| [1] Reusch JE, Manson JE. Management of type 2 diabetes in 2017: Getting to Goal. JAMA.2017;317(10):1015-1016.[2] Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, et al. Prevalence and ethnic pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in China in 2013.JAMA.2017; 317(24):2515-2523.[3] Hagg S, Thorn LM, Forsblom CM, et al. Different risk factor profiles for ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Stroke.2014;45(9):2558-2562.[4] Koekkoek PS, Kappelle LJ, van den Berg E, et al. Cognitive function in patients with diabetes mellitus: guidance for daily care. Lancet Neurol.2015;14(3):329-340.[5] Stirban A. Microvascular dysfunction in the context of diabetic neuropathy. Curr Diab Rep.2014;14(11):541.[6] Bogush M, Heldt NA, Persidsky Y. Blood brain barrier injury in diabetes: unrecognized effects on brain and cognition. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.2017;12(4):593-601.[7] Zlokovic BV. Neurovascular pathways to neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and other disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011;12(12):723-738.[8] Moskowitz MA, Grotta JC, Koroshetz WJ, et al. The NINDS stroke progress review group final analysis and recommendations. Stroke.2013;44(8):2343-2350.[9] Kisler K, Nelson AR, Montagne A, et al. Cerebral blood flow regulation and neurovascular dysfunction in Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurosci.2017;18(7):419-434.[10] Marie Simard GA, Takahiro Takano, Qing Song Liu, and Maiken Nedergaard. Signaling at the gliovascular interface. J Neurosci.2003;23(27):9254-9262.[11] Giaume C, Koulakoff A, Roux L, et al. Astroglial networks: a step further in neuroglial and gliovascular interactions. Nat Rev Neurosci.2010;11(2):87-99.[12] Iadecola C. Neurovascular regulation in the normal brain and in Alzheimer's disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2004;5(5): 347-360.[13] Andreone BJ, Lacoste B, Gu C. Neuronal and vascular interactions. Annu Rev Neurosci.2015;38:25-46.[14] Jukkola P, Gu C. Regulation of neurovascular coupling in autoimmunity to water and ion channels. Autoimmun Rev. 2015;14(3):258-267.[15] Dunn KM, Hill-Eubanks DC, Liedtke WB, et al. TRPV4 channels stimulate Ca2+-induced Ca2+ release in astrocytic endfeet and amplify neurovascular coupling responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci US A.2013;110(15):6157-6162.[16] Pappas AC, Koide M, Wellman GC. Astrocyte Ca2+ Signaling Drives Inversion of Neurovascular Coupling after Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. J Neurosci.2015;35(39): 13375-13384.[17] Merlini M, Meyer EP, Ulmann-Schuler A, et al. Vascular beta-amyloid and early astrocyte alterations impair cerebrovascular function and cerebral metabolism in transgenic arcAbeta mice. Acta Neuropathol.2011;122(3): 293-311.[18] MacVicar BA, Newman EA. Astrocyte regulation of blood flow in the brain. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.2015,7(5). pii: a020388.[19] Chen Y, Mancuso J, Zhao Z, et al. Vasodilation by in vivo activation of astrocyte endfeet via two-photon calcium uncaging as a strategy to prevent brain ischemia. J Biomed Opt.2013;18(12):126012.[20] Zhang M, Zhang L, Hu J, et al. MST1 coordinately regulates autophagy and apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy in mice. Diabetologia.2016;59(11):2435-2447.[21] Di Benedetto B, Malik VA, Begum S, et al. Fluoxetine Requires the Endfeet Protein Aquaporin-4 to Enhance Plasticity of Astrocyte Processes. Front Cell Neurosci.2016; 10:8.[22] Rajkowska G, Hughes J, Stockmeier CA, et al. Coverage of blood vessels by astrocytic endfeet is reduced in major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry.2013;73(7):613-621.[23] Holland PR, Searcy JL, Salvadores N, et al. Gliovascular disruption and cognitive deficits in a mouse model with features of small vessel disease. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35(6):1005-1014.[24] Duncombe J, Lennen RJ, Jansen MA, et al. Ageing causes prominent neurovascular dysfunction associated with loss of astrocytic contacts and gliosis. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2017;43(6):477-491.[25] Bragg F, Holmes MV, Iona A, et al. Association between diabetes and cause-specific mortality in rural and urban areas of China. JAMA.2017;317(3):280-289.[26] Feher J, Taurone S, Spoletini M, et al. Ultrastructure of neurovascular changes in human diabetic retinopathy. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.2018;31:394632017748841.[27] Gardner TW, Davila JR. The neurovascular unit and the pathophysiologic basis of diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol.2017;255(1):1-6.[28] Kolibabka M, Friedrichs P, Dietrich N, et al. Dicarbonyl Stress Mimics Diabetic Neurovascular Damage in the Retina. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes.2016;124(7):437-439.[29] Zhao Z, Nelson AR, Betsholtz C, et al. Establishment and Dysfunction of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Cell.2015; 163(5): 1064-1078.[30] Min LJ, Mogi M, Shudou M, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma activation with angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade is pivotal for the prevention of blood-brain barrier impairment and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetic mice. Hypertension. 2012;59(5): 1079-1088.[31] Pak RW, Hadjiabadi DH, Senarathna J, et al. Implications of neurovascular uncoupling in functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) of brain tumors. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2017:271678X17707398.[32] Kimbrough IF, Robel S, Roberson ED, et al. Vascular amyloidosis impairs the gliovascular unit in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Brain.2015;138(Pt 12):3716-3733.[33] Nicchia GP, Pisani F, Simone L, et al. Glio-vascular modifications caused by Aquaporin-4 deletion in the mouse retina. Exp Eye Res.2016;146:259-268.[34] Thomsen MS, Routhe LJ, Moos T. The vascular basement membrane in the healthy and pathological brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.2017;37(10):3300-3317.[35] Huang J, Sun SQ, Lu WT, et al. The internalization and lysosomal degradation of brain AQP4 after ischemic injury. Brain Res.2013;1539:61-72.[36] de Senna PN, Xavier LL, Bagatini PB, et al. Physical training improves non-spatial memory, locomotor skills and the blood brain barrier in diabetic rats. Brain Res.2015;1618:75-82.[37] Skucas VA, Mathews IB, Yang J, et al. Impairment of select forms of spatial memory and neurotrophin-dependent synaptic plasticity by deletion of glial aquaporin-4. J Neurosci.2011;31(17):6392-6397.[38] Zeppenfeld DM, Simon M, Haswell JD, et al. Association of perivascular localization of aquaporin-4 with cognition and alzheimer disease in aging brains. JAMA Neurol.2017; 74(1):91-99.[39] Xu Z, Xiao N, Chen Y, et al. Deletion of aquaporin-4 in APP/PS1 mice exacerbates brain Abeta accumulation and memory deficits. Mol Neurodegener.2015;10:58.[40] Wijesekara N, Ahrens R, Sabale M, et al. Amyloid-beta and islet amyloid pathologies link Alzheimer's disease and type 2 diabetes in a transgenic model. Faseb J.2017;31(12): 5409-5418.[41] Michalicova A, Banks WA, Legath J, et al. Tauopathies-focus on changes at the neurovascular unit. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2017;14(7):790-801.[42] Szu JI, Binder DK. The role of astrocytic aquaporin-4 in synaptic plasticity and learning and memory. Front Integr Neurosci.2016;10:8. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
建立持续性高血糖小鼠模型:先予以50 mg/kg链脲佐菌素连续5 d腹腔注射,诱导胰岛细胞β大量的破坏,建立高血糖模型,然后长达4个月予以普通饮食喂养,该方法主要模拟持续性高血糖状态对机体的生理病理影响。
胶质血管连接:血管周围星形胶质细胞足突上表达的水通道蛋白4通过肌营养不良相关蛋白复合物镶嵌在微血管基底膜上组成胶质血管连接结构和神经血管单元,维持大脑内环境稳定,调节脑血流量及血脑屏障的通透性,在脑微血管病变中具有重要的作用。
文题释义:
建立持续性高血糖小鼠模型:先予以50 mg/kg链脲佐菌素连续5 d腹腔注射,诱导胰岛细胞β大量的破坏,建立高血糖模型,然后长达4个月予以普通饮食喂养,该方法主要模拟持续性高血糖状态对机体的生理病理影响。
胶质血管连接:血管周围星形胶质细胞足突上表达的水通道蛋白4通过肌营养不良相关蛋白复合物镶嵌在微血管基底膜上组成胶质血管连接结构和神经血管单元,维持大脑内环境稳定,调节脑血流量及血脑屏障的通透性,在脑微血管病变中具有重要的作用。.jpg) 文题释义:
建立持续性高血糖小鼠模型:先予以50 mg/kg链脲佐菌素连续5 d腹腔注射,诱导胰岛细胞β大量的破坏,建立高血糖模型,然后长达4个月予以普通饮食喂养,该方法主要模拟持续性高血糖状态对机体的生理病理影响。
胶质血管连接:血管周围星形胶质细胞足突上表达的水通道蛋白4通过肌营养不良相关蛋白复合物镶嵌在微血管基底膜上组成胶质血管连接结构和神经血管单元,维持大脑内环境稳定,调节脑血流量及血脑屏障的通透性,在脑微血管病变中具有重要的作用。
文题释义:
建立持续性高血糖小鼠模型:先予以50 mg/kg链脲佐菌素连续5 d腹腔注射,诱导胰岛细胞β大量的破坏,建立高血糖模型,然后长达4个月予以普通饮食喂养,该方法主要模拟持续性高血糖状态对机体的生理病理影响。
胶质血管连接:血管周围星形胶质细胞足突上表达的水通道蛋白4通过肌营养不良相关蛋白复合物镶嵌在微血管基底膜上组成胶质血管连接结构和神经血管单元,维持大脑内环境稳定,调节脑血流量及血脑屏障的通透性,在脑微血管病变中具有重要的作用。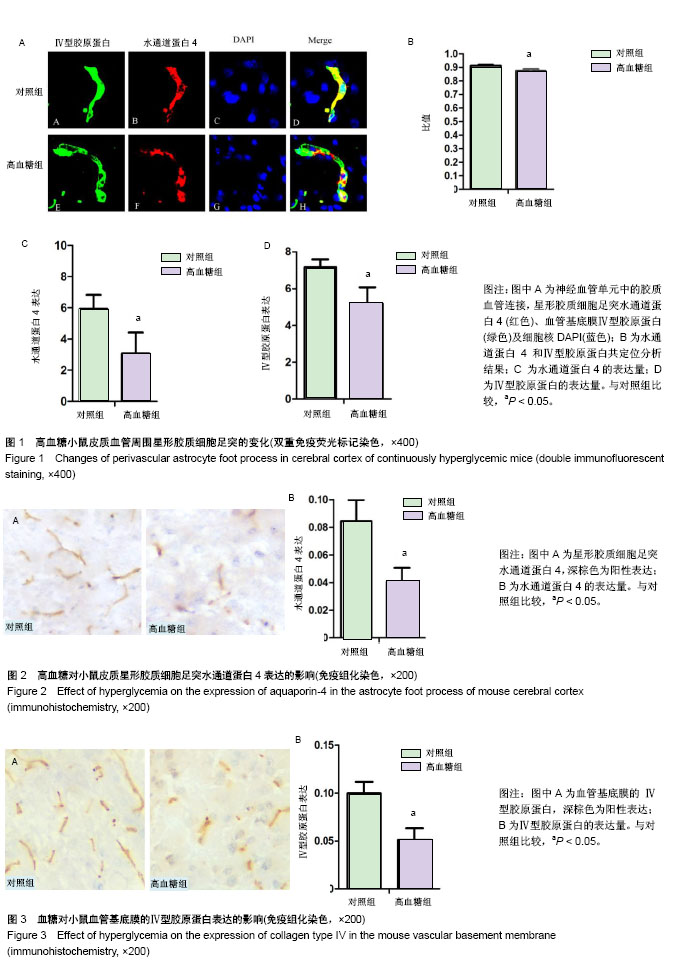
.jpg) 文题释义:
建立持续性高血糖小鼠模型:先予以50 mg/kg链脲佐菌素连续5 d腹腔注射,诱导胰岛细胞β大量的破坏,建立高血糖模型,然后长达4个月予以普通饮食喂养,该方法主要模拟持续性高血糖状态对机体的生理病理影响。
胶质血管连接:血管周围星形胶质细胞足突上表达的水通道蛋白4通过肌营养不良相关蛋白复合物镶嵌在微血管基底膜上组成胶质血管连接结构和神经血管单元,维持大脑内环境稳定,调节脑血流量及血脑屏障的通透性,在脑微血管病变中具有重要的作用。
文题释义:
建立持续性高血糖小鼠模型:先予以50 mg/kg链脲佐菌素连续5 d腹腔注射,诱导胰岛细胞β大量的破坏,建立高血糖模型,然后长达4个月予以普通饮食喂养,该方法主要模拟持续性高血糖状态对机体的生理病理影响。
胶质血管连接:血管周围星形胶质细胞足突上表达的水通道蛋白4通过肌营养不良相关蛋白复合物镶嵌在微血管基底膜上组成胶质血管连接结构和神经血管单元,维持大脑内环境稳定,调节脑血流量及血脑屏障的通透性,在脑微血管病变中具有重要的作用。