中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (36): 5795-5799.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.36.010
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
骨髓间充质干细胞移植脑梗死模型后的CT、MRI特征分析
杨廷双
- 天津医科大学总医院滨海医院放射科,天津市 300480
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for cerebral infarction: CT and MRI characteristics
Yang Ting-shuang
- Department of Radiology, Binhai Hospital, General Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300480, China
摘要:
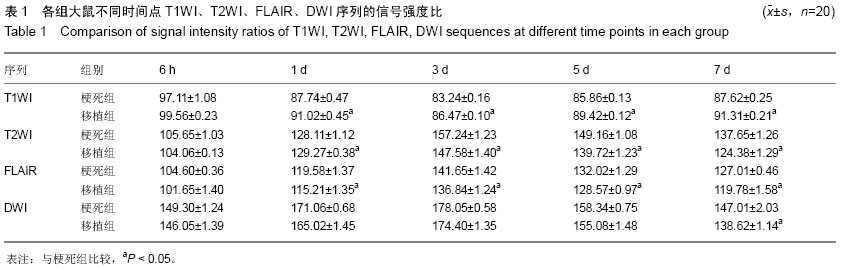
背景:研究表明骨髓间充质干细胞可通过多种途径发挥促进脑组织功能恢复的作用。 目的:分析骨髓间充质干细胞移植脑梗死模型大鼠的CT、MRI特征。 方法:将40只脑梗死模型大鼠随机分为2组,梗死组通过尾静脉注射1 mL PBS、移植组通过尾静脉注射1 mL细胞浓度为2.0×109 L-1的细胞悬液。于移植后1,2,3周进行神经功能缺损评分(mNSS),评价神经功能恢复情况;于移植后的6 h,1,3,5,7 d对各组大鼠行CT及MRI扫描,观察脑梗死区TIWI、T2WI、FLAIR、DWI序列的信号改变特征,梗死体积大小。测量脑梗死区域T1WI、T2WI、FLAIR、DWI序列的信号强度比(SIR)及其相对变化率(?SIR),并与正常对侧相应解剖区域进行比较。 结果与结论:移植后1,2,3周,移植组的神经功能缺损评分明显低于梗死组(P < 0.05);移植后3,5,7 d时移植组脑梗死体积较梗死组显著减少(P < 0.05),移植组T1WI序列SIR均明显高于梗死组,T2WI、FLAIR序列SIR较梗死组显著降低,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);移植后7 d时移植组DWI序列SIR较梗死组明显降低(P < 0.05)。移植组T1WI序列?SIR与梗死组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),移植组T2WI、FLAIR及DWI序列?SIR较梗死组显著增高,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。结果显示MRI可显示大脑任意角度的切面像,对骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死的疗效评价起重要作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: