中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (17): 2767-2774.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3198
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
微小RNA调控组蛋白去乙酰化酶治疗骨相关疾病的发展现状
张 为1,崔帅帅1,周志超2,胡小华2,杨晓红1
- 遵义医科大学附属口腔医院,1修复科,2颌面外科,贵州省遵义市 563003
-
收稿日期:2020-08-05修回日期:2020-08-08接受日期:2020-09-19出版日期:2021-06-18发布日期:2021-01-08 -
通讯作者:杨晓红,博士,副教授,遵义医科大学附属口腔医院修复科,贵州省遵义市 563003 -
作者简介:张为,女,湖南省岳阳市人,汉族,遵义医科大学在读硕士,主要从事骨质疏松方面的研究。 -
基金资助:2016年国家自然科学基金资助项目(8166040198),项目负责人:杨晓红
MicroRNA regulates histone deacetylase in the treatment of bone-related diseases
Zhang Wei1, Cui Shuaishuai1, Zhou Zhichao2, Hu Xiaohua2, Yang Xiaohong1
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, 2Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2020-08-05Revised:2020-08-08Accepted:2020-09-19Online:2021-06-18Published:2021-01-08 -
Contact:Yang Xiaohong, MD, Associate professor, Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhang Wei, Master candidate, Department of Prosthodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China in 2016, No. 8166040198 (to YXH)
摘要:
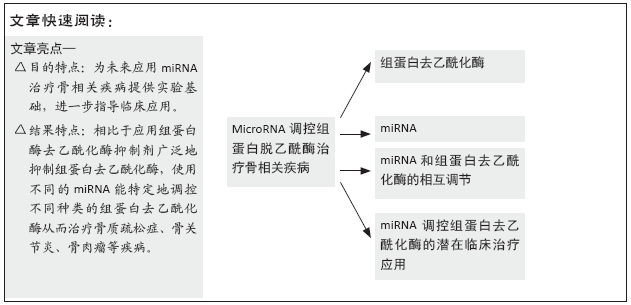
文题释义:
MicroRNA(miRNA):即微小RNA,是真核生物中广泛存在的一类长21-23个核苷酸的小RNA分子,能特异性结合靶基因的信使核糖核酸(mRNA),从而抑制转录后基因表达,在调控基因表达、细胞周期、生物体发育时序等方面起重要作用。
组蛋白去乙酰化酶:属于蛋白酶类,在染色体的结构修饰和基因表达调控中起着重要作用。组蛋白具有α/β脱乙酰酶折叠的晶体结构,组蛋白具有长的N末端延伸结构。
背景:组蛋白去乙酰化酶的表观遗传在骨相关疾病中起着关键作用,近年来研究发现miRNA作为一种新的治疗抑制剂,能与不同种类的组蛋白去乙酰化酶靶向结合影响其表达,进而影响骨相关疾病的发生发展。
目的:综述miRNA特异性调控不同类型组蛋白去乙酰酶治疗各种骨相关疾病的治疗进展,为以后临床治疗骨相关疾病提供新的治疗方向。
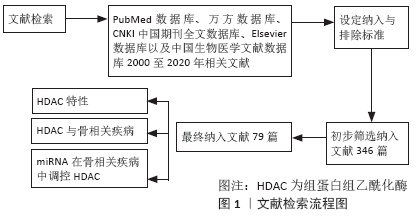
方法:检索PubMed数据库、万方数据库、CNKI中国期刊全文数据库、Elsevier数据库以及中国生物医学文献数据库2000至2020年收录的相关文献。英文检索词为“HDAC,miRNA,bone,mesenchymal stem cells,osteoclast,chondrocyte,osteoarthrosis,osteosarcoma”,中文检索词为“组蛋白去乙酰化酶,微小RNA,骨,间充质干细胞,破骨细胞,软骨细胞,骨关节炎,骨肉瘤”,最终纳入79篇文献进行归纳总结。
结果与结论:①研究发现组蛋白去乙酰化酶通过调控间充质干细胞成骨成脂分化、破骨细胞增殖与活力、骨肉瘤细胞侵袭与转移影响骨相关疾病如骨质疏松症、骨关节炎和骨肉瘤等的发生发展;②miRNA是一类参与基因转录后负向调节的内源性非编码RNA,研究报道miRNA能针对骨骼中的组蛋白去乙酰化酶进行调控,影响骨相关疾病发展。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6945-6629 (张为)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
张 为, 崔帅帅, 周志超, 胡小华, 杨晓红. 微小RNA调控组蛋白去乙酰化酶治疗骨相关疾病的发展现状[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(17): 2767-2774.
Zhang Wei, Cui Shuaishuai, Zhou Zhichao, Hu Xiaohua, Yang Xiaohong. MicroRNA regulates histone deacetylase in the treatment of bone-related diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2767-2774.
HDAC参与骨疾病过程,如:①HDAC能影响其成骨基因(碱性磷酸酶、RUNX-2、骨钙蛋白、骨桥蛋白和Osterix等)表达,成脂基因(过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ等)参与调控干细胞的成骨成脂分化过程,影响骨质疏松症的发生发展;②HDAC参与骨关节炎进展的过程,如影响软骨细胞增殖、肥大、基质合成和降解等;③在骨肿瘤疾病发现HDAC表达量明显高,使用其抑制剂能显著降低骨肉瘤细胞的增殖、分化,抑制骨肉瘤疾病的发生发展[9]。综上,HDAC影响骨疾病的发生发展,因此需要使用一种抑制剂使HDAC表达降低,抑制骨疾病发生。近年来研究发现miRNA能靶向多种HDAC在转录翻译水平上抑制其表达治疗骨疾病。
2.2 miRNA miRNA存在于多种真核细胞中,miRNA首先在细胞核中由RNA聚合酶ⅡDrosha酶转录生成具有7MGpppG和多聚腺苷酸尾巴的一个初始的长转录链pri-miRNA,随后Drosha酶在Pasha因子辅助下切割pri-miRNA,产生长度为60-70核苷酸、具有茎环结构的前体miRNA(pre-miRNA)。随后RanGTP和输出蛋白5将pre-miRNA从细胞核转运到细胞质,pre-miRNA在细胞质中被Dicer RNA剪切酶加工成长约22 nt的双链的成熟miRNA。成熟miRNA其中一条链可被加载到AGO蛋白中形成RNA诱导的沉默复合物[10-11],成熟的miRNA蛋白复合体可通过碱基配对与靶基因mRNA的3’非翻译区(3’-UTR)结合,在RNA沉默和基因表达的转录后调控中发挥作用,通过将mRNA链切割成两段、缩短其聚(A)尾使mRNA失稳和/或通过降低核糖体将mRNA翻译成蛋白质的效率来调节基因表达[12]。另外miRNA参与调节多种生物学过程,包括细胞增殖和凋亡、器官发育、肿瘤发生等。近年来研究发现miRNA在各种骨代谢疾病中被异常表达,调控骨髓间充质干细胞定向分化,影响骨组织中成骨分化代谢平衡。目前发现miRNA促进成骨分化的有miR-291a-3p、
miR-98、Let-7f-5p和miR-27a-3p等[12-15],miRNA抑制成骨分化的有miR-705、miR-224、miR-579-3P、miR-139-5p、miR-488和miR-9-5p等[16-21]。
2.3 miRNA和HDAC的相互调节 很多学者研究发现microRNA 可调节人体中1/3的基因[22]。而miRNA和HDAC之间的互相调节已得到证实,HDAC可以调节miRNA的表达,miRNA也可以调节HDAC和组蛋白的乙酰化,两者对细胞的稳态起着重要作用。近来发现miRNA和HDAC在骨质疏松症、骨关节炎、骨肉瘤等骨相关疾病中起着重要影响[23],这为以后治疗骨代谢疾病提供了新的治疗靶点和方向。以下将简要综述HDAC的类型,以及miRNA如何调控它们影响成骨成软骨破骨细胞。
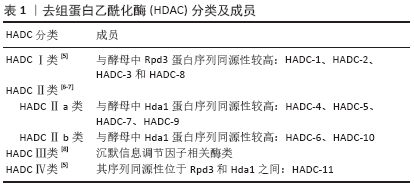
2.3.1 HDAC-Ⅰ类 Ⅰ类HDAC能控制组蛋白尾部赖氨酸侧链乙酰化状态,介导表观遗传基因调控。此类与酵母
Rpd3(yRpd3)有高度同源的序列,包含4个成员——HDAC-1,2,3和8,它们依赖Zn2+,一些成员在细胞质和细胞核之间穿梭,充当各种蛋白质复合物的催化亚基,当其与基因组相互作用时可抑制基因表达[24]。Ⅰ类HDAC对曲古抑菌素A等抑制剂敏感[25],还与其他一些分子(如Sin3和N-CoR)密切相关,这些蛋白质亚基可帮助它们完成去乙酰化和抑制的功能[26],包括HDAC-1,2,3和8。
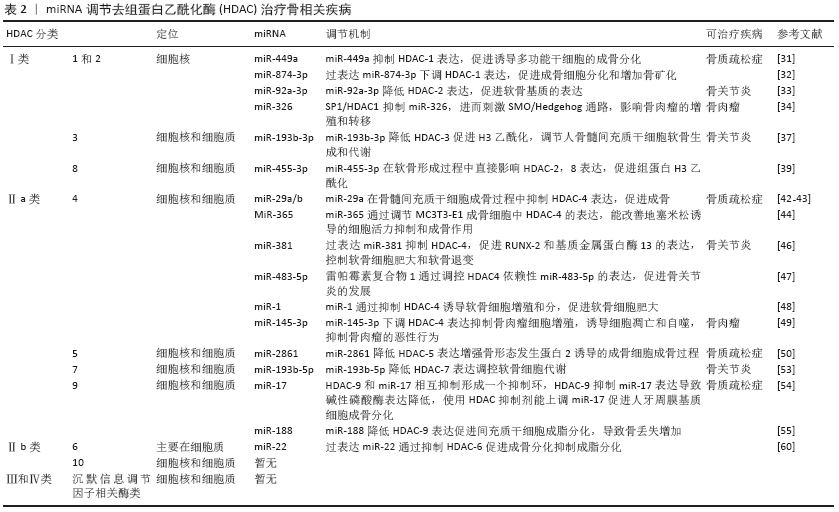
(1)HDAC-1和HDAC-2:HDAC-1,2可与CoREST(元件1沉默转录因子的共同抑制因子)、MiDAC(有丝分裂去乙酰化酶复合物)、NuRD(核小体重塑和去乙酰化)和Sin3A组成复合物,也可与转录抑制因子形成复合物,通过局部组蛋白乙酰化作用在基因沉默中发挥作用[27]。DNA甲基化和乙酰化可在表观遗传方面影响干细胞分化[28]。2006年LEE等[29]发现,培养人骨髓细胞成骨分化时HDAC表达明显下降,抑制HDAC-1表达可显著促进成骨相关基因碱性磷酸酶、骨钙蛋白、骨桥蛋白和Osterix的表达,表明HDAC-1可影响成骨分化。ZHANG等[30]建立糖皮质激素骨质疏松小鼠模型培养骨髓间充质干细胞时,发现HDAC-1和HDAC-2在成骨过程中发挥作用,使用HDAC-1,2的抑制剂曲古抑菌素A上调了成骨基因表达,促进骨形成增加。综上所述,HDAC-1具有抑制成骨作用,促进骨质疏松症的发生发展。而LIU等[31]在诱导人诱导多能干细胞时发现过表达miR-449a水平后4 d内就可以诱导成骨细胞标志物的表达,显著缩短了诱导时间。其机制是miR-449a促进RUNX-2产生,并靶向抑制HDAC-1表达,从而促进人诱导多能干细胞的成骨分化。妇女在生殖的哺乳期和断奶期间骨吸收和形成不停地转换,在哺乳期会出现骨丢失,在断奶期会合成新的骨来补充母体的骨丢失。KUSHWAHA
等[32]研究发现miR-874-3p在断奶期表达增加,体外进一步研究发现miR-874-3p的过度表达可通过增加RUNX-2转录和下调HDAC-1表达,促进成骨细胞分化和增加骨矿化。miRNA还可以调控骨关节炎疾病的发生发展,MAO等[33]发现正常人软骨细胞和骨关节炎原代软骨细胞中miR-92a-3p可与HDAC-2 3’翻译区结合使之表达下降,增强软骨寡聚蛋白表达和Ⅱ型胶原A1启动子的H3乙酰化作用,促进软骨基质的表达。SP1/HDAC-1通过促进组蛋白去乙酰化而抑制
miR-326基因的转录,miR-326缺乏则刺激了SMO/Hedgehog通路,而SMO/Hedgehog通路参与骨肉瘤的增殖和转移[34]。
(2)HDAC-3:骨骼发育早期可检测到HDAC-3存在,HDAC-3是骨骼形成和维持所必需的,对成骨调节至关重要,HDAC-3敲除可导致胚胎死亡[35]。HDAC-3缺乏会导致间充质干细胞成骨能力下降,成脂能力上升[36-37]。临床试验发现在骨关节炎患者中,miR-193b-3p在外体血浆中的水平降低。进一步研究发现在人骨髓间充质干细胞成软骨分化中miR-193b-3p表达增加,转染过表达miR-193b-3p通过与3’UTR靶向结合降低HDAC-3表达,促进了软骨基因Ⅱ型胶原α1、性别决定区Y框蛋白9、聚集蛋白聚糖、寡聚蛋白表达。因此,miR-193b-3p直接靶向HDAC-3可促进H3乙酰化,调节人骨髓间充质干细胞软骨生成和代谢[38],对治疗骨关节炎有重要意义。
(3)HDAC-8:HDAC-8对成骨分化具有重要意义。FU等[39]实验发现HDAC抑制剂丙戊酸促进了组蛋白H3赖氨酸9乙酰化的表达,显著提高了成骨相关基因碱性磷酸酶、RUNX-2、骨钙蛋白、Osterix和骨桥蛋白的表达。而过表达HDAC-8可明显降低H3赖氨酸9乙酰化水平,通过去除组蛋白H3K9的乙酰化作用而抑制成骨相关基因的表达,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。HDAC-8同样也在软骨发育中起到重要作用,研究发现miR-455-3p在软骨形成中被上调,miR-455-3p通过直接靶向与HDAC-2和8-3’翻译区相结合抑制HDAC-2,8表达,促进人SW-1353软骨细胞Ⅱ型胶原α1启动子的组蛋白H3乙酰化,而HDAC-2/8基因敲除可增加性别决定区Y框蛋白9和RUNX-2的表达。因此,miR-455-3p在软骨形成过程中直接影响HDAC-8和HDAC-2表达,促进组蛋白H3乙酰化,发挥重要作用[40]。
综上所述,miRNA可与Ⅰ类HDAC相互作用,影响HDAC表达,促进成骨成软骨分化,对治疗骨质疏松和骨关节炎疾病具有重要意义。
2.3.2 HDAC-Ⅱ类 Ⅱ类HDAC主要参与非组蛋白底物修饰,与酵母Hda1有高度同源性,并且在表达方面具有组织特异性。Ⅱ类HDAC根据核定位信号和酶活性(锌)存在的不同进一步分为两大亚类,即Ⅱa类和Ⅱb类。
(1)HDAC-Ⅱa类:Ⅱa类在细胞质和细胞核之间移动,在细胞质中产生,当被需要时HDAC转入到细胞核。Ⅱa类特征是在其调控N-端结构域中存在2个或3个保守的丝氨酸残基,这些残基受到可逆的磷酸化作用,使HDAC与14-3-3蛋白的结合,HDAC从核转出且抑制靶基因,它们对曲古抑菌素A及其他类型抑制物的抑制表现出敏感性。Ⅱa类HDAC的核浆转运受多种激酶和磷酸酶的调节,这些激酶和磷酸酶可作用于多种生物途径的下游[41],包括HDAC-4,5,7,9。
HDAC-4:HDAC-4在成骨细胞和肥大的软骨细胞中均有表达。NAKATANI等[42]在HDAC-4敲除小鼠中发现皮质骨厚度和骨面积明显减少,其中皮质骨占骨量的80%以上,小梁骨无明显差异。进一步研究发现HDAC-4通过抑制基质金属蛋白酶13和骨硬化蛋白的表达从而抑制骨吸收,HDAC-4的敲除可防止甲状旁腺激素在皮质骨中的分解作用。TAN等[43]实验结果表明miR-29a在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨过程中靶向抑制HDAC-4表达,基质矿化增加,成骨特异性基因表达上调,从而促进成骨。LI等[44]发现miR-29家族中的miR-29b在诱导成骨细胞矿化阶段中胶原蛋白增多,Ⅰ型胶原α1、Ⅴ型胶原α3和Ⅳ型胶原α2 活性增强,还可直接下调成骨细胞分化抑制剂如HDAC-4、转化生长因子β3、ACVR2A、CTNBIP-1和DUSP-2蛋白表达进而促进成骨作用。此外miR-29b还可通过ERK、Smad、Wnt和p38 MAPK等信号转导途径影响体内成骨;还有研究发现miR-365通过调节MC3T3-E1成骨细胞中HDAC-4的表达,改善地塞米松诱导的细胞活力抑制和成骨作用[45]。软骨细胞肥大可由 RUNX-2和基质金属蛋白酶13调控,是软骨变性和骨关节炎发病过程中的重要影响因素。HDAC-4可直接作用于RUNX-2,并使RUNX-2失活,从而抑制软骨细胞肥大和软骨内形成。研究发现过表达miR-381抑制HDAC-4,促进RUNX-2和基质金属蛋白酶13的表达,控制软骨细胞肥大和软骨退变[46]。雷帕霉素复合物1在软骨细胞中的过度激活可加速内侧半月板引起的与年龄相关的骨关节炎表型不稳定的严重程度,并伴有软骨细胞肥大和血管生成。研究发现miR-483-5p参与了雷帕霉素复合物 1激活的骨关节炎,而雷帕霉素复合物 1通过调控HDAC-4依赖性
miR-483-5p的表达,促进软骨细胞肥大、细胞外基质降解和软骨下骨血管生成,从而启动和加速骨关节炎的发展[47]。另一个参与软骨形成的miRNA是miR-1,研究证明HDAC4以剂量依赖式抑制RUNX-2活性,miR-1通过抑制HDAC-4增加了RUNX-2、Ⅹ型胶原和Ihh的表达诱导软骨细胞增殖和分化,促进软骨细胞肥大[48]。miRNA在骨肉瘤的发生发展中起着关键作用,研究显示miR-145-3p通过下调HDAC-4表达显著抑制骨肉瘤细胞的增殖,诱导细胞凋亡和自噬,抑制骨肉瘤的恶性行为[49]。
HDAC-5:WEIN等[50]发现在小鼠的ocy454骨细胞中,HDAC-5负调控体内外骨硬化蛋白的表达,HDAC-5结合并抑制骨硬化蛋白表达关键因子肌细胞增强因子2C ,从而促进骨矿化。过表达的miR-2861可增强骨形态发生蛋白 2诱导的成骨细胞成骨过程,其机制是靶向结合HDAC-5降低其表达而上升RUNX-2、碱性磷酸酶、骨钙蛋白等成骨相关转录因子的表达,体内实验发现尾静脉注射miR-2861抑制剂到小鼠体内后骨形成降低,骨量下降[51]。
HDAC-7:HDAC-7是破骨和骨吸收的负调节因子,HDAC-7过表达抑制破骨细胞形成,而HDAC-7缺失促进破骨细胞形成。在缺乏核因子受体激活因子κB配体(receptor activator of nuclear factor Kappa B ligand,RANKL)的情况下,HDAC-7抑制β-catenin功能和cyclinD-1的表达,从而减少前体增殖;在RANKL激活后,HDAC-7抑制NFATc-1,阻止β-catenin下调,从而阻断破骨细胞分化。破骨细胞HDAC-7缺失导致骨量减少26%,骨吸收增加102%[52]。研究表明在C2C12细胞系中,HDAC-7结合RUNX-2并抑制其活性;转染沉默HDAC7抑制剂后可加速骨形态发生蛋白2依赖的成骨分化过程[53]。白细胞介素1β诱导的原代人软骨细胞和骨关节炎软骨中,miR-193b-5p直接靶向HDAC-7 3’UTR,降低HDAC-7、基质金属蛋白酶3和基质金属蛋白酶 13表达,调控软骨细胞代谢[54]。
HDAC-9:目前研究发现HDAC-9对成骨成脂分化等均有重要影响。HDAC-9缺失可促进体外破骨细胞分化,HDAC-9的过度表达使体外破骨细胞分化减弱。HDAC-9基因敲除得小鼠骨吸收增加,骨量降低。而HDAC-9和miR-17相互抑制形成一个抑制环,HDAC-9抑制miR-17导致碱性磷酸酶表达降低,使用HDAC抑制剂能上调miR-17促进人牙周膜基质细胞成骨分化[55]。HDAC-9和与MTOR复合物2是miR-188的直接靶点,miR-188可结合HDAC-9和 MTOR复合物2促进间充质干细胞成脂分化,使骨髓脂肪累积,导致骨丢失增加[56]。研究发现HDAC-9在骨肉瘤组织中表达上调,与癌旁正常组织相比差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。体外研究进一步表明,在U2OS和MG 63细胞中,HDAC-9的过表达促进了细胞的增殖和侵袭。免疫共沉淀实验发现HDAC-9通过与其近端启动子区结合而抑制p53的转录,表明HDAC-9/p53调控通路在骨肉瘤的进展中起重要作用[57]。
(2)HDAC-Ⅱb类:HDAC-Ⅱb类对非组蛋白底物进行去乙酰化,因为它们缺乏核定位信号,严格来说是细胞质脱乙酰基酶[58]。HDAC-Ⅱb类比HDAC- Ⅰ类在组织中更具特异性分布,包括HDAC-6,10。
HDAC-6:在糖皮质激素引起的骨质疏松症中连续的地塞米松处理会导致分化成骨细胞的成熟潜能降低,这一现象与糖皮质激素受体表达减少、降解加速和亚细胞定位受损有关。HDAC-6表达受地塞米松调控,与糖皮质激素受体共定位,该复合物占据成骨细胞晚期标志骨钙蛋白的启动子区域。联合抑制HDAC-6和糖皮质激素受体可增强骨钙蛋白的表达,促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[59]。WESTENDORF等[60]研究发现,HDAC-6可与RUNX-2的羧基末端相互作用,并作为RUNX-2的核心阻遏因子,抑制小鼠前成骨细胞MC-3T3细胞中的p21启动子。miR-22在调节人脂肪间充质干细胞的脂肪/成骨过程中具有双重性质,miR-22在成骨分化时上调,在成脂分化过程中下调,过表达miR-22后可通过抑制靶基因HDAC-6促进成骨分化抑制成脂分化,虽然miR-22的过表达和HDAC-6的抑制都促进了成骨细胞的形成,但不影响Runx-2的表达水平,这可能和HDAC-6直接与RUNX-2蛋白相互作用有关,调节成骨分化,从而抑制成骨相关基因[61]。众多研究发现HDAC-6在细胞迁移、细胞间相互作用、肿瘤生长和发育事件等多种生物学过程中发挥着重要作用[62-64]。HDAC-6在骨肉瘤细胞株中介导转录因子STAT3下调了肿瘤细胞表达的程序性死亡受体配体1水平,这是一种重要的协同刺激分子,可激活T细胞中的抑制调节通路程序性死亡受体1,使用选择性HDAC-6抑制剂能抑制体内骨肉肿瘤的发生[9]。
HDAC-10:HDAC-10基于与HDAC-6的相似性被归为Ⅱ类亚家族成员。HDAC-10的基因组结构由20个外显子组成,HDAC-10有2个序列变异体,HDAC-10 v1和HDAC-10 v2,HDAC-10 v1和HDAC-10 v2通过17外显子被发现是相同的,但是在这个外显子之后发生了分化。HDAC-10 v2有一个82 bp的交替外显子,可以产生移码并将序列缩短11个氨基酸。目前关于HDAC-10对骨代谢疾病影响的研究较少,HDAC-10多参与肿瘤疾病的发生。
综上所述,miRNA可调节Ⅱ类HDAC对治疗骨质疏松、骨关节炎和骨肉瘤疾病具有重要意义。
2.3.3 HDAC-Ⅲ和Ⅳ类 现阶段有关于Ⅲ类HDAC与骨向分化的研究甚少,多在于研究沉默信息调节因子相关酶类。研究证明在骨髓间充质干细胞中,沉默信息调节因子1对成骨细胞分化过程中脂肪细胞的形成有调节作用[65]。沉默信息调节因子通过抑制过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ表达,进而抑制细胞成脂分化促进成骨分化。沉默信息调节因子 1对雌性小鼠软骨内骨化同样必不可少,沉默信息调节因子 1缺乏可增加p53介导的细胞凋亡,产生严重的发育缺陷[66],包括身材变短、颅面畸形、软骨细胞凋亡增加、软骨内骨化和皮质厚度减少[67-68]。
Ⅳ类HDAC仅包含HDAC-11,HDAC-11是研究最少的,可能与目前对HDAC-11的结构或功能了解不足有关,针对这类HDAC的miRNA尚未被研究。
综上,miRNA通过调控不同类型的HDAC治疗骨相关疾病的文献分析见表2。
2.4 miRNA 调控HDAC的潜在治疗应用 研究发现miRNA在骨相关疾病中起到关键作用,如去骨组织中miR-21小鼠去势后时间延长其表达逐渐降低,研究机制发现miR-21靶向调控Smad7表达,miR-21表达与骨密度值呈正相关,而Smad7与骨密度值呈负相关[69]。潘欣等[70]用补肾方含药血清干预骨髓间充质干细胞能上调miR-195-5p,通过降低其靶基因骨形态发生蛋白受体1α的表达而降低骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化,能改善骨质疏松症状。陶云霞等[71]发现miR-106b抑制剂能够抑制破骨细胞活化,ELISA结果显示,miR-106b inhibitor能促进骨保护素的分泌,抑制RANKL表达,使RANKL/骨保护素比值明显降低,减轻胶原诱导的关节炎模型小鼠骨关节破坏。miR-143在多种肿瘤细胞中低水平表达,如前列腺癌、子宫颈癌、卵巢癌和细胞淋巴瘤
等[72],并作为肿瘤抑制因子在多种癌症中发挥作用。徐泽等[73]发现了miRNA-30e-5p在骨肉瘤U2OS细胞增殖及癌旁正常组织中的表达,miRNA-30e-5p在肿瘤组织中的表达明显低于癌旁正常组织,在临床试验中miRNA-30e-5p表达下调,且骨内瘤患者有转移,晚期肿瘤生存率低。进一步转染
miRNA-30e-5p模拟物能抑制U2OS细胞增殖,促进细胞凋亡,抑制骨内瘤的侵袭和转移,综上所述,miRNA治疗骨相关疾病具有潜在的应用价值。
众多研究发现在多种骨疾病中HDAC活性异常,HDAC已成为一个有吸引力的治疗靶点。现如今多用HDAC抑制剂抑制HDAC的表达,影响骨疾病的发生;但用HDAC抑制剂培养小鼠和人骨髓基质细胞后,可导致DNA损伤、细胞周期阻滞和细胞凋亡[74];而且HDAC抑制剂治疗应用存在一些主要问题,如缺乏特异性、异构体选择性以及缺乏已知靶点等[75]。研究发现miRNA能特异性靶向结合负向调控HDAC表达,对治疗骨相关疾病具有重要意义。综其前所述,体外实验表明
miR-449a、miR-29a/miR-29a b、miR-2861、miR-17、miR-188、miR-22等通过降低HDAC的表达促进成骨,miR-92a-3p、
miR-193b-3p、miR-193b-3p、miR-455-3p、miR-381、miR-1、miR-193b-5p等抑制HDAC表达进而促进软骨形成,miR-145-3p等则通过调控HDAC降低骨肉瘤的发生率。SONG等[76]在内侧半月板失稳模型小鼠的膝关节内注射含有miR-222的慢病毒,使之在软骨组织中过度表达,降低体内HDAC-4的表达,对股骨内侧和胫骨内侧进行Safranin-O染色显示,miR-222过表达可明显减轻内侧半月板失稳手术引起的软骨破坏。
| [1] TSUKASAKI M, TAKAYANAGI H. Osteoimmunology: evolving concepts in bone-immune interactions in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19(10):626-642. [2] BERENDSEN AD, OLSEN BR. Bone development. Bone. 2015;80: 14-18. [3] HUYNH NC, EVERTS V, PAVASANT P, et al. Inhibition of Histone Deacetylases Enhances the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Periodontal Ligament Cells. J Cell Biochem. 2016;117(6):1384-1395. [4] GALLINARI P, DI MARCO S, JONES P, et al. HDACs, histone deacetylation and gene transcription: from molecular biology to cancer therapeutics. Cell Res. 2007;17(3):195-211. [5] GREGORETTI IV, LEE YM, GOODSON HV. Molecular evolution of the histone deacetylase family: functional implications of phylogenetic analysis. J Mol Biol. 2004;338(1):17-31. [6] GROZINGER CM, CHAO ED, BLACKWELL HE, et al. Identification of a class of small molecule inhibitors of the sirtuin family of NAD-dependent deacetylases by phenotypic screening. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276(42):38837-38843. [7] DE RUIJTER AJ, VAN GENNIP AH, CARON HN, et al. Histone deacetylases (HDACs): characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J. 2003;370(Pt 3):737-749. [8] SMITH BC, HALLOWS WC, DENU JM. Mechanisms and molecular probes of sirtuins. Chem Biol. 2008;15(10):1002-1013. [9] KEREMU A, AIMAITI A, LIANG Z, et al. Role of the HDAC6/STAT3 pathway in regulating PD-L1 expression in osteosarcoma cell lines. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2019;83(2):255-264. [10] HA M, KIM VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(8):509-524. [11] IORIO MV, PIOVAN C, CROCE CM. Interplay between microRNAs and the epigenetic machinery: an intricate network. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010;1799(10-12):694-701. [12] LI ZH, HU H, ZHANG XY, et al. MiR-291a-3p regulates the BMSCs differentiation via targeting DKK1 in dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020;36(1):35-42. [13] GAO XL, CAO MG, AI GG, et al. Mir-98 reduces the expression of HMGA2 and promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(11):3311-3317. [14] SHEN GY, REN H, HUANG JJ, et al. Plastrum Testudinis Extracts Promote BMSC Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation by Regulating Let-7f-5p and the TNFR2/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(6):2307-2318. [15] FU YC, ZHAO SR, ZHU BH, et al. MiRNA-27a-3p promotes osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells through targeting ATF3. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(3 Suppl):73-80. [16] 杨晓红,杨琨,廖立,等.微RNA-705对MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化能力的影响[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2016,45(6):575-580. [17] LUO Y, CAO X, CHEN J, et al. MicroRNA-224 suppresses osteoblast differentiation by inhibiting SMAD4. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(10): 6929-6937. [18] LUO B, YANG JF, WANG YH, et al. MicroRNA-579-3p promotes the progression of osteoporosis by inhibiting osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through regulating Sirt1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(16):6791-6799. [19] FENG Y, WAN P, YIN L, et al. The Inhibition of MicroRNA-139-5p Promoted Osteoporosis of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Targeting Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling Pathway by NOTCH1. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020;30(3):448-458. [20] HUANG Y, HOU Q, SU H, et al. miR‑488 negatively regulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by psoralen by targeting Runx2. Mol Med Rep. 2019;20(4):3746-3754. [21] ZHANG HG, WANG XB, ZHAO H, et al. MicroRNA-9-5p promotes osteoporosis development through inhibiting osteogenesis and promoting adipogenesis via targeting Wnt3a. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(2):456-463. [22] COSKUN M, BJERRUM JT, SEIDELIN JB, et al. MicroRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease--pathogenesis, diagnostics and therapeutics. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(34):4629-4634. [23] MOHANAKRISHNAN V, BALASUBRAMANIAN A, MAHALINGAM G, et al. Parathyroid hormone-induced down-regulation of miR-532-5p for matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in rat osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(7):6181-6193. [24] ITOH T, FAIRALL L, MUSKETT FW, et al. Structural and functional characterization of a cell cycle associated HDAC1/2 complex reveals the structural basis for complex assembly and nucleosome targeting. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(4):2033-2044. [25] WATSON PJ, FAIRALL L, SCHWABE JW. Nuclear hormone receptor co-repressors: structure and function. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2012;348(2): 440-449. [26] BANTSCHEFF M, HOPF C, SAVITSKI MM, et al. Chemoproteomics profiling of HDAC inhibitors reveals selective targeting of HDAC complexes. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29(3):255-265. [27] CANTLEY MD, FAIRLIE DP, BARTOLD PM, et al. Inhibiting histone deacetylase 1 suppresses both inflammation and bone loss in arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(9):1713-1723. [28] CHO YD, KIM BS, KIM WJ, et al. Histone acetylation together with DNA demethylation empowers higher plasticity in adipocytes to differentiate into osteoblasts. Gene. 2020;733:144274. [29] LEE HW, SUH JH, KIM AY, et al. Histone deacetylase 1-mediated histone modification regulates osteoblast differentiation. Mol Endocrinol. 2006;20(10):2432-2443. [30] ZHANG Y, MA C, LIU X, et al. Epigenetic landscape in PPARγ2 in the enhancement of adipogenesis of mouse osteoporotic bone marrow stromal cell. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1852(11):2504-2516. [31] LIU T, HOU L, ZHAO Y, et al. Epigenetic silencing of HDAC1 by miR-449a upregulates Runx2 and promotes osteoblast differentiation. Int J Mol Med. 2015;35(1):238-246. [32] KUSHWAHA P, KHEDGIKAR V, SHARMA D, et al. MicroRNA 874-3p Exerts Skeletal Anabolic Effects Epigenetically during Weaning by Suppressing Hdac1 Expression. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(8):3959-3966. [33] MAO G, ZHANG Z, HUANG Z, et al. MicroRNA-92a-3p regulates the expression of cartilage-specific genes by directly targeting histone deacetylase 2 in chondrogenesis and degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(4):521-532. [34] HUANG JH, XU Y, LIN FY. The inhibition of microRNA-326 by SP1/HDAC1 contributes to proliferation and metastasis of osteosarcoma through promoting SMO expression. J Cell Mol Med. 2020;24(18):10876-10888. [35] BHASKARA S, KNUTSON SK, JIANG G, et al. Hdac3 is essential for the maintenance of chromatin structure and genome stability. Cancer Cell. 2010;18(5):436-447. [36] MCGEE-LAWRENCE ME, CARPIO LR, SCHULZE RJ, et al. Hdac3 Deficiency Increases Marrow Adiposity and Induces Lipid Storage and Glucocorticoid Metabolism in Osteochondroprogenitor Cells. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(1):116-128. [37] FEIGENSON M, SHULL LC, TAYLOR EL, et al. Histone Deacetylase 3 Deletion in Mesenchymal Progenitor Cells Hinders Long Bone Development. J Bone Miner Res. 2017;32(12):2453-2465. [38] MENG F, LI Z, ZHANG Z, et al. MicroRNA-193b-3p regulates chondrogenesis and chondrocyte metabolism by targeting HDAC3. Theranostics. 2018;8(10):2862-2883. [39] FU Y, ZHANG P, GE J, et al. Histone deacetylase 8 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells by inhibiting histone H3K9 acetylation and RUNX2 activity. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014;54:68-77. [40] CHEN W, CHEN L, ZHANG Z, et al. MicroRNA-455-3p modulates cartilage development and degeneration through modification of histone H3 acetylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863(12):2881-2891. [41] MARTIN M, KETTMANN R, DEQUIEDT F. Class IIa histone deacetylases: regulating the regulators. Oncogene. 2007;26(37):5450-5467. [42] NAKATANI T, CHEN T, JOHNSON J, et al. The Deletion of Hdac4 in Mouse Osteoblasts Influences Both Catabolic and Anabolic Effects in Bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(7):1362-1375. [43] TAN K, PENG YT, GUO P. MiR-29a promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via targeting HDAC4. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(11):3318-3326. [44] LI Z, HASSAN MQ, JAFFERJI M, et al. Correction: Biological functions of miR-29b contribute to positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2019;294(25):10018. [45] XU D, GAO Y, HU N, et al. miR-365 Ameliorates Dexamethasone-Induced Suppression of Osteogenesis in MC3T3-E1 Cells by Targeting HDAC4. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(5):977. [46] CHEN W, SHENG P, HUANG Z, et al. MicroRNA-381 Regulates Chondrocyte Hypertrophy by Inhibiting Histone Deacetylase 4 Expression. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(9):1377. [47] WANG H, ZHANG H, SUN Q, et al. Chondrocyte mTORC1 activation stimulates miR-483-5p via HDAC4 in osteoarthritis progression. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(3):2730-2740. [48] LI P, WEI X, GUAN Y, et al. MicroRNA-1 regulates chondrocyte phenotype by repressing histone deacetylase 4 during growth plate development. FASEB J. 2014; 28(9): 3930-3941. [49] WU G, YU W, ZHANG M, et al. MicroRNA-145-3p suppresses proliferation and promotes apotosis and autophagy of osteosarcoma cell by targeting HDAC4. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018; 46(sup2):579-586. [50] WEIN MN, SPATZ J, NISHIMORI S, et al. HDAC5 controls MEF2C-driven sclerostin expression in osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(3): 400-411. [51] LI H, XIE H, LIU W, et al. A novel microRNA targeting HDAC5 regulates osteoblast differentiation in mice and contributes to primary osteoporosis in humans. J Clin Invest. 2009;119(12):3666-3677. [52] JIN Z, WEI W, DECHOW PC, et al. HDAC7 inhibits osteoclastogenesis by reversing RANKL-triggered β-catenin switch. Mol Endocrinol. 2013; 27(2):325-335. [53] JENSEN ED, SCHROEDER TM, BAILEY J, et al. Histone deacetylase 7 associates with Runx2 and represses its activity during osteoblast maturation in a deacetylation-independent manner. J Bone Miner Res. 2008;23(3):361-372. [54] ZHANG C, ZHANG Z, CHANG Z, et al. miR-193b-5p regulates chondrocytes metabolism by directly targeting histone deacetylase 7 in interleukin-1β-induced osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(8): 12775-12784. [55] LI L, LIU W, WANG H, et al. Mutual inhibition between HDAC9 and miR-17 regulates osteogenesis of human periodontal ligament stem cells in inflammatory conditions. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):480. [56] LI CJ, CHENG P, LIANG MK, et al. MicroRNA-188 regulates age-related switch between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(4):1509-1522. [57] ZHAO YX, WANG YS, CAI QQ, et al. Up-regulation of HDAC9 promotes cell proliferation through suppressing p53 transcription in osteosarcoma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(7):11818-11823. [58] FALKENBERG KJ, JOHNSTONE RW. Histone deacetylases and their inhibitors in cancer, neurological diseases and immune disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2014;13(9):673-691. [59] RIMANDO MG, WU HH, LIU YA, et al. Glucocorticoid receptor and Histone deacetylase 6 mediate the differential effect of dexamethasone during osteogenesis of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). Sci Rep. 2016;6:37371. [60] WESTENDORF JJ, ZAIDI SK, CASCINO JE, et al. Runx2 (Cbfa1, AML-3) interacts with histone deacetylase 6 and represses the p21(CIP1/WAF1) promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(22):7982-7992. [61] HUANG S, WANG S, BIAN C, et al. Upregulation of miR-22 promotes osteogenic differentiation and inhibits adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by repressing HDAC6 protein expression. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(13):2531-2540. [62] VALENZUELA-FERNÁNDEZ A, CABRERO JR, SERRADOR JM, et al. HDAC6: a key regulator of cytoskeleton, cell migration and cell-cell interactions. Trends Cell Biol. 2008;18(6):291-297. [63] LEE YS, LIM KH, GUO X, et al. The cytoplasmic deacetylase HDAC6 is required for efficient oncogenic tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2008; 68(18):7561-7569. [64] KALUZA D, KROLL J, GESIERICH S, et al. Class IIb HDAC6 regulates endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis by deacetylation of cortactin. EMBO J. 2011;30(20):4142-4156. [65] XU Y, WANG S, TANG C, et al. Upregulation of long non-coding RNA HIF 1α-anti-sense 1 induced by transforming growth factor-β-mediated targeting of sirtuin 1 promotes osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(5):7233-7238. [66] CHENG HL, MOSTOSLAVSKY R, SAITO S, et al. Developmental defects and p53 hyperacetylation in Sir2 homolog (SIRT1)-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(19):10794-10799. [67] GABAY O, SANCHEZ C, DVIR-GINZBERG M, et al. Sirtuin 1 enzymatic activity is required for cartilage homeostasis in vivo in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheum. 2013;65(1):159-166. [68] MERCKEN EM, MITCHELL SJ, MARTIN-MONTALVO A, et al. SRT2104 extends survival of male mice on a standard diet and preserves bone and muscle mass. Aging Cell. 2014;13(5):787-796. [69] 邓纯博, 刘林, 肖正俊, 等.骨质疏松小鼠骨组织中miR-21及Smad7的表达及其与骨密度的相关性[J].中国医科大学学报, 2019,48(1):44-47. [70] 潘欣, 曾思良, 梁兴伦, 等.MicroRNA-195-5p调节Bmpr1α表达对骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化的影响[J].同济大学学报(医学版), 2017,38(3):1-7+13. [71] 陶云霞, 王亮亮, 候振扬, 等.微小RNA-106b通过调控核因子-κB受体活化因子配体/骨保护素对胶原诱导的小鼠关节炎骨质破坏的作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2019,36(7):1243-1246. [72] WANG L, HE J, XU H, et al. MiR-143 targets CTGF and exerts tumor-suppressing functions in epithelial ovarian cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(6):2716-2726. [73] 徐泽, 黄威, 马锐祥, 等.miRNA-30e-5p抑制骨肉瘤细胞增殖、转移的机制研究[J].山西医科大学学报,2020,51(6):506-511. [74] BRADLEY EW, MCGEE-LAWRENCE ME, WESTENDORF JJ. Hdac-mediated control of endochondral and intramembranous ossification[J]. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2011;21(2):101-113. [75] CHANG J, VARGHESE DS, GILLAM MC, et al. Differential response of cancer cells to HDAC inhibitors trichostatin A and depsipeptide[J]. Br J Cancer. 2012;106(1):116-125. [76] SONG J, JIN EH, KIM D, et al. MicroRNA-222 regulates MMP-13 via targeting HDAC-4 during osteoarthritis pathogenesis. BBA Clin. 2015;3: 79-89. [77] LAWLOR L, YANG XB. Harnessing the HDAC-histone deacetylase enzymes, inhibitors and how these can be utilised in tissue engineering. Int J Oral Sci. 2019;11(2):20. [78] AUTIN P, BLANQUART C, FRADIN D. Epigenetic Drugs for Cancer and microRNAs: A Focus on Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(10):1530. [79] SUN X, GUO Q, WEI W, et al. Current Progress on MicroRNA-Based Gene Delivery in the Treatment of Osteoporosis and Osteoporotic Fracture. Int J Endocrinol. 2019;2019:6782653. |
| [1] | 林清凡, 解一新, 陈婉清, 叶振忠, 陈幼芳. 人胎盘源间充质干细胞条件培养液可上调缺氧状态下BeWo细胞活力和紧密连接因子的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [3] | 徐 峰, 康 辉, 魏坦军, 席金涛. 椎弓根螺钉不同固定方法治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | 姜 勇, 罗 翼, 丁永利, 周 勇, 闵 理, 唐 凡, 张闻力, 段 宏, 屠重棋. 骶骨精准切除影响骨盆稳定性的冯米斯应力特征及临床验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | 张同同, 王中华, 文 杰, 宋玉鑫, 刘 林. 3D打印模型在颈椎肿瘤手术切除与重建中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | 张 宇, 田少奇, 曾国波, 胡 川. 初次下肢全关节置换后发生心肌梗死的危险因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | 韦 玮, 李 剑, 黄林海, 兰敏东, 卢显威, 黄绍东. 全膝或全髋关节置换后老年人首次活动时跌倒恐惧的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | 王金军, 邓增发, 刘 康, 何智勇, 余新平, 梁建基, 李 晨, 郭洲洋. 全膝关节置换静脉滴注氨甲环酸联合含氨甲环酸鸡尾酒局部应用的止血效果及安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | 肖国庆, 刘选泽, 严钰皓, 钟喜红. 后交叉韧带替代型假体全膝关节置换术后屈曲受限的影响因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | 彭智浩, 冯宗权, 邹勇根, 牛国庆, 吴 峰. 活动平台单髁置换后下肢力线与外侧间室骨关节炎进展的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [11] | 黄泽晓, 杨 妹, 林诗炜, 何和与. 血清n-3多不饱和脂肪酸水平与全膝关节置换早期股四头肌肌力变化的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [12] | 张 冲, 刘志昂, 姚帅辉, 高军胜, 姜 岩, 张 陆. 局部应用氨甲环酸减少老年股骨颈骨折全髋关节置换后引流的安全和有效性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [13] | 姚汝斌, 王仕永, 杨开舜. 微创经椎间孔椎间融合治疗单节段腰椎管狭窄症对腰椎-骨盆平衡的改善作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1387-1392. |
| [14] | 王海莹, 吕 冰, 李 辉, 王顺义. 减压植骨融合内固定治疗退变性腰椎滑脱:基于脊柱骨盆参数预测患者的功能预后[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [15] | 吕 振, 白金柱. 基于McKenzie技术的腰椎运动链训练应用于腰椎间孔镜术后分期康复的前瞻性研究[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
现治疗骨质疏松症的药物目前临床上分为两大类:抑制破骨细胞吸收的抗吸收剂和诱导成骨细胞骨形成的合成代谢剂。虽然这些药物在临床上已取得效果,但是需要长期服用,患者的耐受性差,也带来一定的不良反应如乳腺癌、骨肉瘤风险增加、骨坏死、骨转换过度抑制等;另外这些药物只能短暂地减缓骨质流失速率,无法从根本上解决骨质丢失。许多研究表明miRNA能靶向结合HDAC负向调节其表达从而有效逆转骨丢失,治疗骨质疏松疾病。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.2 纳入与排除标准
纳入标准:①与HDAC特性相关的文献;②HDAC与骨相关疾病的文献;③miRNA在骨相关疾病当中调控HDAC的文献。
排除标准:①文章内容与HDAC或与miRNA调控HDAC内容相关度较低;②资料无法提取的部分文献;③重复性研究且研究目的无关的文献。
1.3 数据的提取 共检索到文献 346篇,排除与研究目的相关性差及内容重复文献 ,纳入79篇符合标准的文献进行综述,见图1。
miRNA调控HDAC为临床治疗骨相关疾病提供了理论基础和实践经验,相比HDAC抑制剂治疗缺乏特异性、选择性以及已知靶点,miRNA的特异性靶向治疗较HDAC抑制剂好,且miRNA在所有体液中都是稳定且易于检测的[78]。
未来临床试验中哪些miRNA纳入治疗以及这些miRNA的临床给药途径和用药浓度都急待深入研究,且miRNA药物用于未来临床治疗面临着两大障碍,一是miRNA穿透宿主细胞膜的能力差和选择性地分配所需的组织或细胞;二是由于血流或细胞内的大量核酸酶会降解miRNA,导致裸体合成寡核苷酸的有限半衰期。因此致力于miRNA的临床应用需要更进一步的探索[79]。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程

文题释义:#br# MicroRNA(miRNA):即微小RNA,是真核生物中广泛存在的一类长21-23个核苷酸的小RNA分子,能特异性结合靶基因的信使核糖核酸(mRNA),从而抑制转录后基因表达,在调控基因表达、细胞周期、生物体发育时序等方面起重要作用。#br# 组蛋白去乙酰化酶:属于蛋白酶类,在染色体的结构修饰和基因表达调控中起着重要作用。组蛋白具有α/β脱乙酰酶折叠的晶体结构,组蛋白具有长的N末端延伸结构。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||