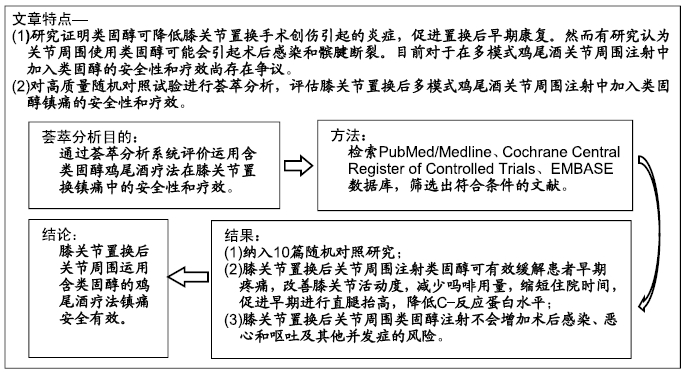
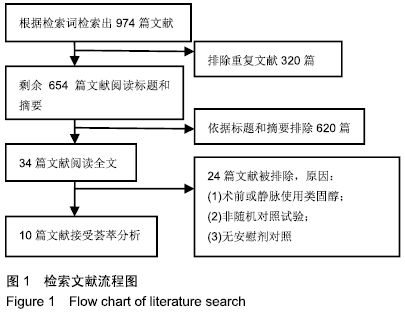
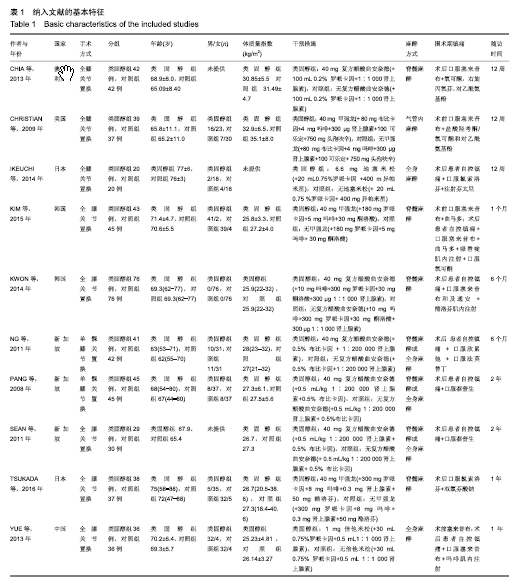
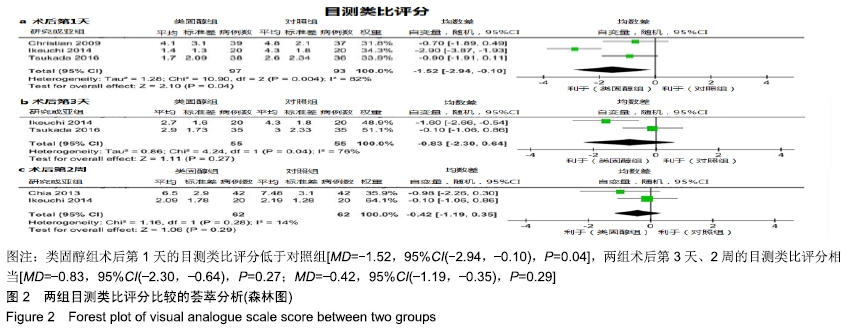
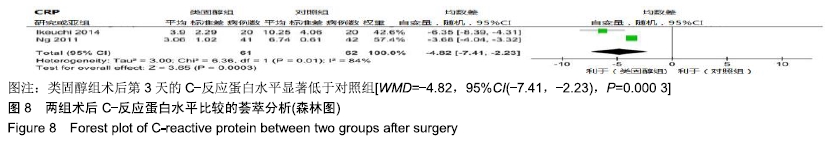
[1] ADIGWEME OO, LEE GC.Tranexamic acid: the new gold standard? Tech Orthop.2017;32(1):17-22.
[2] MA J, HUANG Z, SHEN B, et al.Blood management of staged bilateral total knee arthroplasty in a single hospitalization period.J Orthop Surg Res.2014;9:116.
[3] KOH IJ, CHANG CB, LEE JH, et al.Preemptive low-dose dexamethasone reduces postoperative emesis and pain after TKA:a randomized controlled study.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2013;471(9): 3010-3020.
[4] FAN Z, MA J, KUANG M, et al.The efficacy of dexamethasone reducing postoperative pain and emesis after total knee arthroplasty:A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg.2018;52:149-155.
[5] GIBBS DM, GREEN TP, ESLER CN.The local infiltration of analgesia following total knee replacement:a review of current literature.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2012;94(9):1154-1159.
[6] YANG XY, XIAO J, CHEN YH, et al.Dexamethasone alone vs in combination with transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation or tropisetron for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in gynaecological patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery.Br J Anaesth. 2015;115(6):883-889.
[7] LUNA IE, KEHLET H, JENSEN CM, et al.The Effect of Preoperative Intra-Articular Methylprednisolone on Pain After TKA: A Randomized Double-Blinded Placebo Controlled Trial in Patients With High-Pain Knee Osteoarthritis and Sensitization.J Pain.2017;18(12):1476-1487.
[8] HARTMAN J, KHANNA V, HABIB A, et al.Perioperative systemic glucocorticoids in total hip and knee arthroplasty:A systematic review of outcomes.J Orthop.2017;14(2):294-301.
[9] NAJA Z, KANAWATI S, AL KR, et al.The effect of IV dexamethasone versus local anesthetic infiltration technique in postoperative nausea and vomiting after tonsillectomy in children:A randomized double-blind clinical trial.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol.2017;92:21-26.
[10] ABE M, HIRASHIMA Y, KASAMATSU Y, et al.Efficacy and safety of olanzapine combined with aprepitant,palonosetron,and dexamethasone for preventing nausea and vomiting induced by cisplatin-based chemotherapy in gynecological cancer:KCOG-G1301 phase II trial.Support Care Cancer.2016;24(2):675-682.
[11] SALERNO A, HERMANN R.Efficacy and safety of steroid use for postoperative pain relief. Update and review of the medical literature.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006;88(6):1361-1372.
[12] CHRISTENSEN CP, JACOBS CA, JENNINGS HR.Effect of periarticular corticosteroid injections during total knee arthroplasty.A double-blind randomized trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91(11):2550-2555.
[13] CUI Z, LIU X, TENG Y, et al.The efficacy of steroid injection in total knee or hip arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015; 23(8):2306-2314.
[14] ZHAO X, QIN J, TAN Y, et al.Efficacy of steroid addition to multimodal cocktail periarticular injection in total knee arthroplasty:a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res.2015;10:75.
[15] TRAN J, SCHWARZKOPF R.Local infiltration anesthesia with steroids in total knee arthroplasty:A systematic review of randomized control trials.J Orthop.2015;12(Suppl 1):S44-S50.
[16] MENG J, LI L.The efficiency and safety of dexamethasone for pain control in total joint arthroplasty:A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore).2017;96(24):e7126.
[17] MOHAMMAD HR, HAMILTON TW, STRICKLAND L, et al. Perioperative adjuvant corticosteroids for postoperative analgesia in knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop.2018;89(1):71-76.
[18] LI X, XU G, XIE W, et al.The efficacy and safety of dexamethasone for pain management after total knee arthroplasty:A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg.2018;53:65-71.
[19] LIU G, GONG M, WANG Y, et al.Effect of Methylprednisolone on Pain Management in Total Knee or Hip Arthroplasty:A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Clin J Pain. 2018; 34(10): 967-974.
[20] XING D, YANG Y, MA XL, et al.Dose Intraarticular Steroid Injection Increase the Rate of Infection in Subsequent Arthroplasty:Grading the Evidence through a Meta-Analysis.J Orthop Surg Res.2014;9:107.
[21] PANG HN, LO NN, YANG KY, et al.Peri-articular steroid injection improves the outcome after unicondylar knee replacement:a prospective, randomised controlled trial with a two-year follow-up.J Bone Joint Surg Br.2008;90(6):738-744.
[22] TSUKADA S, WAKUI M, HOSHINO A.The impact of including corticosteroid in a periarticular injection for pain control after total knee arthroplasty:a double-blind randomised controlled trial.Bone Joint J. 2016.98-B:194-200.
[23] KIM TW, PARK SJ, LIM SH, et al.Which analgesic mixture is appropriate for periarticular injection after total knee arthroplasty? Prospective, randomized,double-blind study.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2015;23(3):838-845.
[24] KWON SK, YANG IH, BAI SJ, et al. Periarticular injection with corticosteroid has an additional pain management effect in total knee arthroplasty.Yonsei Med J.2014;55(2):493-498.
[25] YUE DB, WANG BL, LIU KP, et al.Efficacy of multimodal cocktail periarticular injection with or without steroid in total knee arthroplasty. Chin Med J (Engl).2013;126:3851-3855.
[26] IKEUCHI M, KAMIMOTO Y, IZUMI M, et al.Effects of dexamethasone on local infiltration analgesia in total knee arthroplasty:a randomized controlled trial.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2014;22(7):1638-1643.
[27] CHIA SK, WERNECKE GC, HARRIS IA, et al.Peri-articular steroid injection in total knee arthroplasty:a prospective,double blinded,randomized controlled trial.J Arthroplasty.2013;28(4):620-623.
[28] NG YC, LO NN, YANG KY, et al.Effects of periarticular steroid injection on knee function and the inflammatory response following Unicondylar Knee Arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2011;19(1):60-65.
[29] SEAN VW, CHIN PL, CHIA SL, et al.Single-dose periarticular steroid infiltration for pain management in total knee arthroplasty:a prospective,double-blind,randomised controlled trial.Singapore Med J.2011;52(1):19-23.
[30] CREAMER P.Intra-articular corticosteroid injections in osteoarthritis:do they work and if so,how?Ann Rheum Dis.1997;56:634-636.
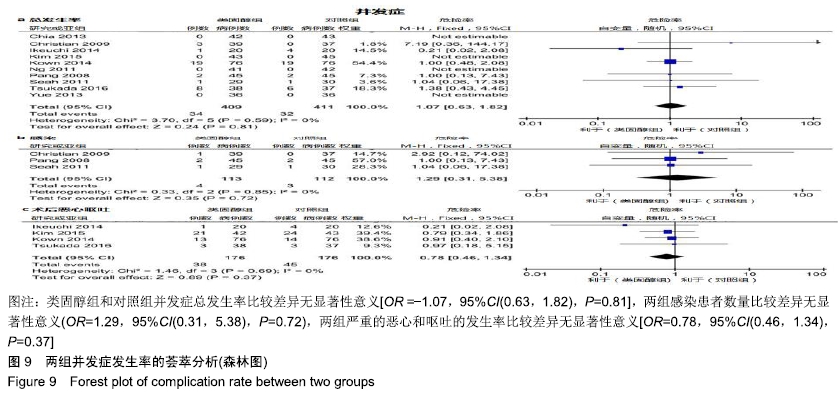
|