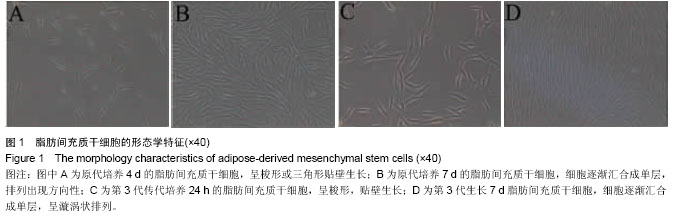
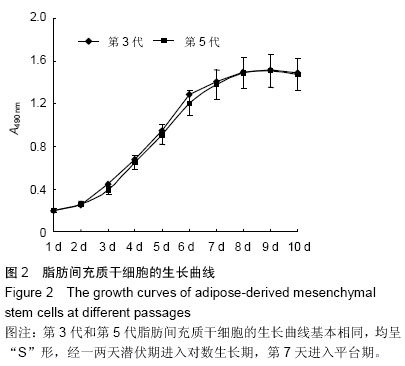
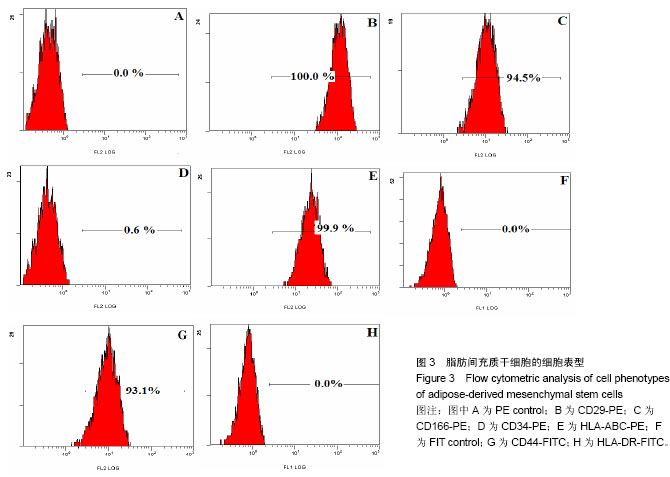
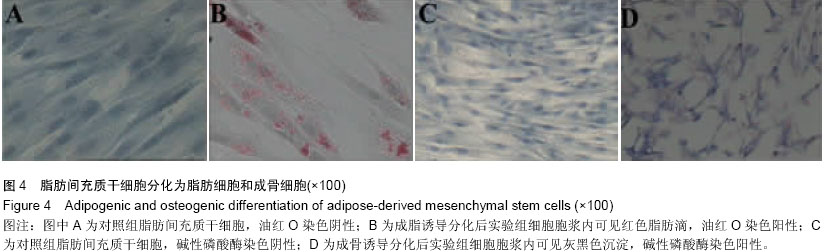
1.1 设计 细胞学体外观察实验。
1.2 时间及地点 于2013年1月至2014年12月在吉林省肝胆病医院科研室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 脂肪组织 脂肪组织来源于10例行门静脉分流术的乙型肝炎肝硬化患者,其中男6例,女4例,年龄35-55岁。乙型肝炎肝硬化诊断标准符合2010年版《中国慢性乙型肝炎防治指南》[9],患者血清HBV DNA平均浓度为8.5×108 IU/L,HBsAg、HBeAg和HBcAb 阳性。研究方案经医院伦理委员会批准,患者知情并签署知情同意书。无菌操作取患者腹部皮下脂肪组织约30 g,置于装有生理盐水的无菌50 mL离心管,用标本运送箱运送至实验室进行分离培养。
1.3.2 主要试剂和仪器 Ⅰ型胶原酶(美国Sigma公司),DMEM/F12培养基、胎牛血清(美国Gibco公司),鼠抗人CD34-PE、CD29-PE、CD166-PE、HLA-ABC-PE、CD44-FITC,HLA-DR -FITC单克隆抗体,PE-IgG1、FITC- IgG1同型对照(美国BD公司),成脂肪、成骨分化诱导培养基(广州赛业生物技术有限公司),油红O染色试剂盒、碱性磷酸酶染色试剂盒(北京雷根生物技术有限公司),CO2培养箱(美国Thermo公司),流式细胞仪(美国Beckman Coulter公司),倒置显微镜(日本Olympus公司)。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 脂肪间充质干细胞的分离培养 按照参考文献[24-25]的方法分离培养人脂肪间充质干细胞。取患者皮下脂肪组织约30 g,用含有青霉素和链霉素的PBS冲洗2遍,体式显微镜下用眼科镊剔除脂肪组织表面血管及黏膜,PBS冲洗2遍,用眼科剪将脂肪组织剪碎成糊状,加入2倍体积0.075%的Ⅰ型胶原酶,37 ℃摇床消化60 min,加入等体积含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的F12/DMEM培养基终止消化,2 000 r/min离心5 min,弃上清,F12/DMEM培养基重悬细胞,200目筛网过滤除去未完全消化的组织块。用生长培养液(F12/DMEM,体积分数为10%胎牛血清,100 g/L链霉素,100 U/mL青霉素)重悬细胞并调整浓度,以3×106/皿接种于60 mm培养皿置于37 ℃,体积分数为5%CO2培养箱培养,48 h后换液,PBS洗去未贴壁细胞,以后每周换液2次,培养7-10 d细胞生长达80%-90%融合后,0.25%胰蛋白酶消化,1︰3传代培养。
1.4.2 MTT法测定脂肪间充质干细胞生长曲线 收集第3代和第5代对数生长期脂肪间充质干细胞,制备单细胞悬液,计数,以每孔1×103细胞接种于96孔板(150 μL/孔),置恒温37 ℃、饱和湿度、体积分数5%的CO2培养箱中培养,培养24 h后取出1块96孔板,每孔加入20 μL MTT溶液(5 g/L),培养4 h后吸弃孔内培养液,每孔加入150 μL 二甲基亚砜,酶标仪490 nm处测定各孔吸光度值。每一天的同一时间取出一块96孔板重复以上操作,连续培养10 d,以培养时间作为横坐标,吸光度作为纵坐标,绘制细胞生长曲线。
1.4.3 流式细胞术检测人脂肪间充质干细胞的细胞表型 参照文献[26-27]方法并稍做改动。收集第3代脂肪间充质干细胞,PBS洗涤细胞,1 000 r/min离心5 min,共2次,制成单细胞悬液,调整细胞浓度为5×109 L-1,加入荧光标记鼠抗人CD34-PE、CD29-PE、CD166-PE、HLA-ABC-PE、CD44-FITC和 HLA-DR-FITC单抗5 μL, PE-IgG1、FITC-IgG1为同型对照,室温避光染色30 min,PBS洗3遍,500 μL PBS重悬细胞,流式细胞仪检测荧光强度。
1.4.4 体外诱导脂肪间充质干细胞分化为脂肪细胞 收集第3代脂肪间充质干细胞消化后接种于6孔板中(孔中预先放置无菌盖玻片),待细胞生长约80%融合时培养基更换为间充质干细胞专用成脂肪细胞诱导培养基,主要成分为含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的完全DMEM培养基加入10-6 mol/L地塞米松、0.5 mmol/L吲哚美辛、0.1 mmol/L抗坏血酸,每3 d换液1次,观察细胞形态。阴性对照组为同批次细胞常规培养基培养。
成脂诱导培养7 d和14 d取出盖玻片,40 g/L多聚甲醛固定10 min,PBS冲洗3遍,油红O染色,苏木精染色液复染,显微镜下观察。油红O染色阳性细胞可见细胞核呈浅蓝色,胞浆内脂肪滴呈橘红色。
1.4.5 体外诱导脂肪间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞 收集第3代脂肪间充质干细胞消化后接种于6孔板中(孔中预先放置无菌盖玻片),待细胞生长约80%融合时培养基更换为间充质干细胞专用成骨细胞诱导培养基,主要成分为含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基中加入10-7 mol/L地塞米松、0.05 mmol/L抗坏血酸和10 mmol/L β-甘油磷酸钠,每周换液2次,观察细胞形态,阴性对照组为同批次细胞常规培养基培养。
成骨诱导培养7 d和14 d取出盖玻片,40 g/L多聚甲醛固定10 nin,碱性磷酸酶染色,显微镜下观察。碱性磷酸酶染色阳性细胞可见细胞内有灰黑色或黑色沉淀。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①HBV感染者脂肪间充质干细胞的体外培养成功率、原代培养时间。②脂肪间充质干细胞形态。③脂肪间充质干细胞生长曲线。④脂肪间充质干细胞的细胞表型。⑤脂肪间充质干细胞体外分化潜能。
1.6 统计学分析 由通讯作者采用SPSS 13.0软件对数据进行统计分析,实验数据以x±s表示,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。