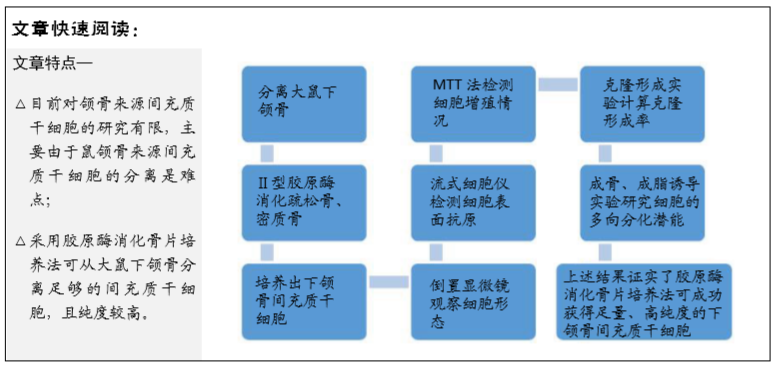
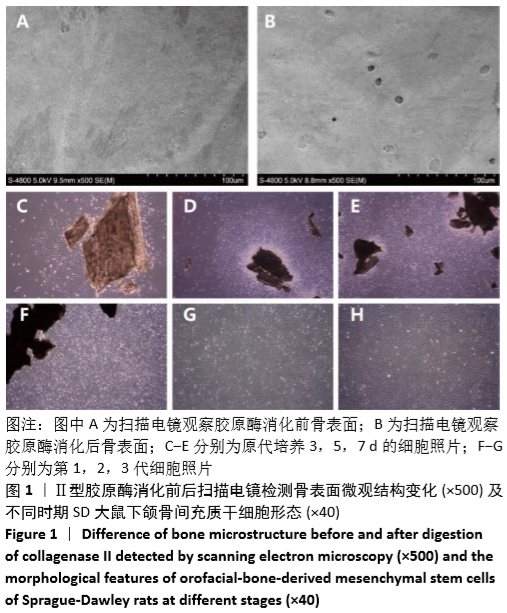
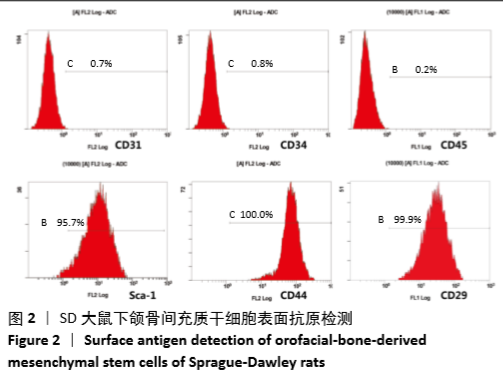
[1] CHAN CK, SEO EY, CHEN JY, et al. Identification and specification of the mouse skeletal stem cell. Cell. 2015;160(1-2):285-298.
[2] CASIRAGHI F, PERICO N, CORTINOVIS M, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells in renal transplantation: opportunities and challenges. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016;12(4):241-253.
[3] LU MM, WU PS, GUO XJ, et al. Osteoinductive effects of tantalum and titanium on bone mesenchymal stromal cells and bone formation in ovariectomized rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(21): 7087-7104.
[4] MASTROLIA I, FOPPIANI EM, MURGIA A, et al. Challenges in Clinical Development of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells: Concise Review. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(11):1135-1148.
[5] LEUCHT P, KIM JB, AMASHA R, et al. Embryonic origin and Hox status determine progenitor cell fate during adult bone regeneration. Development. 2008;135(17):2845-2854.
[6] LLOYD B, TEE BC, HEADLEY C, et al. Similarities and differences between porcine mandibular and limb bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2017;77:1-11.
[7] PARK JB, CHO SH, KIM I, et al. Evaluation of the bisphosphonate effect on stem cells derived from jaw bone and long bone rabbit models: A pilot study. Arch Oral Biol. 2018;85:178-182.
[8] DAI J, KUANG Y, FANG B, et al. The effect of overexpression of Dlx2 on the migration, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of cranial neural crest stem cells. Biomaterials. 2013;34(8):1898-1910.
[9] YAMAZA T, REN G, AKIYAMA K, et al. Mouse mandible contains distinctive mesenchymal stem cells. J Dent Res. 2011;90(3):317-324.
[10] NAKAJIMA R, ONO M, HARA ES, et al. Mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell isolation from tooth extraction sockets. J Dent Res. 2014;93(11):1133-1140.
[11] SHORT BJ, BROUARD N, SIMMONS PJ. Prospective isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse compact bone. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;482:259-268.
[12] ZHU H, GUO ZK, JIANG XX, et al. A protocol for isolation and culture of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse compact bone. Nat Protoc. 2010;5(3):550-560.
[13] LEE DJ, KWON J, CURRENT L, et al. Osteogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells from rat mandible to regenerate critical sized calvarial defect. J Tissue Eng. 2019;10:2041731419830427.
[14] GUO Z, LI H, LI X, et al. In vitro characteristics and in vivo immunosuppressive activity of compact bone-derived murine mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells. 2006;24(4):992-1000.
[15] ANDRZEJEWSKA A, LUKOMSKA B, JANOWSKI M. Concise Review: Mesenchymal Stem Cells: From Roots to Boost. Stem Cells. 2019;37(7): 855-864.
[16] MUSHAHARY D, SPITTLER A, KASPER C, et al. Isolation, cultivation, and characterization of human mesenchymal stem cells. Cytometry A. 2018;93(1):19-31.
[17] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.
[18] GALIPEAU J, SENSÉBÉ L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):824-833.
[19] WIATER J, NIEDZIELA M, POSMYSZ A, et al. Identification of perivascular and stromal mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells in porcine endometrium. Reprod Domest Anim. 2018;53(2):333-343.
[20] GOODISON S, URQUIDI V, TARIN D. CD44 cell adhesion molecules. Mol Pathol. 1999;52(4):189-196.
[21] DONG Q, WANG Y, MOHABATPOUR F, et al. Dental Pulp Stem Cells: Isolation, Characterization, Expansion, and Odontoblast Differentiation for Tissue Engineering. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1922:91-101.
[22] VAN PHAM P, TRUONG NC, LE PT, et al. Isolation and proliferation of umbilical cord tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells for clinical applications. Cell Tissue Bank. 2016;17(2):289-302.
[23] BORZABADI-FARAHANI A. Effect of low-level laser irradiation on proliferation of human dental mesenchymal stem cells; a systemic review. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2016;162:577-582.
[24] COURTNEY JM, SUTHERLAND BA. Harnessing the stem cell properties of pericytes to repair the brain. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(6): 1021-1022.
[25] CORRADETTI B, TARABALLI F, POWELL S, et al. Osteoprogenitor cells from bone marrow and cortical bone: understanding how the environment affects their fate. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(9):1112-1123.
[26] REISSIS D, TANG QO, COOPER NC, et al. Current clinical evidence for the use of mesenchymal stem cells in articular cartilage repair. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2016;16(4):535-557.
[27] MUKHAMEDSHINA YO, GRACHEVA OA, MUKHUTDINOVA DM, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells and the neuronal microenvironment in the area of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(2):227-237.
[28] PITTENGER MF, MACKAY AM, BECK SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411): 143-147.
[29] LEE BK, CHOI SJ, MACK D, et al. Isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from the mandibular marrow aspirates. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2011;112(6):e86-93.
[30] JEON YJ, KIM J, CHO JH, et al. Comparative Analysis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived From Bone Marrow, Placenta, and Adipose Tissue as Sources of Cell Therapy. J Cell Biochem. 2016; 117(5): 1112-1125.
[31] NANCARROW-LEI R, MAFI P, MAFI R, et al. A Systemic Review of Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cell Sources and their Multilineage Differentiation Potential Relevant to Musculoskeletal Tissue Repair and Regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;12(8):601-610. |