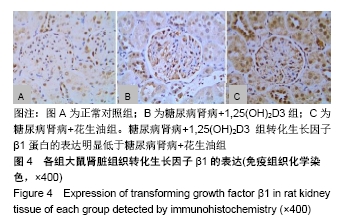
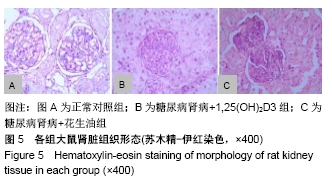
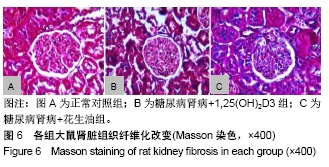
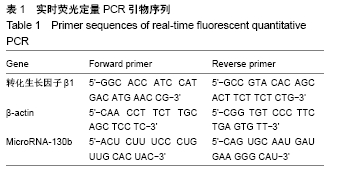
[1] AWAD AS, YOU H, GAO T, et al.Macrophage-derived tumor necrosis factor-α mediates diabetic renal injury.Kidney Int.2015;88(4):722-733.
[2] XIAO L, WANG M, YANG S, et al. A glimpse of the pathogenetic mechanisms of Wnt/bate-catenin signaling in diabetic nephropathy. Biomed Res Int.2013:987064.
[3] SUTARIYA B, JHONSA D, SARAF MN.TGF-beta: the connecting link between nephropathy and fibrosis. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2016; 38(1):39-49.
[4] YAO L , LI J, LI L, et al .Coreopsis tinctoria Nutt ameliorates high glucose-induced renal fibrosis and inflammation via the TGF-beta1/ SMADS/AMPK/NF-kappaB pathways.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019;19(1):14.
[5] 杨烨.张园园.田燕燕,等.活性维生素D3对糖尿病肾病大鼠转化生长因子β1及相关因子的调节作用[J].中华内分泌代谢病学杂志,2015,31(1):66-70.
[6] YU R, MAO J, YANG Y, et al.Protective effects of calcitriol on diabetic nephropathy are mediated by down regulation of TGF-β1 and CIP4 in diabetic nephropathy rat.Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(4):3503-3512.
[7] DONG D, FAN TT, JI YS, et al.Spironolactone alleviates diabetic nephropathy through promoting autophagy in podocytes. Int Urol Nephrol. 2019;51(4):755-764.
[8] BARTEL DP.Metazoan microRNAs. Cell.2018;173:20-51.
[9] SUN Z, MA Y, CHEN F, et al.miR-133b and miR-199b knockdown attenuate TGF-beta1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis by targeting SIRT1 in diabetic nephropathy. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;837:96-104.
[10] MA J, ZHANG L, HAO J, et al.Up-regulation of microRNA-93 inhibits TGF-beta1-induced EMT and renal fibrogenesis by down-regulation of Orai1.J Pharmacol Sci. 2018;136(4):218-227.
[11] HU XY, LI L, WU HT, et al.Serum MicroRNA-130b level, an ideal marker for monitoring the recurrence and prognosis of primary hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation treatment. Pathol Res Pract. 2018;214(10):1655-1660.
[12] LIU L, LIU H, CHEN M, et al.miR-301b~MicroRNA-130b- PPAR gamma axis underlies the adipogenic capacity of mesenchymal stem cells with different tissue origins.Sci Rep.2017;7(1):1160.
[13] ZHENG Y, WANG L,CHEN M, et al.Upregulation of MicroRNA-130b protects against cerebral ischemic injury by targeting water channel protein aquaporin 4 (AQP4).Am J Transl Res.2017;9(7):3452-3461.
[14] WANG Y, DU JH, NIU XM, et al. MiR-130a-3p attenuates activation and induces apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells in nonalcoholic fibrosing steatohepatitis by directly targeting TGFBR1 and TGFBR2. Cell Death Dis.2017;8.e2792.
[15] 张翠静,唐宏霞,鲍喜静.血清中表达在评估2型糖尿病患者MicroRNA-130b早期肾脏损伤中的价值[J].中国临床医生杂志, 2018,46(1)35-38.
[16] PAN S, YANG X, JIA Y, et al. Microvesicle-shuttled MicroRNA-130b reducesfatdeposition in recipient primary cultured porcine adipocytes by inhibiting PPAR-g expression.JCell Physiol. 2014,229(5):631-639.
[17] CASTRO NE, KATO M, PARK JT, et al. Transforming growth factor beta1 (TGF-beta1) enhances expression of profibrotic genes through a novel signaling cascade and microRNAs in renal mesangial cells.J Biol Chem. 2014;289(42):29001-29013.
[18] QINNA NA, BADWAN AA. Impact of streptozotocin on altering normal glucose homeostasis during insulin testing in diabetic rats compared to normoglycemic rats.Drug Design Dev Ther.2015;9:2515-2525.
[19] 郭啸华,刘志红,李恒,等.高糖高脂饮食诱导的2型糖尿病大鼠模型及其肾病特点[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2002,10(5):290-294.
[20] HILLS CE, SQUIRES PE.The role of TGF-beta and epithelial-to mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.2011; 22:131-139.
[21] LI Y, LI L, ZENG O.et al.H2S improves renal fibrosis in STZ-induced diabetic rats by ameliorating TGF-beta1 expression.Ren Fail. 2017; 39(1):265-272.
[22] TORSELLO B, BIANCHI C, MEREGALLI C, et al.Arg tyrosine kinase modulates TGF-beta1 production in human renal tubular cells under high-glucose conditions.J Cell Sci.2016;129(15):2925-2936.
[23] LU Q, WANG WW, ZHANG MZ, et al.ROS induces epithelial- mesenchymal transition via the TGF-beta1/PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in diabetic nephropathy.Exp Ther Med.2019.17(1):835-846.
[24] ZHOU T, LI HY, ZHONG H, et al.Relationship between transforming growth factor-beta1 and type 2 diabetic nephropathy risk in Chinese population.BMC Med Genet.2018;19(1):201.
[25] KATO M.Noncoding RNAs as therapeutic targets in early stage diabetic kidney disease.Kidney Res Clin Pract.2018;37:197-209.
[26] SIMPSON K, WONNACOTT A, FRASER DJ, et al.MicroRNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy: From Biomarkers to Therapy.Curr Diab Rep.2016.16: 35.
[27] KATO M, NATARAJAN R.MicroRNAs in diabetic nephropathy: functions, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets.Ann N Y Acad Sci.2015; 1353(1): 72–88.
[28] LIU X, KONG C, ZHANG Z.MicroRNA-130b promotes bladder cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting VGLL4.Oncol Rep. 2018;39(5):2324-2332.
[29] XIAO ZQ, YIN TK, LI YX, et al.MicroRNA-130b regulates the proliferation, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells via targeting of CYLD.Oncol Rep.2017;38(1):167-174.
[30] 何峰,陈曦,程方雄,等.MicroRNA-130b调控RAB34的表达在胰腺癌发生发展中的作用[J].肿瘤防治研究,2018,45(3):144-147.
[31] ZHOU D, ZHANG L, SUN W, et al.Cytidine monophosphate kinase is inhibited by the TGF-beta signaling pathway through the upregulation of miR-130b-3p in human epithelial ovarian cancer.Cell Signal.2017; 35:197-207.
[32] ORTEGA FJ, MERCADER JM, MORENO-NAVARRETE JM, et al. Profiling of circulating microRNAs reveals common microRNAs linked to type 2 diabetes that change with insulin sensitization.Diabetes Care.2014; 37(5):1375-1383.
[33] BAI X, GENG J, ZHOU Z.MicroRNA-130b improves renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis via repression of Snail-induced epithelial- mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy.Sci Rep.2016;6: 20475.
[34] KIM MJ, FRANKEL AH, DONALDSON M, et al.Oral cholecalciferol decreases albuminuria and urinary TGF-beta1 in patients with type 2 diabetic nephropathy on established renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibition.Kidney Int.2011;80(8):851-860.
[35] 胡小俊.郭诚.1,25-二羟维生素D3对糖尿病肾病的保护作用研究进展[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2014.28(6):526-528.
|