中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (19): 3110-3116.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3524
• 干细胞循证医学 evidence-based medicine of stem cells • 上一篇
干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变的Meta分析
夏稳伸1,2,何仁姣2,艾金伟2,3,王 君4,李德胜2,裴 斌1,3
- 1锦州医科大学湖北医药学院研究生培养基地,湖北省襄阳市 441000;湖北医药学院附属襄阳市第一人民医院,2骨三科,3循证医学中心,4心血管内科,湖北省襄阳市 441000
Stem cell transplantation for diabetic patients with lower-extremity arterial disease: a meta-analysis
Xia Wenshen1, 2, He Renjiao2, Ai Jinwei2, 3, Wang Jun4, Li Desheng2, Pei Bin1, 3
- 1Postgraduate Training Basement of Jinzhou Medical University, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China; 2Third Department of Orthopedics, 3Evidence-Based Medicine Center, 4Department of Cardiology, Xiangyang No.1 People’s Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, Xiangyang 441000, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
干细胞分类:根据干细胞所处的发育阶段分为胚胎干细胞和成体干细胞;根据干细胞的发育潜能分为全能干细胞、多能干细胞和单能干细胞。
糖尿病下肢血管病变:是下肢血管,尤其是中小动脉慢性、进行性发生狭窄和闭塞,同时多伴有肢体感觉神经受损,早期症状主要表现为肢体发冷、乏力,随即出现间歇性跛行、静息痛,随病情的发展,最终可导致肢/趾体坏死,是糖尿病严重并发症之一。
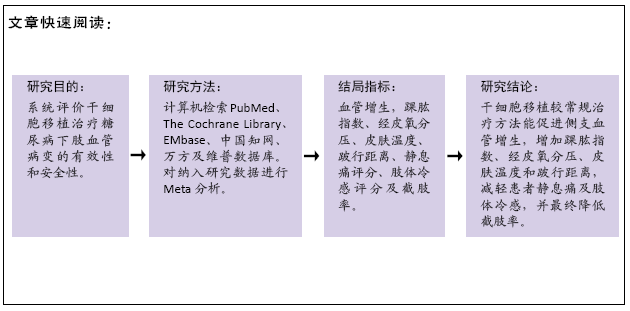
目的:干细胞移植已用于糖尿病下肢血管病变的临床治疗,因各研究样本量小,研究结论不一致。文章系统评价干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变的有效性和安全性。
