[1] GUTIERREZ JM, CALVETE JJ, HABIB AG, et al. Snakebite envenoming.Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17063.
[2] 黄培颖,曾仲意,刘强,等.竹叶青蛇咬伤的流行病学调查及院前影响因素分析[J].临床急诊杂志,2020,21(5):393-396+401.
[3] GUTIERREZ JM, WARRELL DA, WILLIAMS DJ, et al. The need for full integration of snakebite envenoming within a global strategy to combat the neglected tropical diseases: the way forward. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7(6):e2162.
[4] BOLON I, FINAT M, HERRERA M, et al. Snakebite in domestic animals: First global scoping review. Prev Vet Med. 2019;170:104729.
[5] 王湘君,陈文,杜宇,等.台湾竹叶青蛇的分类学研究[J].安徽农业科学, 2011,39(32): 19885-19887+19890.
[6] 郭鹏. 广义竹叶青蛇属的分类及系统发育研究(蛇亚目:蝮亚科)[D].成都: 四川大学, 2005.
[7] 王湘君,陈文,杜宇,等.关于我国竹叶青蛇毒的研究概述[J]. 内江科技, 2019,40(2):112-114.
[8] 谭杜勋,谭新宇,高寒,等.87例竹叶青蛇咬伤急诊救治临床研究[J].中国医药科学,2019,9(11):183-186.
[9] 杨成彬,黄剑宝,卢旺,等.竹叶青毒蛇咬伤早期对凝血功能的影响[J].基层医学论坛,2020,24(16):2241-2243.
[10] VIKRANT S, JARYAL A, PARASHAR A. Clinicopathological spectrum of snake bite-induced acute kidney injury from India. World J Nephrol. 2017;6(3): 150-161.
[11] KASTURIRATNE A, WICKREMASINGHE AR, DE SILVA N, et al. The global burden of snakebite: a literature analysis and modelling based on regional estimates of envenoming and deaths.PLoS Med. 2008;5(11):e218.
[12] 文丹,何卫东,王缓缓,等.蛇伤胶囊对竹叶青蛇伤兔凝血功能的影响[J].中华危重病急救医学,2014,26(3):193-194.
[13] 研究发现猪拥有与人类非常相似的基因特征[J].生物学教学,2013, 38(5):77.
[14] 王威,李其斌,陈泉芳,等.广西境内两种竹叶青蛇咬伤中毒患者的临床特点分析[J].中国全科医学,2013,16(19):1798-1800.
[15] 李满珠,黄小函,徐自强.毒蛇咬伤的护理及对策[J].全科护理, 2010, 8(21):1928-1929.
[16] WAN SG, JIN Y, LEE WH, et al. Cloning of two novel P-III class metalloproteinases from Trimeresurus stejnegeri venom gland.Toxicon. 2006;47(4):465-472.
[17] 罗毅,张剑锋,李其斌,等.竹叶青属毒蛇的毒理机制与临床治疗新进展[J].蛇志,2019,31(4):446-449.
[18] ZHANG YJ, WANG JH, LEE WH, et al. Molecular characterization of Trimeresurus stejnegeri venom L-amino acid oxidase with potential anti-HIV activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;309(3):598-604.
[19] 孟红亚.Bliss法测定YL-N1415对小鼠的半数致死量(LD_(50))[J]. 凯里学院学报,2017,35(3):104-107.
[20] 何冬凌,黄智,廖明,等.四种不同方法注射眼镜蛇蛇毒对小鼠LD_(50)的影响分析[J].蛇志,2019,31(3):311-314.
[21] 黎七雄,汪晖,肖清秋,等.半数致死量(LD_(50))Bliss法的评价及计算[J].数理医药学杂志,1995,8(4):318-320.
[22] 代骏豪,郑强.Probit和Logit模型计算半数反应量的差异研究[J].中国新药杂志,2019,28(6): 651-655.
[23] 周一平. 用SPSS软件计算新药的LD_(50)[J].药学进展,2003,27(5):314-316.
[24] 赵伟, 孙国志.不同种实验动物间用药量换算[J].畜牧兽医科技信息, 2010(5):52-53.
[25] 吴婷婷,屈会化,胡丽娜,等.基于树鼩体表面积的树鼩与人类及其它实验动物等效剂量换算系数的测算[J].中华中医药杂志,2015,30(1): 203-205.
[26] 李紫元,刘逸雷,梁伟燊,等.鸡与其他实验动物体表面积等效换算系数的测算[J].动物医学进展,2018,39(6):129-131.
