1.1 设计 回顾性病例对照试验。
1.2 时间及地点 试验于2017年10月至2019年9月在贵州医科大学附属口腔医院正畸科完成。
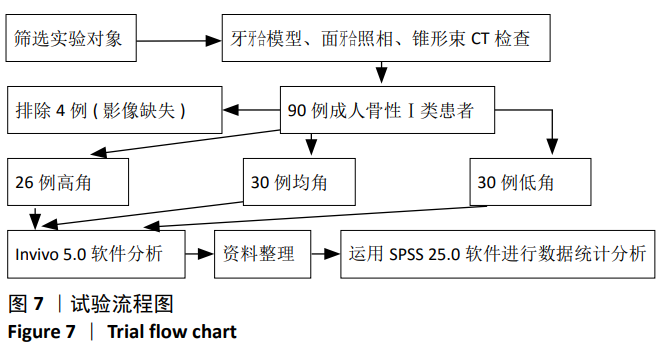
1.3 对象 选取2017年10月至2019年9月就诊于贵州医科大学附属口腔医院正畸科行锥形束CT扫描的患者,年龄20-35岁,原始图像中选择骨性Ⅰ类:0°<ANB(上牙槽座点、鼻根点、下牙槽座点构成的角)< 5°,不同垂直骨面型共90例。
纳入标准:①女性,年龄20-35岁,贵州地区汉族人;②面型左右基本对称,牙列完整(颏点偏离正中矢状面< 2 mm);③锥形束CT影像清晰,体素0.3 mm,影像范围包括发迹至颏部。
排除标准:①有口颌外伤史;②有正畸治疗史、颌面部外伤手术史;③有严重的颌面部软硬组织病变;④有系统性疾病;⑤锥形束CT图像模糊、扭曲、伪影和重叠,影响辨识和测量者。
最终纳入患者共86例,按ANB角将选取不同的矢状骨面型中骨性Ⅰ类患者:0°<ANB ≤5°;按GoGn-SN角[11](下颌平面与前颅底平面构成的夹角)将患者分为不同的垂直骨型:低角型30例,GoGn-SN角≤29°;均角型30例,29°<GoGn-SN角≤39°;高角型26例,GoGn-SN角>39°(因在软件三维重构过程中出现影像缺失而被排除4例)。参与者均知晓其CT资料用途,并签署同意书。
1.4 方法
1.4.1 拍摄锥形束CT图像 受试者锥形束CT原始容积数据图像均由经验丰富的放射科医生在同一条件下拍摄,拍摄仪器为Kava 3D exam(KaVo公司,美国),按以下参数进行全扫描:球管电流5 mA,球管电压120 kV,曝光时间4.0 s,体素0.3 mm,范围由发际线至颏部。取端坐位,于正中牙合位下拍摄,所得图像以医学数字成像和通信(DICOM)格式保存。
1.4.2 锥形束CT图像三维重建及测量 原始图像导入MIMCS 19.0进行三维重建,矫正头位,重建坐标系。确定参考平面[10]:①眶耳平面(FH):过双侧耳点与右侧眶下点所构成的平面;②正中矢状面(MSP):过蝶鞍中心点、鼻根点且同时与眶耳平面、冠状面垂直的平面;③冠状面(CP):过鼻根点与另两个平面(眶耳平面和正中矢状面)相互垂直的平面,见图1。

1.4.3 测量项目分类
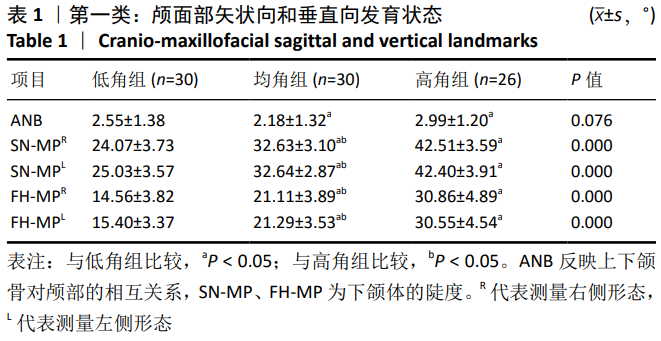
第一类:颅面部矢状向和垂直向发育状态,包括ANB,下颌平面与颅底平面的夹角(MP-SN角),眶耳平面与下颌平面的夹角(FH-MP角)(左右两侧分别测量)。
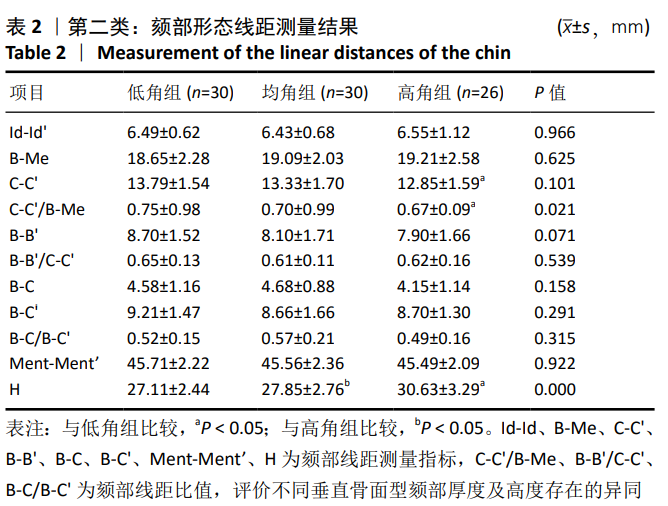
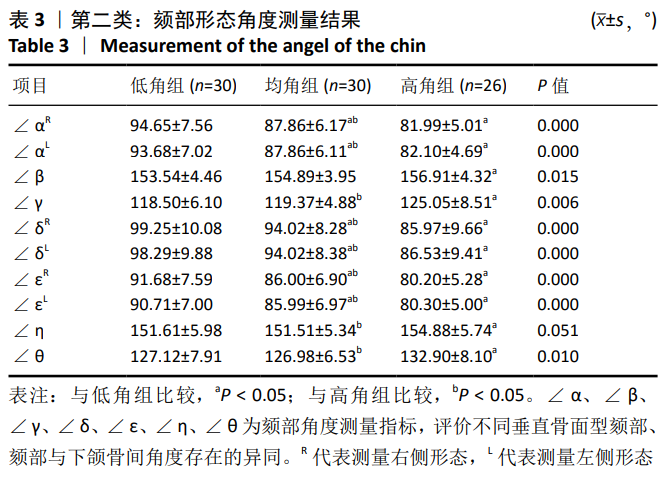
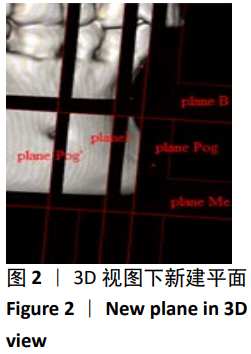
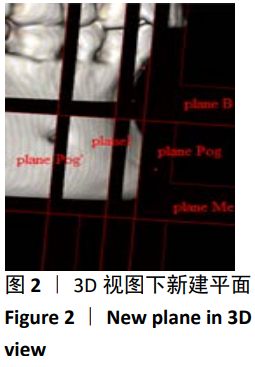
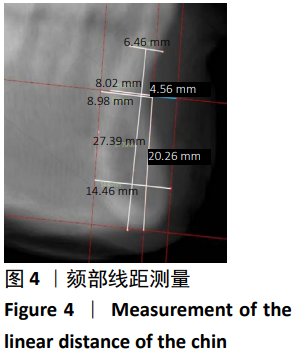
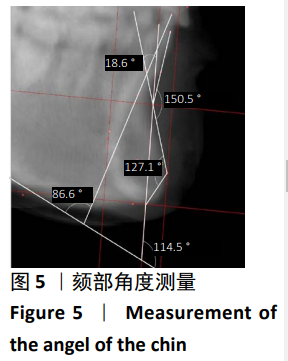
第二类:颏部形态测量。调整头位于正中矢状面,过B点(下牙槽座点)和Me点(颏下点)作与正中矢状面垂直的平面planeⅠ,矢状面观为颏部长轴Ⅰ;过颏部前后最突点作与planeⅠ平行的平面plane Pog与plane Pog’,矢状面观为分别与颏长轴平行的两条平行线a,b;过B点做垂直于正中矢状面及plane Ⅰ的平面plane B,过Me点做与plane B平行的平面plane Me。矢状观为分别过B点、Me点与a、b两条线相互垂直的垂线c、d,分别交a、b于C、C’与D、D’。从矢状面观,a、b、c、d四条线组成一个矩形,见图2,3。图4为颏部线距测量图,线距测量包括:①牙槽骨宽度(Id-Id’);②颏高度(B-Me);③颏厚度(C-C’);④颏厚度/颏高度(C-C’/B-Me);⑤颏最小厚度(B-B’);⑥颏最小厚度/颏厚度(B-B’/C-C’);⑦颏前厚度(B-C);⑧颏后厚度(B-C’);⑨颏前厚度/颏后厚度(B-C/B-C’);⑩颏孔宽度(Ment-Ment’);⑪下颌切牙区牙槽骨高度(h):连接下切牙颊舌侧牙槽嵴顶的连线(L1)的中点与颏部颊舌侧最突点的连线(L2)的中点的直线(L)交下颌体外缘的交点与L1中点连线的距离。图5为颏部角度测量图,角度测量包括:①颏角∠α:颏长轴与下颌平面(MP)相交的后上角;②颏曲度∠β:B点与Pog点的连线与颏长轴相交的后上夹角;③颏孔间角∠γ:连接两侧颏孔与颏前点形成的夹角;④下颌平面角∠δ:下切牙牙体长轴与下颌平面的夹角;⑤下颌基骨倾斜度∠ε:L与下颌平面(MP)的夹角;⑥∠η:分别连接下前牙最突点、B点、颏前点形成的夹角;⑦∠θ:分别连接B点、颏前点、颏下点形成的夹角。
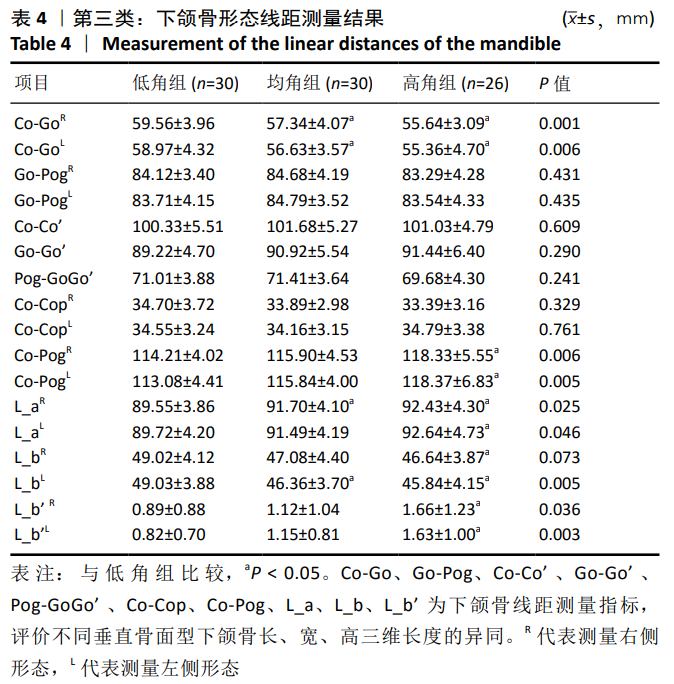
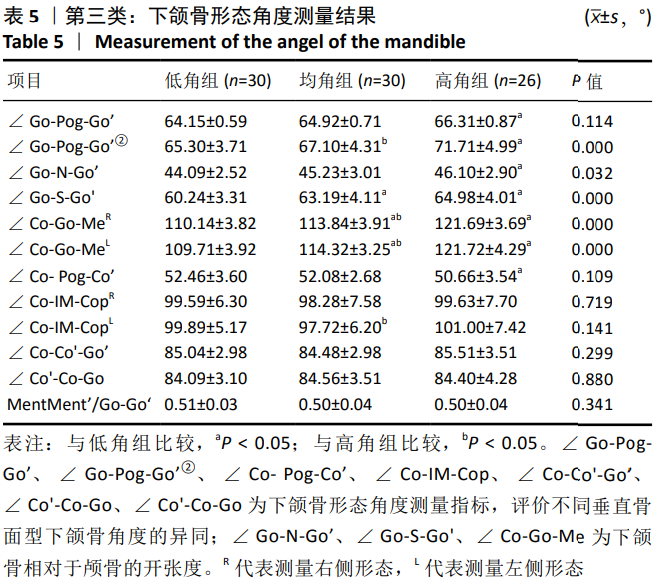
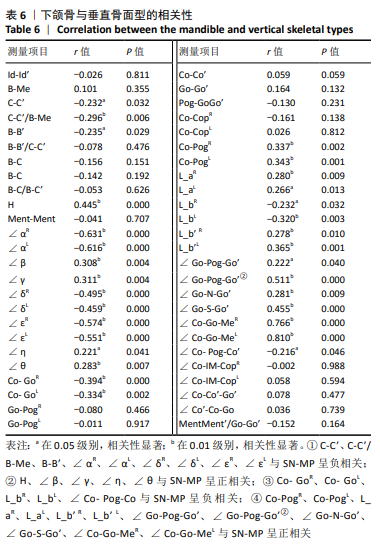
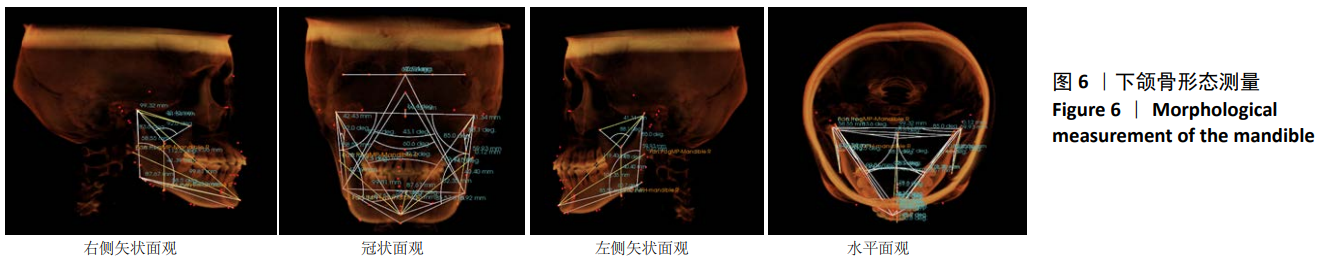
第三类:下颌骨形态测量,见图6。线距测量包括:①Co-Go(R/L):左右髁突最上点到下颌角点的直线距离,表达左右侧下颌支的后段长度;②Go-Pog(R/L):下颌角点到颏前点的直线距离,表达下颌体部下缘的长度;③Co-Co’:两侧髁突最高点之间的直线距离,表达下颌骨上端的宽度;④Go-Go’:两侧下颌角点之间的直线距离,表达下颌骨下端的宽度;⑤Pog-GoGo’:颏前点到GoGo’连线的垂直距离,代表下颌骨深度的指标;⑥Co-Cop(R/L):髁突最上点到喙突嘴上点,代表下颌支上段宽度;⑦Co-Pog(R/L):髁突最上点到颏前点的直线距离,代表下颌骨容积的最大距离;⑧下颌体长度L_a(R/L):过颏前点作与下颌平面的平行线交下颌支后缘的交点与颏前点的距离,代表下颌体中段长度;⑨L_b下颌支长度(R/L):过乙状切记最下点(IM)作与眶耳平面(FH)垂直的垂线交下颌体下缘的交点与IM的距离,代表下颌支中段长度;⑩L_b’(R/L):过乙状切记最下点(IM)作与眶耳平面(FH)垂直的垂线交下颌体下缘的交点到MP的距离。角度测量包括:①∠Go-Pog-Go’:两侧下颌角点与颏下点形成的角,此角度反映下颌体部相对于颏下点在水平向上的开张度;②∠Go-Pog-Go’:两侧下颌角点与颏下点投射于水平面形成的角;②∠Go-N-Go’:两侧下颌角点与鼻根点所成的角,此角反映下颌体部相对于鼻根点垂直向的开张度;③∠Go-S-Go’:两侧下颌角点与蝶鞍点所成的角,此角反映下颌体部相对于蝶鞍点垂直向的开张度;④∠Co-Go-Me(R/L):髁突顶点、下颌角点所形成的直线和下颌角点与颏下点所形成直线的交角,此角度反映下颌角的大小;⑤∠Co-Pog-Co’:两侧髁突最高点与颏前点所形成的角,表明下颌骨水平向的开张度;⑥∠Co-IM-Cop(R/L):髁突顶点和乙状切记最下点所形成的直线与乙状切记最下点和喙突顶点所形成的直线的夹角,代表下颌支上端曲度;⑦∠Co-Co’-Go’(R/L):两侧髁突顶点形成的直线和髁突顶点与下颌角点形成的直线的夹角,代表下颌支的斜度。以上所有数据均采用INVIVO 5软件测量分析,所有测量均由第一作者完成,反复3次,取均值。测量项目为左右两侧(R/L)分别测量。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①成年女性骨性Ⅰ类不同垂直骨面型下颌骨及颏部形态差异:②测量下颌骨和颏部左右两侧线距及角度,分析成年女性高角、均角、低角下颌骨及颏部形态的异同。
1.6 统计学分析 将所测得数据导出为csv格式进行整理后应用SPSS 25.0对其进行统计分析,首先使用独立样本t检验与单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA)进行正态性检验及方差齐性检验,所有测量项目用x±s的方式记录,若方差齐性使用SNK-q检验对各组间数据进行对比,若方差不齐则使用秩和检验,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。