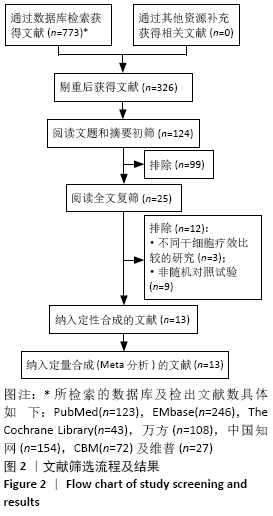
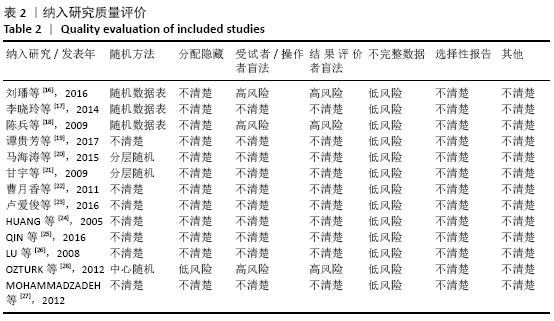
方法:计算机检索PubMed、The Cochrane Library(2019年第11期)、EMbase、中国知网、CBM、维普、万方数据库中干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变的随机对照试验,检索时间均为建库至2019年12月10日。由2名研究者独立筛选文献、提取资料并评价纳入研究的偏倚风险后,采用RevMan 5.3软件进行统计分析。
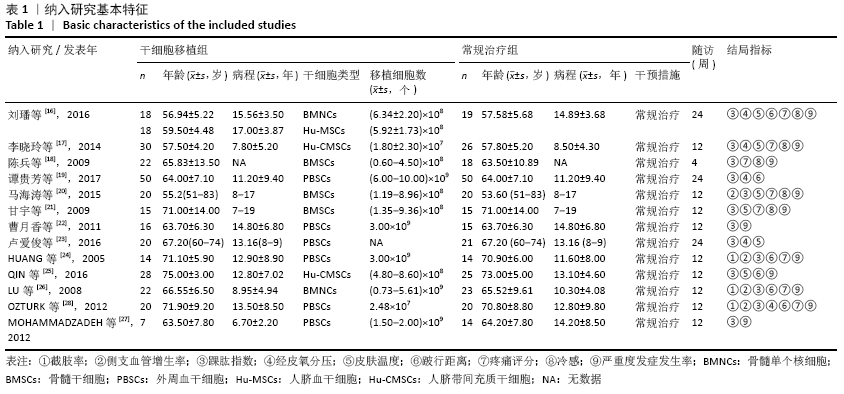
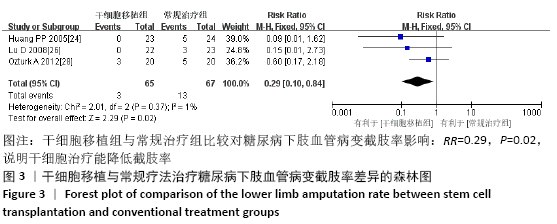
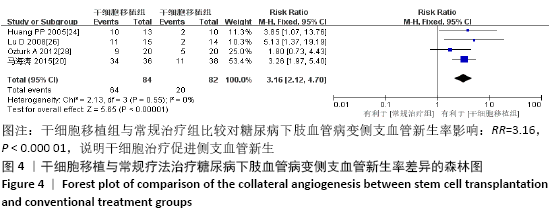
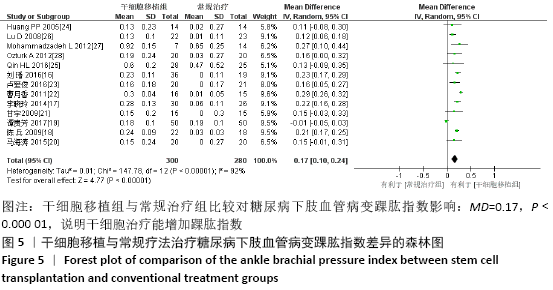
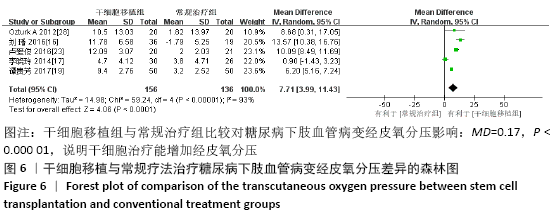
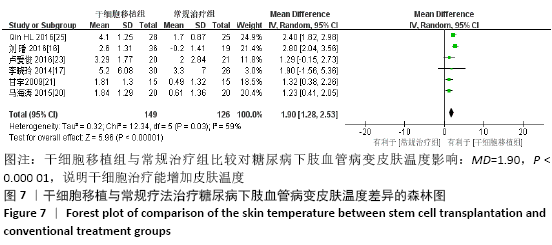
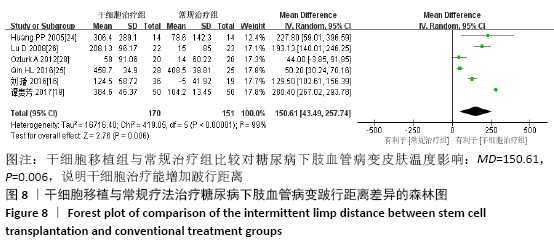
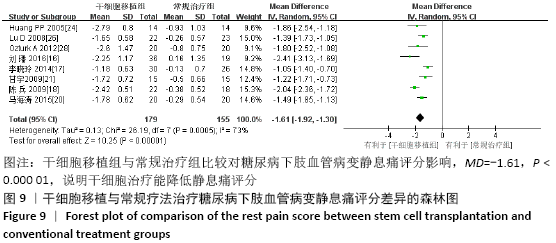
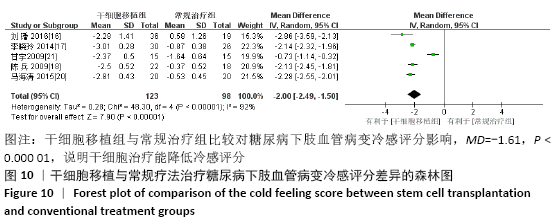
结果:纳入13个随机对照试验,包括糖尿病下肢血管病变患者546例,其中干细胞移植组287例,常规治疗组259例。Meta分析结果显示:与常规治疗相比,干细胞移植能降低截肢率(RR=0.29,95%CI:0.10-0.84,P=0.02),促进侧支血管新生(RR=3.16,95%CI:2.12-4.70,P < 0.000 01),增加踝肱指数(MD=0.17,95%CI:0.10-0.24,P < 0.000 01)、经皮氧分压(MD=7.71,95%CI:3.99-11.43,P < 0.000 01)、皮肤温度(MD=1.90,95%CI:1.28-2.53,P < 0.000 01)和跛行距离(MD=150.61,95%CI:43.49-257.74,P=0.006),还可降低静息痛评分(MD= -1.16,95%CI:-1.92至-1.30,P < 0.000 01)和肢体冷感评分(MD= -2.00,95%CI:-2.49至-1.50,P < 0.000 01)。各研究均无死亡、肿瘤及肝肾功能损害等严重并发症发生。
结论:干细胞移植治疗糖尿病下肢血管病变是一种安全、有效的治疗方法,但由于受纳入研究数量和质量限制,未来文章结论尚需大样本、高质量、长期随访的随机对照试验予以证实。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: