1.1 设计 细胞学实验观察。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2018年11月至2019年11月在河南中医药大学基础医学院科研实验中心和中医内科重点开放实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 细胞株 人正常支气管上皮细胞株BEAS-2B购于中国科学院上海生命科学院研究院细胞资源中心。在37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2条件下,用含体积分数为10%胎牛血清、100 U/mL青霉素、100 mg/L链霉素的DMEM高糖培养基培养,用0.25%胰酶消化液(含EDTA)消化、传代。实验所用细胞均处于对数生长期。
1.3.2 药物和试剂 黄芩苷(上海麦克林公司,纯度95%,批号B802696);DMEM高糖培养基(Solarbio公司,批号20190905);胎牛血清(BI公司,批号04-001-1A);胰蛋白酶(Solarbio公司,批号T1350);脂多糖(来源于大肠杆菌,批号L2880,Sigma公司);三磷酸腺苷溶液(Solarbio公司,批号20191101);噻唑蓝(Solarbio公司,批号M8180);PBS(Solarbio公司,批号20191125);二甲基亚砜(批号D8371,Sigma公司);肿瘤坏死因子α检测试剂盒(批号EHC103a)、白细胞介素1β检测试剂盒(批号EHC002b)、白细胞介素6检测试剂盒(批号EHC007)均购自欣博盛生物科技有限公司;活性氧检测试剂盒(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);超氧化物歧化酶活性检测试剂盒(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);丙二醛检测试剂盒(苏州科铭生物科技有限公司)。药物黄芩苷、脂多糖在临用前用细胞培养液稀释至所需浓度,过滤除菌备用。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 细胞培养 人正常支气管上皮细胞系BEAS-2B用含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM高糖培养基置于37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中静置培养,隔天用无菌PBS对细胞润洗2遍后更换新鲜培养液,待细胞生长至对数期时,用0.25%胰酶消化液(含EDTA)消化,每3 d按1∶3比例传代。将细胞传至3代,观察细胞状态稳定后用于实验研究,所有操作均按照无菌操作标准执行。
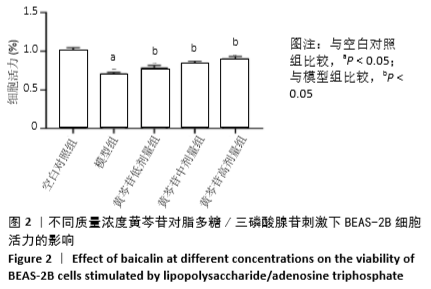
1.4.2 实验分组 取生长至对数期且状态良好的细胞,倒掉上清液,用PBS轻轻润洗2遍,加入0.25%胰酶消化液(含EDTA)消化,观察细胞变圆漂浮时加入新鲜培养基终止消化,重悬离心后对细胞进行计数。MTT实验中细胞以5×103个/孔接种于96孔板中;ELISA、qRT-PCR、蛋白质印迹实验以及氧化相关指标检测实验中细胞以1×105个/孔接种于6孔板中。待细胞贴壁后继续培养12 h,将细胞随机分成5组:空白对照组(含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的培养基)、模型组(10 mg/L脂多糖+5 mmol/L三磷酸腺苷)、黄芩苷低剂量组(黄芩苷2.5 mg/L)、黄芩苷中剂量组(黄芩苷5 mg/L)和黄芩苷高剂量组(黄芩苷10 mg/L)。黄芩苷低、中、高剂量组先加入不同质量浓度的黄芩苷溶液预处理,空白对照组和模型组细胞均加入等体积的含血清培养基,培养3 h后,除空白对照组外,其他组均加入脂多糖使终质量浓度达到10 mg/L,继续培养24 h后再加入三磷酸腺苷溶液使终浓度达到5 mmol/L,空白对照组加入等体积的含血清培养基,在37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2恒温箱中共同培养30 min,取细胞或细胞上清检测相关指标。
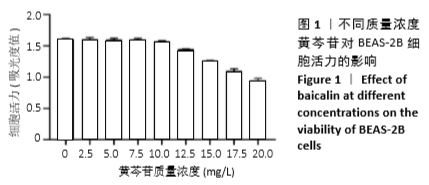
1.4.3 MTT法检测不同质量浓度黄芩苷对各组细胞活力的影响 取生长状态良好的对数期细胞,吸弃上清液,用PBS润洗2遍,尽量去除孔内液体,制成细胞浓度为5×107 L-1的细胞悬液,接种至96孔板,每孔100 μL,每组设6个复孔。检测不同质量浓度黄芩苷对细胞活力的影响时,待细胞贴壁后弃去上清液,分别加入不同质量浓度的黄芩苷溶液(0,2.5,5,7.5,10,12.5,15,17.5,20 mg/L)处理细胞24 h;检测脂多糖/三磷酸腺苷刺激后黄芩苷对细胞活力的影响时,按1.4.2对细胞进行分组处理。将处理后的细胞每孔加入 5 g/L的MTT溶液20 μL,避光操作,继续培养4 h后吸弃上清,尽量去除孔内液体,每孔加入150 μL二甲基亚砜振荡10 min,使结晶物充分溶解。采用酶联免疫检测仪在波长570 nm和参比波长630 nm下检测各孔吸光度值,记录结果。细胞活力(%)=实验组细胞吸光度值/空白组细胞吸光度值×100%。
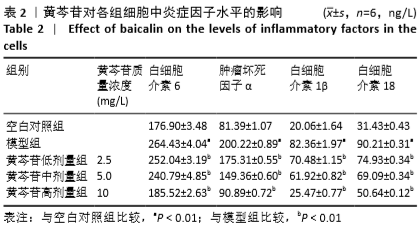
1.4.4 酶联免疫吸附法测定细胞上清中肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素18水平 取生长状态良好的对数期细胞,按1.4.2对细胞进行处理后,收集细胞上清液,4 ℃,2 000 r/min离心5 min后吸取上清液转移至新的EP管中,具体方法严格按照试剂盒说明书进行操作,包被液稀释抗原,封板膜封板后于37 ℃恒温孵育1.5 h;每孔加入100 μL生物素化抗体,封板膜封板后于37 ℃恒温孵育1 h;每孔加入100 μL酶结合物,封板膜封板后于37 ℃恒温避光孵育30 min;接着每孔加入100 μL显色底物继续孵育15 min,加入终止液,充分混匀,待颜色由蓝色变为黄色,于酶标仪450 nm处进行检测,绘制标准曲线并计算各炎症因子水平。
1.4.5 细胞内活性氧水平测定 实验采用DCFH-DA作为活性氧探针,按1.4.2对细胞进行分组处理后,吸弃培养液,温PBS润洗2次,加入1 mL稀释过的DCFH-DA(1∶1 000),37 ℃避光孵育20 min,细胞用0.25%胰酶消化1 min,加入含血清培养基终止消化,制成细胞悬液,1 000 r/min离心5 min收集细胞。将收集好的细胞沉淀物重悬,用荧光酶标仪检测荧光强度(激发光波长500 nm,发射光波长525 nm),重复6次。
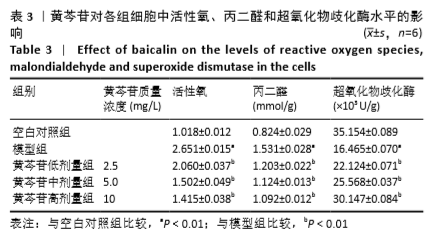
1.4.6 细胞中超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛水平测定 取生长状态良好的对数期细胞,按1.4.2进行分组处理后,PBS润洗2次,用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化细胞,将细胞混悬于裂解液,冰上放置30 min,4 ℃、12 000×g离心10 min,收集细胞裂解液。按照试剂盒说明书所述步骤操作后检测吸光度值,并绘制标准曲线,根据标准曲线计算超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛水平。
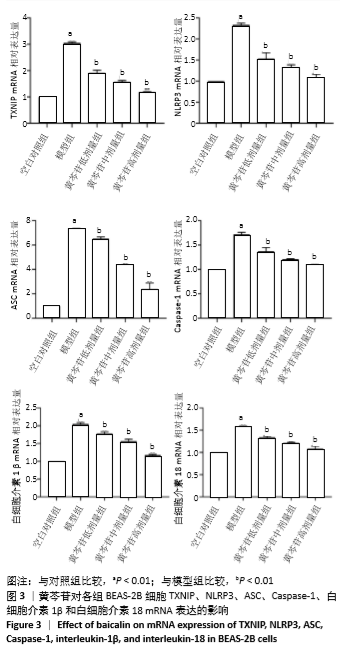
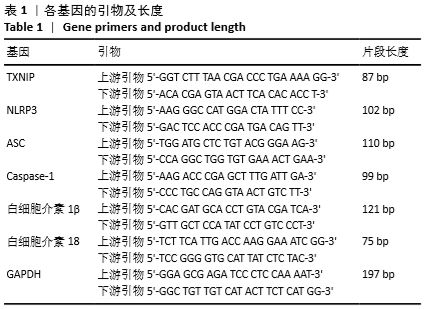
1.4.7 实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)检测细胞内TXNIP、NLRP3、ASC、Caspase-1、白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素18 mRNA的表达量 按照Trizol试剂说明书提取各组细胞总RNA,于紫外分光光度计检测所提RNA浓度及纯度,确保A260 nm/A280 nm在1.8-2.0为合格。按照反转录试剂盒说明,以42 ℃,60 min/80 ℃,10 min为反应条件将RNA为模版反转录成cDNA,反转录体系总体积为20 μL。以cDNA为模版扩增目的基因,反应体系总体积为5 μL(引物3 μL,cDNA 2 μL)。扩增结束后,由电脑自动生成标准曲线、熔解曲线及荧光扩增曲线,分析数据。各基因的引物及长度,见表1。
1.4.8 Western blot法检测细胞内TXNIP、Caspase-1、NLRP3蛋白表达量 细胞按1.4.2处理后,PBS润洗2遍,用0.25%胰蛋白酶消化后收集细胞,加入RIPA裂解液4 ℃ 12 000 r/min离心15 min提取细胞总蛋白,BCA法检测蛋白浓度。制备聚丙烯酰氨凝胶,每个样本取50 μg至对应上样孔中,75 V/120 V恒压电泳后转至PVDF膜;300 mA恒流转膜30 min,5%脱脂奶粉溶液封闭1 h;加入一抗4 ℃孵育过夜,1×TBST洗涤3次,每次10 min;加入二抗孵育1 h,1×TBST洗涤3次,每次10 min;超敏发光液显影曝光摄取,Bio-Rad软件分析蛋白条带灰度值。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①黄芩苷干预细胞炎症模型的最佳质量浓度;②荧光探针DCFH-DA法检测各组细胞内活性氧水平,酶标仪检测超氧化物歧化酶和丙二醛水平;③qRT-PCR法检测通路相关基因的表达水平;④ELISA法检测各组细胞炎症因子水平;⑤Western blot 检测各组TXNIP、NLRP3和Caspase-1蛋白的表达。
1.6 统计学分析 采用SPSS 15.0软件,计量资料以x±s表示,进行单因素方差分析(ONE-WAYANOVA),组间比较采用Dunnett检验,用GraphPad Prism 8.0软件作图,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。