, et al. The role of adipokines in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2019;35(9):737-751.
|