| [1] Broadhead ML, Clark JC, Myers DE, et al. The molecular pathogenesis of osteosarcoma: a review. Sarcoma. 2011;2011:959248.
[2] Kawano Y, Kypta R.Secreted antagonists of the Wnt signalling pathway.J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 13): 2627-2634.
[3] 江黎珠,陈鸿雁.WIF-1 与肿瘤关系的研究进展[J].中国癌症杂志,2010,20(4):299-302.
[4] Chuang JC, Warner SL, Vollmer D, et al. S110, a 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine-containing dinucleotide, is an effective DNA methylation inhibitor in vivo and can reduce tumor growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(5): 1443-1450.
[5] Rubin EM, Guo Y, Tu K,et al.Wnt inhibitory factor 1 decreases tumorigenesis and metastasis in osteosarcoma.Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(3):731-741.
[6] Blattmann C, Thiemann M, Stenzinger A,et al. Establishment of a patient-derived orthotopic osteosarcoma mouse model.J Transl Med. 2015;13:136.
[7] 田大为,熊敏,张鹏,等.不同细胞系在骨肉瘤动物模型中的成瘤差异性比较[J].湖北医药学院学报,2014,33(4): 327-331.
[8] Schmidt J, Strauss GP, Schön A,et al.Establishment and characterization of osteogenic cell lines from a spontaneous murine osteosarcoma.Differentiation. 1988;39(3):151-160.
[9] Matsuzaki K, Katayama K, Takahashi Y,et al.Human osteoclast-like cells are formed from peripheral blood mononuclear cells in a coculture with SaOS-2 cells transfected with the parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related protein receptor gene. Endocrinology. 1999;140(2):925-932.
[10] 王晋,邹昌业,沈靖南,等.同源性骨肉瘤新细胞系Zos和Zos-M的生物学比较研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(1): 71-78.
[11] 刘巍峰,郭卫,牛晓辉,等.移植性人骨肉瘤OS-732裸鼠模型的建立[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2008,7(4):204-207.
[12] 袁赤亭,朱敏,范利荣,等.糖皮质激素受体在3种人成骨肉瘤细胞株MG63、U2-OS及HOS中表达及差异[J].医学研究杂志,2014,43(11):144-146.
[13] 韩康,赵廷宝,卞娜,等.利用慢病毒载体观察microRNA- 194对人骨肉瘤细胞系U2-OS生物学特性的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(23):4401-4405.
[14] 钟永翔,林晓,王恩智,等. 三氧化二砷、VEGF对人骨肉瘤Saos-2细胞TRAF-2和STAT-6表达的影响[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2015,20(9):993-997.
[15] 蔡文涛,夏虹,陈安民.缺氧条件下骨肉瘤MG-63细胞中TG2通过线粒体途径调节细胞凋亡的机制[J].肿瘤防治研究,2015,42(2):130-135.
[16] 安奇君,马月宏,程为民.线粒体融合蛋白基因对人成骨肉瘤MG-63细胞的促凋亡作用研究[J].中国药物与临床, 2015,15(9):1266-1267.
[17] 王一凡,许永涛.构建瘤细胞模型:NS-398对低氧状态下MG-63细胞侵袭能力的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015, 19(40):6408-6412.
[18] Ory B, Heymann MF, Kamijo A,et al.Zoledronic acid suppresses lung metastases and prolongs overall survival of osteosarcoma-bearing mice.Cancer. 2005; 104(11):2522-2529.
[19] 曾恒,陈安民,李锋,等.骨肉瘤诱导分化与多药耐药表型的生物学性状比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(13): 1019-1022.
[20] 李华,杨英年.骨肉瘤动物模型的建立[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(33): 6258-6262.
[21] Lambiv WL, Vassallo I, Delorenzi M,et al.The Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (WIF1) is targeted in glioblastoma and has a tumor suppressing function potentially by induction of senescence.Neuro Oncol. 2011;13(7):736-747.
[22] 丁振,钱叶本,朱立新,等.肝细胞癌中WIF-1基因启动子甲基化状态及mRNA表达的研究[J].肝胆外科杂志,2008, 16(4):304-307.
[23] Das AV, Bhattacharya S, Zhao X,et al.The canonical Wnt pathway regulates retinal stem cells/progenitors in concert with Notch signaling.Dev Neurosci. 2008;30(6): 389-409.
[24] Garcia MI, Ghiani M, Lefort A,et al.LGR5 deficiency deregulates Wnt signaling and leads to precocious Paneth cell differentiation in the fetal intestine.Dev Biol. 2009;331(1):58-67.
[25] Yee DS, Tang Y, Li X,et al.The Wnt inhibitory factor 1 restoration in prostate cancer cells was associated with reduced tumor growth, decreased capacity of cell migration and invasion and a reversal of epithelial to mesenchymal transition.Mol Cancer. 2010;9:162.
[26] Chan SL, Cui Y, van Hasselt A,et al.The tumor suppressor Wnt inhibitory factor 1 is frequently methylated in nasopharyngeal and esophageal carcinomas. Lab Invest. 2007;87(7):644-650.
[27] 侯贝贝,王妍,张娟,等.软骨肉瘤WIF-1基因甲基化及Wnt-5a蛋白表达的临床病理意义[J].山东大学学报:医学版, 2013,51(2):70-74.
[28] 何畔,梁珊.骨肉瘤组织中XIAP mRNA、Caspase-9 mRNA的表达变化及意义[J].山东医药,2010,50(14): 13-15.
[29] 崔忠惠,孙华文,赵鹏展. WIF-1基因启动子区甲基化在胃癌组织中的检测[J].临床外科杂志,2011,19(11):769-771.
[30] Ng RC, Matsumaru D, Ho AS,et al.Dysregulation of Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (Wif1) expression resulted in aberrant Wnt-β-catenin signaling and cell death of the cloaca endoderm, and anorectal malformations.Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(6):978-989.
[31] 蒋平,关伟,戴楠,等.DNA 损伤修复基因以及TS、β-tubulinⅢ在骨肉瘤中的表达及其与临床病理的关系[J].第三军医大学学报,2013,35(1):61-65.
[32] 张松,孔维佳,王彦君,等.5-杂氮-2’-脱氧胞苷对人鼻咽癌裸鼠移植瘤的抑制作用[J].癌症,2005,24(10):1201- 1205.
[33] Wijermans P, Lübbert M, Verhoef G,et al.Low-dose 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine, a DNA hypomethylating agent, for the treatment of high-risk myelodysplastic syndrome: a multicenter phase II study in elderly patients.J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(5):956-962.
[34] 傅斌,郎斌,徐华,等. 5-杂氮脱氧胞苷逆转膀胱癌细胞WIF-1基因转录表达的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2008, 25(3):337-339.
[35] 赵润年,刘晓勇,张亚锋.5-氮杂-2’-脱氧胞苷的研究进展[J].实用医技杂志,2006,13(4):554-556.
[36] 李莲,朱辉.5-氮-2’-脱氧胞苷抗肿瘤作用的研究进展[J].临床肿瘤学杂志,2011,16(3):282-286.
[37] 葛畅,许春伟,王鲁平,等. 5'-氮杂-2'-脱氧胞苷对HT-29和LoVo结直肠癌细胞株中Wif-1基因甲基化状态、mRNA表达及蛋白表达的影响[J].中国医药导报,2014,11(23): 16-21.
[38] 张鹏,李书忠,张金锋,等.WIF-1对人骨肉瘤 MG-63细胞中β-catenin表达的作用研究[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2013,7(21):9590-9594. |
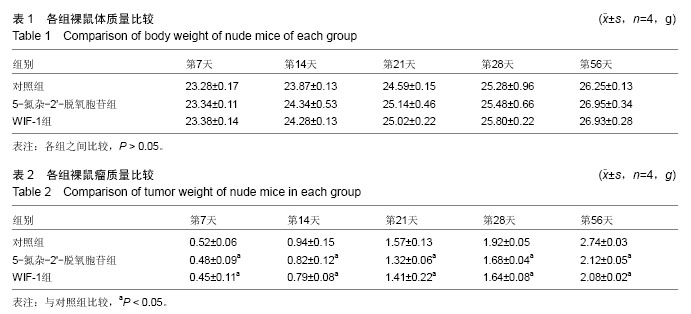
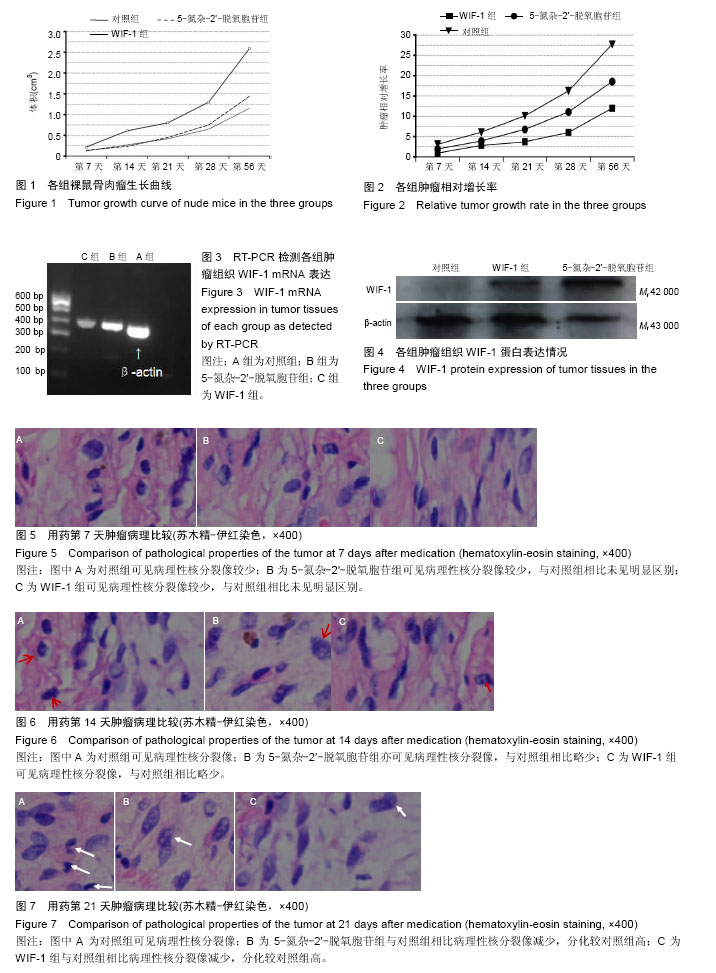
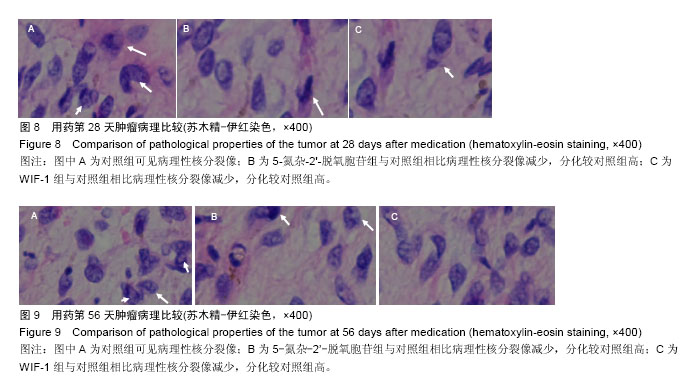
.jpg)
.jpg)