[1] ADIE S, KWAN A, NAYLOR JM, et al.Cryotherapy following total knee replacement.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012; (9):CD007911.
[2] MORSI E.Continuous-flow cold therapy after total knee arthroplasty.J Arthroplasty. 2002;17(6):718-722.
[3] ADIE S, NAYLOR JM, HARRIS IA. Cryotherapy after total knee arthroplasty a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Arthroplasty. 2010;25(5): 709-715.
[4] DANTAS LO, MOREIRA RFC, NORDE FM, et al.The effects of cryotherapy on pain and function in individuals with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Clin Rehabil.2019;33(8):1310-1319.
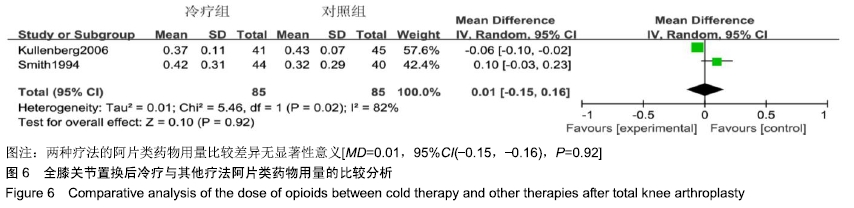
[5] KULLENBERG B, YLIPAA S, SODERLUND K, et al. Postoperative cryotherapy after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective study of 86 patients.J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(8): 1175-1179.
[6] HOLM B, HUSTED H, KEHLET H, et al.Effect of knee joint icing on knee extension strength and knee pain early after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized cross-over study.Clin Rehabil.2012;26(8):716-723.
[7] 王显勋.全膝关节置换后局部加压冷疗结合CPM功能锻炼对早期关节功能恢复的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(7): 998-1003.
[8] 徐飞,吕永明,宋莺春,等.冰敷干预可抑制人工全膝关节置换后血红蛋白降低及疼痛[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(22): 3457-3461.
[9] SMITH J, STEVENS J, TAYLOR M, et al.A randomized, controlled trial comparing compression bandaging and cold therapy in postoperative total knee replacement surgery. Orthop Nurs.2002; 21(2):61-66.
[10] THIJS E, SCHOTANUS MGM, BEMELMANS YFL, et al. Reduced opiate use after total knee arthroplasty using computer-assisted cryotherapy.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2019;27(4):1204-1212.
[11] 包良笑,史占军,赵亮,等.初次膝关节表面置换术后切口皮温测定和冰敷的临床效果[J].广东医学,2017,38(13):2098-2099,2103.
[12] DESTELI EE, IMREN Y, AYDIN N.Effect of both preoperative andpostoperative cryoceutical treatment on hemostasis and postoperative pain following total knee arthroplasty.Int J Clin Exp Med.2015;8(10):19150-19155.
[13] KUYUCU E, BULBUL M, KARA A, et al.Is cold therapy really efficient after knee arthroplasty? Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2015; 4(4):475-478.
[14] KANG JI, KIM YN, CHOI H. Effects of Low-intensity Pulsed Ultrasound and Cryotherapy on Recovery of Joint Function and C-reactive Protein Levels in Patients after Total Knee Replacement Surgery. J Phys Ther Sci. 2014;26(7): 1033-1036.
[15] NADLER SF, WEINGAND K, KRUSE RJ. The physiologic basis and clinical applications of cryotherapy and thermotherapy for the pain practitioner.Pain Physician.2004; 7(3):395-399.
[16] RICHARDSON ML, LOUGH LR, SHUMAN WP, et al.MR appearance of skeletal neoplasms following cryotherapy. Skeletal Radiol.1994;23(2):121-125.
[17] WARREN TA, MCCARTY EC, RICHARDSON AL, et al. Intra-articular knee temperature changes: ice versus cryotherapy device.Am J Sports Med.2004;32(2):441-445.
[18] GLENN RE JR, SPINDLER KP, WARREN TA, et al. Cryotherapy decreases intraarticular temperature after ACL reconstruction.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2004;(421):268-272.
[19] LESSARD LA, SCUDDS RA, AMENDOLA A, et al.The efficacy of cryotherapy following arthroscopic knee surgery.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther.1997;26(1):14-22.
[20] MARTIN SS, SPINDLER KP, TARTER JW, et al.Cryotherapy: an effective modality for decreasing intraarticular temperature after knee arthroscopy.Am J Sports Med.2001;29(3):288-291.
[21] WOOLF SK, BARFIELD WR, MERRILL KD, et al.Comparison of a continuous temperature-controlled cryotherapy device to a simple icing regimen following outpatient knee arthroscopy. J Knee Surg.2008;21(1):15-19.
[22] ALGAFLY AA, GEORGE KP.The effect of cryotherapy on nerve conduction velocity, pain threshold and pain tolerance. Br J Sports Med.2007;41(6):365-369.
[23] STALMAN A, BERGLUND L, DUNGNERC E, et al. Temperature-sensitive release of prostaglandin E(2) and diminished energy requirements in synovial tissue with postoperative cryotherapy: a prospective randomized study after knee arthroscopy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93(21): 1961-1968.
[24] THIENPONT E.Does advanced cryotherapy reduce pain and narcotic consumption after knee arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res.2014;472(11):3417-3423.
[25] FORSYTH AL, ZOURIKIAN N, VALENTINO LA, et al.The effect of cooling on coagulation and haemostasis: should "Ice" be part of treatment of acute haemarthrosis in haemophilia? Haemophilia. 2012;18(6):843-850.
[26] DYKSTRA JH, HILL HM, MILLER MG, et al.Comparisons of cubed ice, crushed ice, and wetted ice on intramuscular and surface temperature changes.J Athl Train. 2009;44(2): 136-141.
[27] RUPP KA, HERMAN DC, HERTEL J, et al.Intramuscular temperature changes during and after 2 different cryotherapy interventions in healthy individuals.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012; 42(8):731-737.
[28] WILKE B, WEINER RD. Postoperative cryotherapy: risks versus benefits of continuous-flow cryotherapy units.Clin Podiatr Med Surg.2003;20(2):307-322.
|