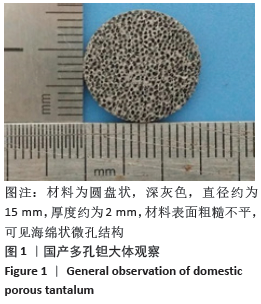
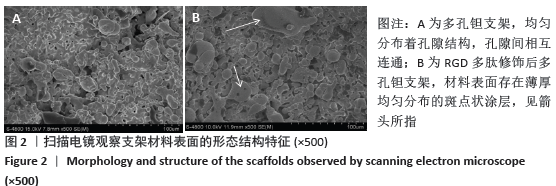
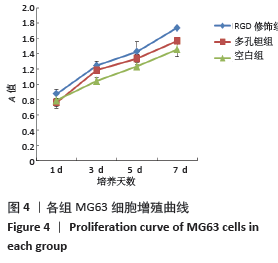
[1] LI HL, YAO Z, ZHANG J, et al. The progress on physicochemical properties and biocompatibility of tantalum-based metal bone implants. SN Appl Sci. 2020;2(3):38-40.
[2] BERMUDEZ MD, CARRION FJ, MARTINEZ NG, et al. Erosion–corrosion of stainless steels,titanium, tantalum and zirconium. Wear. 2005;258(1-4):693-700.
[3] OH IH, NOMURA N, MASAHASHI N, et al. Mechanical properties of porous titanium compacts prepared by powder sintering. Scr Mater. 2003;49(12): 1197-1202.
[4] COHEN R. A porous tantalum trabecular metal: basic science. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2002;31(4):216-217.
[5] LING TX, LI JL, ZHOU K, et al. The use of porous tantalum augments for the reconstruction of acetabular defect in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):453-459.
[6] KONAN S, DUNCAN CP, MASRI BA, et al. Porous tantalum uncemented acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty: a minimum ten-year clinical, radiological and quality of life outcome study. Bone Joint J. 2016;98B:767-771.
[7] LING TX, LI JL, ZHOU K, et al. The use of porous tantalum augments for the reconstruction of acetabular defect in primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(2):453-459.
[8] WITEK L, ALIFARAG AM, TOVAR N, et al. Osteogenic parameters surrounding trabecular tantalum metal implants in osteotomies prepared via osseodensification drilling. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2019;24(6): e764-e769.
[9] ZHAO DW, MA ZJ, WANG TN, et al. Biocompatible Porous Tantalum Metal Plates in the Treatment of Tibial Fracture. Orthop Surg. 2019;11(2):325-329.
[10] 徐基亮,夏荣.精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸修饰钛材料表面的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2016,43(2):190-194.
[11] MAS-MORUNO C, GARRIDO B, RODRIGUEZ D, et al. Biofunctionalization strategies on tantalum-based materials for osseointegrative applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015;26(2): 1-12.
[12] DUQUE-SANCHEZ L, BRACK N, POSTMA A, et al. Engineering the Biointerface of Electrospun 3D Scaffolds with Functionalized Polymer Brushes for Enhanced Cell Binding. Biomacromolecules. 2019;20(2):813-825.
[13] HAMDAN F, BIGDELI Z, ASGHARI SM, et al. Synthesis of Modified RGD-Based Peptides and Their in vitro Activity. ChemMedChem. 2019;14(2):282-288.
[14] 谢玉,周诺.Ⅰ型胶原诱导骨髓间充质干细胞及成骨细胞的成骨分化机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(21):3417-3423.
[15] BLANDIN AF, RENNER G, LEHMANN M, et al. β1 Integrins as Therapeutic Targets to Disrupt Hallmarks of Cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2015;6(157):279.
[16] GOODMAN SL, PICARD M. Integrins as therapeutic targets. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2012;33(7):405.
[17] TAPIAL MARTÍNEZ P, LÓPEZ NAVAJAS P, LIETHA D. FAK Structure and Regulation by Membrane Interactions and Force in Focal Adhesions. Biomolecules. 2020;10(2):179.
[18] Kroese-Deutman HC, van den Dolder J, Spauwen PH, et al. Influence of RGD-loaded titanium implants on bone formation in vivo. Tissue Eng. 2005;11(11-12):1867-1875.
[19] ELMENGAARD B, BECHTOLD JE, SØBALLE K. In vivo study of the effect of RGD treatment on bone ongrowth on press-fit titanium alloy implants. Biomaterials. 2005;26(17):3521-3526.
[20] 甘洪全,王茜,张辉,等.精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸多肽表面修饰多孔钽对软骨细胞黏附、增殖和分泌功能的促进作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2015,41(3):510-516.
[21] 王少华. RGD修饰多孔钽对人成骨细胞增殖及COL-Ⅰ、Integrinβ1、FAK表达影响的实验研究[D].河北:华北理工大学,2018.
[22] 魏晨旭,何怡文,王聃,等.组织工程学中骨修复材料的研究热点与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(10):1615-1621.
[23] NOORI A, ASHRAFI SJ, VAEZ-GHAEMI R, et al. A review of fibrin and fibrin composites for bone tissue engineering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12: 4937-4961.
[24] OLIVEIRA MN, SCHUNEMANN WVH, MATHEW MT, et al. Can degradation products released from dental implants affect peri‐implant tissues? J Periodontal Res. 2018;53(1):1-11.
[25] NAGELS J, STOKDIJK M, ROZING PM. Stress shielding and bone resorption in shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(1):35-39.
[26] ANSELME K. Biomaterials and interface with bone.Osteoporos Int. 2011; 22(6):2037-2042.
[27] BOBYN JD, STACKPOOL GJ, HACKING SA, et al. Characteristics of bone ingrowth and interface mechanics of a new porous tantalum biomaterial. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1999;81(5):907-914.
[28] 李琪佳,王茜,甘洪全,等.多孔钽材料细胞毒性、生物相容性及体内成骨性研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(9):954-961.
[29] GRUSKIN E, DOLL BA, FUTRELL FW, et al. Demineralized bone matrix in bone repair:history and use. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12):1063-1077.
[30] DOLATSHAHI-PIROUZ A, JENSEN T, KRAFT DC, et al. Fibronectin adsorption, cell adhesion, and proliferation on nanostructured tantalum surfaces. ACS Nano. 2010;4(5):2874-2882.
[31] RANA D, ZREIQAT H, ENKIRANE-JESSEL N, et al. Development of decellularized scaffolds for stem cell-driven tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;11(4):942-965.
[32] 赵宏坤,李琪佳,王茜,等.细胞外基质成分修饰骨科植入物的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(11):1390-1394.
[33] 张雅杰,张云涛,王云浩,等. RGD多肽修饰种植体的不同方法及其成骨性研究[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2016,10(18):2799-2802.
[34] WANG H, LI QJ, WANG Q, et al. Enhanced repair of segmental bone defects in rabbit radius by porous tantalum scaffolds modified with the RGD peptide. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(3):50.
[35] 李倩男,洪莉.胶原代谢相关信号通路研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2017, 14(10):56-59.
[36] HASAN A, PANDEY LM. Surface modification of Ti6Al4V by forming hybrid self-assembled monolayers and its effect on Collagen-I adsorption, osteoblast adhesion and integrin expression. Appl Surf Sci. 2019;505:144611.
[37] 杨青,洪莉.整合素的研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2015(6):1023-1025.
[38] LI Z, LIU T, YANG J, et al. Characterization of adhesion properties of the cardiomyocyte integrins and extracellular matrix proteins using atomic force microscopy. J Mol Recognit. 2020;33(4):e2823.
[39] GONZALEZ-PUJANA A, SANTOS-VIZCAINO E, GARCÍA-HERNANDO M, et al. Extracellular matrix protein microarray-based biosensor with single cell resolution: Integrin profiling and characterization of cell-biomaterial interactions. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2019;299:126954.
[40] 李长文,郑启新, 郭晓东,等.RGD多肽修饰的改性PLGA仿生支架材料对骨髓间充质干细胞粘附、增殖及分化影响的研究[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2006,25(2):142-146.
|