[27] 姜允申. 理论毒理学研究进展[J].生态毒理学报,2014,9(6): 1239-1242.
[28] 薛仲三. 曲线配合法在测定半数致死量上面的应用[J].军事医学科学院院刊,1980(2): 201-207.
[29] 何宁宁.半数致死量的意义及其计算方法[J].中国医院药学杂志,1984, 4(7):44-45.
[30] 陈侯君.竹叶青蛇咬伤血液学指标动态变化的研究[J].白求恩医学杂志, 2016,14(5):547-549.
[31] ULLAH A, SOUZA TA, ZANPHORLIN LM, et al. Crystal structure of Jararacussin‐I: The highly negatively charged catalytic interface contributes to macromolecular selectivity in snake venom thrombin‐like enzymes.Protein Sci. 2013;22(1):128-132.
[32] PENG L, XU X, GUO M, et al. Effects of metal ions and disulfide bonds on the activity of phosphodiesterase from Trimeresurus stejnegeri venom. Metallomics. 2013;5(7): 920-927.
[33] 梁剑宁,唐荣德,张跃,等.血常规和超敏C反应蛋白检测结果在毒蛇咬伤治疗前后的变化规律[J].国际检验医学杂志,2015,36(12): 1698-1700+1702.
[34] 马恒辉,周晓军.组织固定处理及包埋常见问题与对策[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2011,27(6):638-641.
[35] 蔡文.在自动化组织病理制片中,包埋和切片的质量控制[J].解剖科学进展,2012,18(5):498-499.
[36] WISNER A, BRAUD S, BON C.Snake venom proteinases as tools in hemostasis studies: structure-function relationship of a plasminogen activator purified from Trimeresurus stejnegeri venom.Haemostasis. 2001;31(3-6):133-140.
[37] 覃永安.竹叶青蛇咬伤致凝血功能损害[J].蛇志,2008,20(3):211-215.
[38] 游剑明,饶新,何炳贵.危型竹叶青蛇伤性DIC的救治[J].蛇志,2003,15(1): 14-16.
[39] 梁剑宁,唐荣德,张跃,等.凝血功能在毒蛇咬伤治疗前后变化规律的研究[J].国际检验医学杂志,2015,36(12):1653-1655.
[40] 张笠.广西巴马小型猪全基因组测序及分析研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2019.
[41] YU L, ZHANG J, FENG J, et al. Dynamic changes of coagulation in patients bitten by Trimeresurus stejnegeri in Guangxi China.Toxicon. 2019;158. |
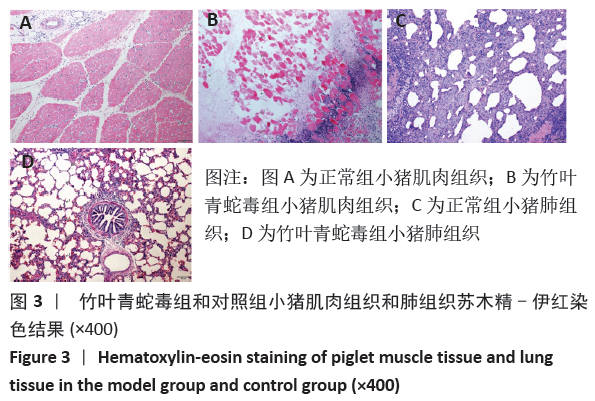
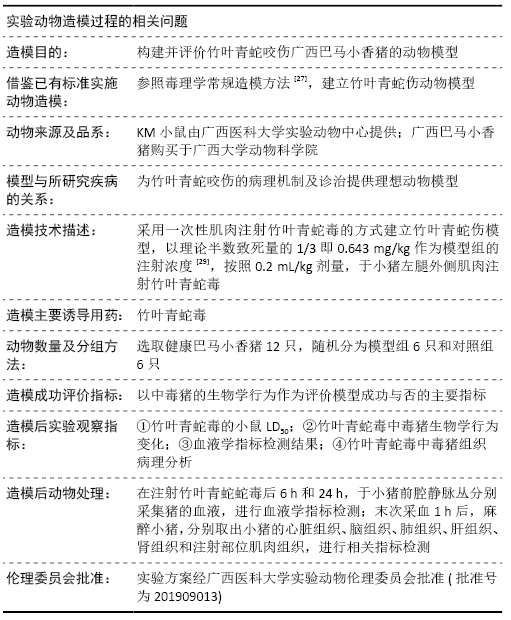
 文题释义:
文题释义: