1.1 设计 随机对照动物实验。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2018年9月至2020年5月在苏州大学医学部心血管病研究所完成。
1.3 材料 人脐带间充质干细胞购于江苏和泽生物科技有限公司;C2C12细胞购于美国ATCC细胞库;piR823的抑制剂si-piR823及引物由广州市锐博生物科技有限公司合成。
1.3.1 实验动物 8周龄雄性C57BL/6J小鼠,用于构建后肢缺血模型,购于昭衍(苏州)新药研究中心有限公司,许可证号:SCXK(苏)2018-0006,饲养于苏州大学实验动物中心。
1.3.2 主要试剂 β-甘油磷酸钠(Sigma,美国);壳聚糖(浙江金壳药业股份有限公司);外泌体分离试剂盒(Life Technology,美国);Annexin V-FITC 凋亡检测试剂盒(BD,荷兰);Cell-LightTM Apollo 567 Stain Kit(锐博生物)。
1.4 实验方法
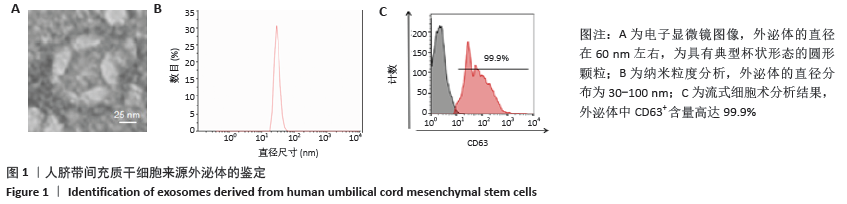
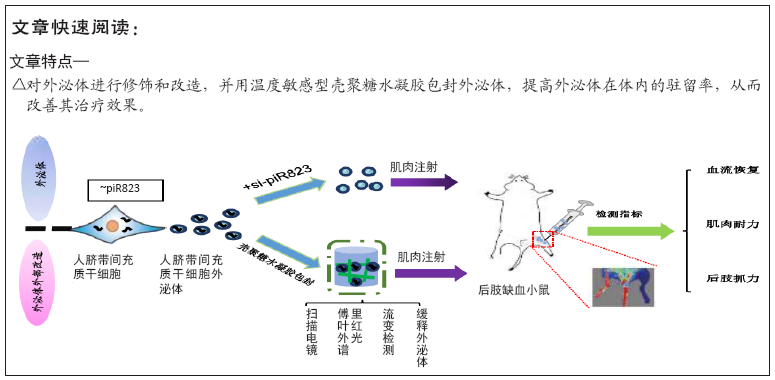
1.4.1 外泌体的获取及鉴定 将胎牛血清100 000 ×g离心7 h,以去除先前存在于其中的外泌体。将人脐带间充质干细胞用含有体积分数10%胎牛血清的培养基培养。培养48 h后,使用外泌体分离试剂盒分离外泌体,将人脐带间充质干细胞的培养基以2 000×g离心30 min以除去死细胞和碎片;吸取上清,与外泌体分离试剂以体积比2∶1加入到新试管中,4 ℃下孵育过夜;次日,4 ℃下以10 000×g离心1 h,沉淀即为分离得到的外泌体。
电子显微镜观察:将外泌体质量浓度调整到0.5 g/L,PBS重悬,加入2.5%戊二醛固定10 min,取20-30 μL固定好的外泌体悬液滴于碳膜包被的铜网上并于室温静置1 min,红外灯下烘干5 min,滴加一滴1%磷酸钨酸于铜网上室温染色 5 min,吸干磷酸钨酸溶液,再次置于红外灯下烘干10 min。最后将铜网置于电子显微镜下,进行观察并成像。
纳米粒度分析:将外泌体质量浓度调整到1 g/L(用量为1 mL),随后使用纳米粒度及Zeta电位分析仪进行测量。
流式细胞术鉴定:取10 μL外泌体悬液到1.5 mL EP管中,加入10 μL醛/硫酸盐乳胶微珠室温孵育15 min。随后向EP管中加入PBS至总体积为1 mL,混匀后室温孵育2 h。2 h后,加入1 mol/L的甘氨酸溶液110 μL,混匀后室温孵育30 min。4 000 r/min离心3 min,弃上清。用含0.5%BSA的PBS洗涤2次外泌体沉淀。100 μL 含0.5%BSA的PBS重悬外泌体,加入10 μL FITC标记的CD63抗体,4 ℃避光孵育1 h。通过0.5%BSA的PBS洗涤外泌体沉淀2次,最后用200 μL含0.5%BSA的PBS重悬,上机检测。
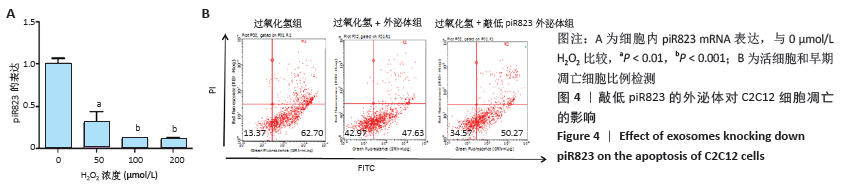
1.4.2 piR823改造和修饰外泌体 采用细胞转染的方法敲低外泌体中的piR823,具体如下:待间充质干细胞密度达到60%-80%时即可进行转染实验,首先将旧的培养基吸出,每孔加入1 mL PBS,冲洗,吸出后每孔加入4 mL基础培养基(无双抗),30 min后开始转染;配制A液:475 μL基础培养基+25 μL Lip2000,B液:475 μL基础培养基+25 μL piR823 inhibitor;室温条件下混匀A液和B液,孵育15 min;然后加入到培养皿中,此时每个培养皿的终体积为5 mL。6 h后转为无外泌体血清的培养基(αMEM基础培养基+通过离心去除外泌体的血清),待细胞长满时即可收集外泌体,此时得到的外泌体即为转染后的外泌体。采用相同方法转染转染piR823的空白对照。利用qRT-PCR法检测piR823 mRNA的表达量。
为了探究piR823在人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体中的作用,检测小鼠各器官中piR823 mRNA的表达量,以及外泌体及其来源人脐带间充质干细胞中piR823 mRNA的表达量。
qRT-PCR检测piR823 mRNA表达量:将组织样品先进行研磨后加入Trizol裂解液提取RNA,细胞及外泌体样品直接加入Trizol裂解液裂解提取RNA。根据PrimeScript RT试剂盒(TaKaRa,日本)对RNA进行反转录,具体反应体系:5×PrimeScript Buffer 2 μL,PrimeScript Enzyme mTX 0.5 μL,Oligo dT Primer(50 μmol/L)0.5 μL,Random primers(100 μmol/L)0.5 μL,Total RNA 500 ng,RNAase Free ddH2O补齐至10 μL;反应程序:16 ℃30 min,30 ℃30 s,42 ℃30 s,50 ℃1 s,85 ℃ 5 s,10 ℃hold。采用SYBR Premix Ex Taq试剂盒对cDNA样品进行qRT-PCR检测,反应体系:SYBR Premix Ex Taq 5 μL,Forward Primer(5 μmol/L)
0.4 μL,Reverse Primer(5 μmol/L)0.4 μL,ROX Reference Dye 0.2 μL,cDNA模板2 μL,RNAase Free ddH2O 2 μL;反应程序:95 ℃1 min,95 ℃2 s,60 ℃30 s,95 ℃15 s,60 ℃1 s。piR823引物序列:AGC GUU GGU GGU AUA GUG GUG AGC AUA GCU GC。
1.4.3 细胞增殖实验 将处于对数生长期、生长状态良好的C2C12细胞均匀接种于96孔板中,培养至正常生长阶段,待细胞密度达到85%以上时即可进行实验,以每孔4×103-1×105个细胞为宜。将C2C12细胞均匀铺到96孔板中,12 h后在培养基内分别加入转染piR823抑制剂的外泌体和转染空白对照的外泌体,两者质量浓度均为100 g/L。培养24 h后,按照锐博生物Cell-LightTM Apollo 567 Stain Kit使用说明进行实验,依次进行EdU标记、细胞固定化、Apollo染色和DNA染色,最后进行图像获取及分析,染色完成后马上进行检测;如果条件限制,应在4 ℃避光条件下保存,但不应超过3 d。
1.4.4 细胞凋亡实验 取对数生长期的C2C12细胞,待细胞密度达到75%-80%时,将细胞培养基分别换成含50,100,200 μmol/L过氧化氢的培养基处理24 h,建立体外细胞凋亡模型。24 h后,通过qRT-PCR检测细胞内piR823 mRNA的表达情况。为进一步检测外泌体及其中piR823对体外细胞凋亡的影响,将对数生长期的C2C12细胞分为3组,分别为过氧化氢处理组、过氧化氢+外泌体组、过氧化氢+敲低piR823外泌体组,过氧化氢浓度均为100 μmol/L,外泌体的质量终浓度均为100 g/L,处理24 h,最后用流式细胞术检测凋亡情况。
1.4.5 外泌体对壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶的影响实验
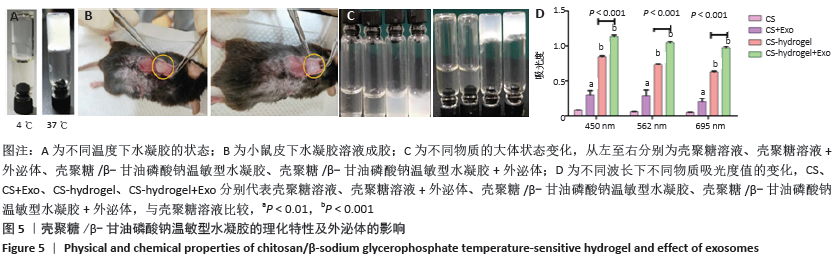
壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶制备:称取2.8 g β-甘油磷酸钠溶解于5 mL去离子水中,使其质量浓度为
560 g/L;将脱乙酰度为95%的壳聚糖粉末(脱乙酰度> 95%)0.2 g溶解于10 mL的0.1 mol/L醋酸溶液中,使其质量浓度为22 g/L,于25 ℃搅拌过夜至完全溶解,以100 μm细胞筛过滤,除去杂质。取壳聚糖乙酸溶液10 mL于小烧杯中,在冰水浴条件下按照10∶1比例逐滴添加1 mL的β-甘油磷酸钠溶液,并不断搅拌。用饱和的磷酸氢钠溶液调节pH值至6.96。将上述配置好的溶液置于37 ℃恒温水浴锅中,待溶液不流动时,即形成壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶。
温敏型水凝胶包封外泌体:在温敏型水凝胶成胶前与外泌体直接混合,保证外泌体的质量浓度为100 g/L。
温敏型水凝胶的成胶性能:将配制好的壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶溶液通过皮下分别注入4只小鼠体内,注射量为100 μL,15 min后剪开小鼠皮肤,如发现产生胶冻样物质,证明可在小鼠体内成胶。
酶标仪检测:取壳聚糖溶液、壳聚糖溶液+外泌体、壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶、壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶+外泌体各100 μL,放入96孔板中,每组3孔。设置450,562,695 nm 3个波长,利用酶标仪进行吸光度值检测。
扫描电镜检测:首先将冷冻干燥的样品黏附在扫描电镜底座的导电胶带上,待离子溅射仪镀膜后入扫描电镜观察。
傅里叶红外光谱检测:将壳聚糖溶液、壳聚糖溶液+外泌体、壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶、壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶+外泌体置于-20 ℃冷冻,待完全凝固后放到冷冻干燥仪中进行冷冻干燥。待完全冻干后取出适量,随后使用VERTEX70红外光谱仪(Thermo Fisher,美国)进行检测。首先将仪器预热30 min,然后将样品取出,放于样品检测台中间的光源透过处,最后进行ATR光谱测量(测量时样品一定要压紧)。
流变学测量:取壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶与包封外泌体的壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶,运用振荡模式,固定频率1 Hz、应变振幅0.01%,温度范围0-40 ℃,升温速率1 ℃/min,平衡3 min后对样品进行温度扫描,考察G’ (储能模量)、G″ (耗能模量) 随温度的变化关系。
水凝胶包封外泌体的缓释动力学:为了检测温敏型水凝胶释放外泌体的速率,使用PKH26荧光染料试剂对外泌体进行荧光标记,将包封外泌体的水凝胶置于24孔板内,用 1 mL PBS浸泡。在37 ℃下每2 d收集一次降解液,并加入新的PBS,最后使用流式细胞仪(Millipore 德国)检测不同时间收集的外泌体的量。将浸泡30 d的缓释液与C2C12细胞共孵育,24 h后通过EdU试剂检测PBS及缓释液对细胞的影响。
1.4.6 不同修饰和改造的外泌体对小鼠缺血后肢恢复的影响
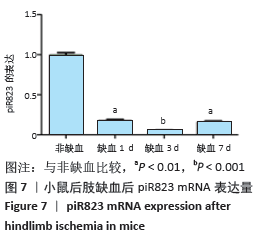
小鼠后肢缺血模型的建立:将30只小鼠随机分为5组,每组6只。首先,使用4%水合氯醛进行腹腔注射,待小鼠麻醉后将其仰卧固定。用脱毛膏对两条后肢脱毛,并用体积分数75%乙醇棉球对皮肤消毒。纵行切开左后肢正中的皮肤,从腹股沟开始,沿腹股沟韧带向远端钝性剥离肌肉至膝关节,分离出股动脉,在腹股沟韧带下结扎股动脉,并结扎与股动脉相连的所有分支。手术结束后,从中间偏下端的位置剪断股动脉,以不出血初步鉴定为建模成功。随后向小鼠的左后肢腓肠肌分别注射PBS(A组)、壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶(B组)、包封外泌体的壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶(C组)、外泌体(D组)、敲低piR823的外泌体(E组),每组试剂60 μL,最后缝合伤口。
qRT-PCR检测:后肢缺血0,1,3,7 d后,利用qRT-PCR检测缺血组织piR823 mRNA表达量。
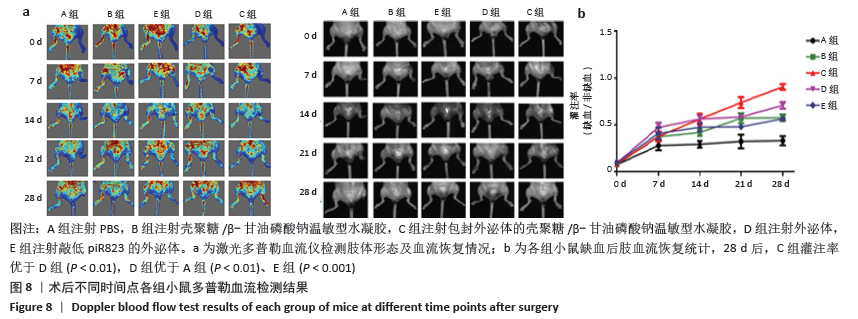
激光多普勒血流仪实验:术后0,7,14,21及28 d,通过激光多普勒血流仪对小鼠后肢血流灌注情况进行检测。建模当天血流灌注率低于15%为建模成功。首先通过小动物呼吸麻醉机对小鼠进行麻醉(2%异氟烷),之后用脱毛膏对小鼠的双后肢进行脱毛处理,并用激光多普勒血流仪检测小鼠后肢血流。具体操作是:在室温下分别于小鼠手术侧和非手术侧的后肢放置激光探头,扫描测量后肢血流(在放松、恒温下所测得的数值)。灌注平均值根据储存的数字彩色编码图像进行计算,灌注率为缺血左肢血流/正常右肢血流。
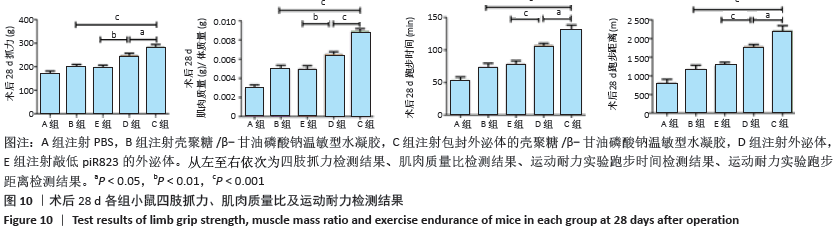
运动耐力实验:术后28 d进行运动耐力实验。先将小鼠置于跑步机上低速运动1 h以适应周围环境,1 h后当小鼠在跑步机上处于稳定运动状态时开始记录跑步时间与距离。首先将跑步机的初始速度设定为6 m/min,之后再将跑步机速度匀速增加至18 m/min并保持不变,直至小鼠处于完全疲惫状态。最终,记录小鼠运动最终总距离与时间。
抓力实验:术后28 d,通过小鼠抓力仪对小鼠四肢力量进行评估测量。首先是将小鼠轻轻放置在抓力板上,抓住鼠尾轻轻向后牵拉(不可猛拉),待动物抓牢抓力板后,均匀用力后拉致使动物松爪,仪器会自动记录小鼠的最大抓力。每只小鼠测量10次,去掉最大值和最小值,取剩余数值的平均值作为最终测量结果值。
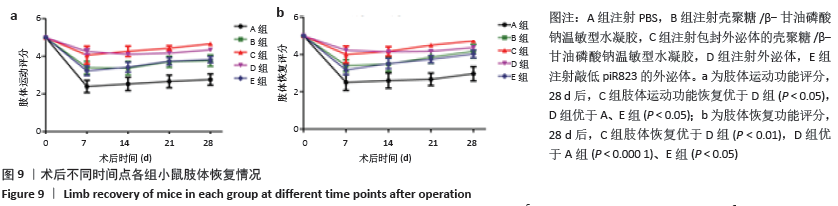
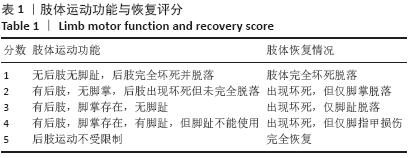
肢体运动功能与恢复评分:根据国际通用的半定量评分系统对小鼠肢体功能与恢复进行评分,具体评分参照标准见表1。
肌肉质量比实验:在术后30 d处死小鼠,称量小鼠体质量,再取出小鼠缺血后肢腓肠肌称质量,以获得其肌肉质量比。
1.5 主要观察指标 敲低piR823的外泌体对C2C12细胞增殖与凋亡的影响;外泌体与壳聚糖/β-甘油磷酸钠温敏型水凝胶的相互作用;外泌体及敲低piR823的外泌体小鼠缺血后肢恢复的影响。
1.6 统计学分析 采用GraphPad 7.0软件进行统计分析,计量资料用x±s表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,各组间两两比较采用t 检验,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。
 文题释义:
文题释义: