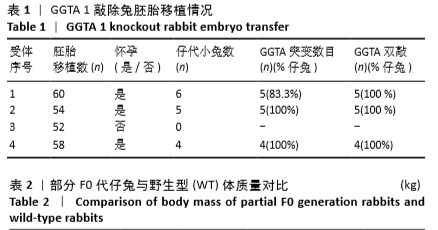
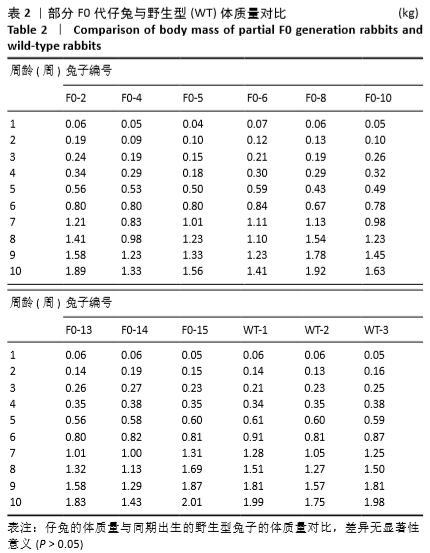
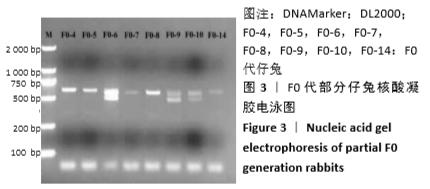
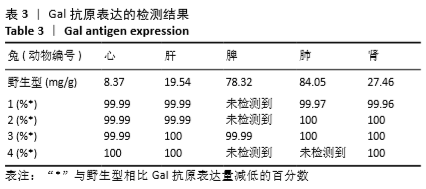
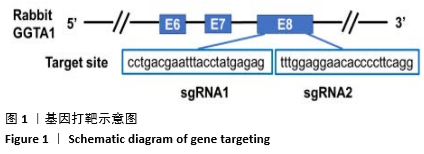
[1] 全国医疗器械生物学评价标准化技术委员会.《动物源医疗器械 第1部分:风险管理应用》[S].YY/T 0771.1.北京,中国标准出版社,2009.
[2] BADYLAK SF, GILBERT TW.Immune Response to Biologic Scaffold Materials.Semin Immunol. 2008;20(2):109-116.
[3] SANDRIN MS, MCKENZIE IF. Gal alpha (1,3)Gal, the major xenoantigen(s) recognised in pigs by human natural antibodies.Immunol Rev. 1994; 141:169-190.
[4] GALILI U, SHOHET SB, KOBRIN E, et al. Man, apes, and Old World monkeys differ from other mammals in the expression of α-galactosyl epitopes on nucleated cells. J Biol Chem.1988; 263:17755-17762.
[5] ORIOL R, YE Y, KOREN E, et al. Carbohydrate antigens of pig tissues reacting with human natural antibodies as potential targets for hyperacute vascular rejection in pig-to-man organ xenotransplantation.Transplantation.1993; 56:1433-1442.
[6] CHOI HJ, KIM MK, LEE HJ, et al. Effect of αGal on corneal xenotransplantation in a mouse model. Xenotransplantation. 2011; 18(3):176-182.
[7] KIM MS, JEONG S, LIM HG, et al. Differences in xenoreactive immune response and patterns of calcification of porcine and bovine tissues in α-Gal knock-out and wild-type mouse. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.2015;48(3):392-399.
[8] 邵安良,魏利娜,范昌发,等.2种Gal抗原缺失小鼠的免疫学特性比较研究[J].药物分析杂志, 2018, 38(8):1288-1295.
[9] SHAO A, LING Y, XU L, et al. Xenogeneic bone matrix immune risk assessment using GGTA1 knockout mice.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(sup3):S359-S369.
[10] 邵安良,魏利娜,范昌发,等.Gal抗原缺失小鼠的应用示范:动物源性硬脑膜补片的免疫原性反应评价[J]. 药物分析杂志, 2018, 38(8):1296-1303.
[11] 魏利娜,邵安良,黄立静,等.去细胞异种角膜基质与去细胞异种结膜基质的免疫原性研究[J].药物分析杂志, 2019, 39(8):1362-1369.
[12] 陈亮,邵安良,魏利娜,等.应用Gal抗原缺失小鼠评价可降解异种脱细胞真皮基质的免疫原性[J],药物分析杂志, 2019,39(8):1370-1378.
[13] WANG X, HUANG Y, JASTANEIAH S, et al. Protective Effects of Soluble Collagen during Ultraviolet-A Crosslinking on Enzyme-Mediated Corneal Ectatic Models. Plos One.PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0136999.
[14] BRACEY DN, SEYLER TM, JINNAH AH, et al. A porcine xenograftヾerived bone scaffold is a biocompatible bone graft substitute: An assessment of cytocompatibility and the alpha gal epitope. Xenotransplantation. 2019;26(5):e12534.
[15] 王亚东, 陈谦学. 生物型人工硬脑膜补片在颅脑损伤大骨瓣减压术中的应用[J]. 中国临床神经外科杂志, 2015,20(3):151-152.
[16] YUAN L, SUI T, CHEN M,et al. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated GJA8 knockout in rabbits recapitulates human congenital cataracts. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22024.
[17] ZHANG J, XIE C, LU Y, et al. Potential Antigens Involved in Delayed Xenograft Rejection in a Ggta1/Cmah Dko Pig-to-Monkey Model. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):10024.
[18] MILLAND J, CHRISTIANSEN D, LAZARUS BD, et al. The Molecular Basis for Gal (1,3)Gal Expression in Animals with a Deletion of the 1,3Galactosyltransferase Gene.J Immunol. 2006;176(4):2448-2454.
[19] 陆艳,单永强,邵安良,等.ELISA抑制法检测动物组织中α1,3-Gal抗原[J].药物分析杂志,2015,35(10):40-46.
[20] 单永强,徐丽明,柯林楠,等.动物源性生物材料中残留α-Gal抗原检测方法[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2015, 32(3):680-687.
[21] LU Y, SHAO A, XU L,et al. A standardized quantitative method for detecting remnant alpha-Gal antigen in animal tissues or animal tissue-derived biomaterials and its application. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):15424.
[22] 徐丽明,邵安良,柯林楠,等.一种检测α-1,3Gal抗原的试剂盒及其应用[P]. CN103983767A,2014-08-13.
[23] 全国外科植入物和矫形器械标准化技术委员会组织工程医疗器械产品分技术委员会.《组织工程医疗器械产品动物源性支架材料的残留α-Gal抗原检测》[S]. YY/T 1561.北京,中国标准出版社,2017.
[24] CHIANG TR, FANGET L, GREGORY R, et al. Anti-GAL antibodies in humans and 1,3 alpha-galactosyltransferase knock-out mice. Transplantation. 2000; 69(12):2593-2600.
[25] PUGA YUNG GL, LI Y, BORSIG L, et al. Complete absence of the α-Gal xenoantigen and isoglobotrihexosyl ceramide in α1,3galactosyltransferase knock-out pigs. Xenotransplantation. 2012;19(3):196-206.
[26] HANCHAO G, CHENGJIANG Z, XI X, et al. Production of α1,3-galactosyltransferase and cytidine monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase gene double-deficient pigs by CRISPR/Cas9 and handmade cloning.J Reprod Dev. 2017; 63(1): 17-26.
[27] RAN FA, HSU P, LIN CY, et al. Double Nicking by RNA-Guided CRISPR Cas9 for Enhanced Genome Editing Specificity. Cell. 2013;154(6):1380-1389.
[28] ZUO E, SUN Y, WEI W, et al. Cytosine base editor generates substantial off-target single-nucleotide variants in mouse embryos. Science. 2019;364(6437):289-292.
[29] ZHANG XH, TEE LY, WANG XG, et al. Off-target Effects in CRISPR/Cas9-mediated Genome Engineering.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2015;4:e264.
[30] SHAO A, XU L, WU X, et al. Gal epitope expression and immunological properties in iGb3S deficient mice. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):15433.
[31] 徐丽明,邵安良,范昌发.一种制备GGTA1和iGb3S双基因敲除的非人哺乳动物的方法及应用[P]. CN104894163A,2015-09-09. |