中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (5): 622-627.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.05.003
• 骨及关节损伤动物模型 Animal models of bone and joint injuries • 上一篇 下一篇
丹参接骨胶囊对闭合性股骨骨折模型大鼠骨折愈合的影响
王希强1,孙仁光1,孙仕润1,孙 军1,王咏梅1,刘太建1,杜辉君1,潘 峰2
- 1青岛市即墨市中医医院骨科,山东省青岛市 266200;2中国医科大学第四医院骨科,辽宁省沈阳市 110000
Effects of salvia miltiorrhiza bone-setting capsule on fracture healing in a rat model of closed femoral fractures
Wang Xi-qiang1, Sun Ren-guang1, Sun Shi-run1, Sun Jun1, Wang Yong-mei1, Liu Tai-jian1, Du Hui-jun1, Pan Feng2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Chinese Medicine Hospital of Jimo City, Qingdao 266200, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Fourth Hospital of China Medical University, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
闭合性骨折:闭合性骨折常常伴有软组织损伤。软组织对钝器伤的反应包括微血管反应和炎症性过程,可分为炎症期,增殖期和修复期。闭合性骨折的软组织损伤常采用 Tscherne 分类法,该分类法可被分为C0,CⅠ,CⅡ,CⅢ共4个等级。
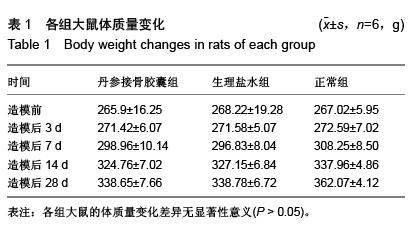
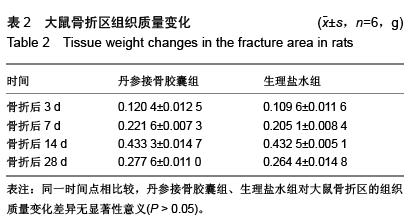
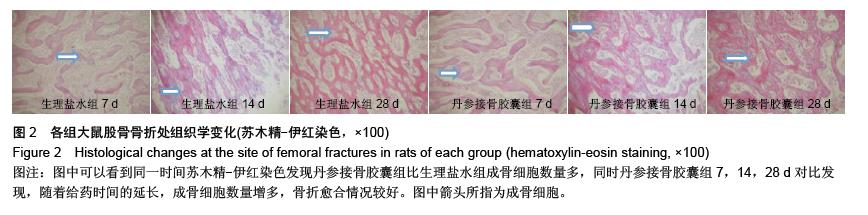
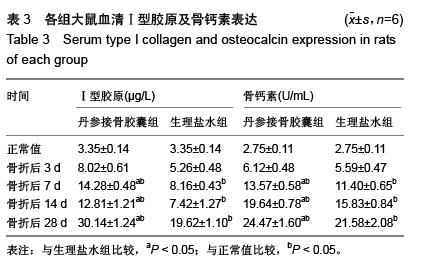
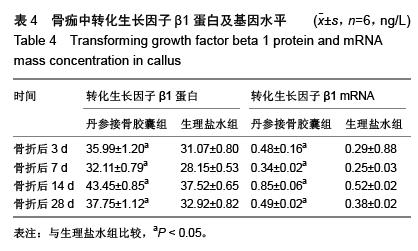
结果与结论:①苏木精-伊红染色显示,骨折后7 d,丹参接骨胶囊组、生理盐水组骨折组织病理变化无显著差异,骨折后14,28 d丹参接骨胶囊组股骨骨折病理修复较生理盐水组明显。②骨折后3,7 d丹参接骨胶囊组、生理盐水组大鼠血清骨钙素、Ⅰ型胶原的表达均明显升高(P < 0.05),两组表达趋势一致,其中丹参接骨胶囊表达量始终较生理盐水组高,且骨折后14,28 d表达量差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。③骨痂转化生长因子β1表达在丹参接骨胶囊组、生理盐水组骨折后第3天出现1个峰值,随后浓度逐渐下降,直至骨折后第14天丹参接骨胶囊组、生理盐水组转化生长因子β1表达又再度升高,出现第2个峰值,至骨折后第28天丹参接骨胶囊组、生理盐水组转化生长因子β1表达浓度再次出现下降。此过程丹参接骨胶囊组、生理盐水组转化生长因子β1表达趋势一致,在7,14,28 d愈合时期,丹参接骨胶囊组大鼠转化生长因子β1表达均高于生理盐水组。④结果证实,丹参接骨胶囊能够促进骨折的愈合,其机制可能与促进血清骨钙素、Ⅰ型胶原及转化生长因子β1的表达有关。
ORCID: 0000-0003-0974-6397(王希强)
.jpg)
.jpg)