中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (6): 869-876.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2435
• 数字化骨科 digital orthopedics • 上一篇 下一篇
学龄期儿童胸椎经“椎弓根-肋骨”单元内固定的数字化测量
和雨洁1,王海燕1,李志军1,2,李筱贺1,蔡永强1,2,戴丽娜1,许阳阳3,王一丹3,徐雪彬3
- 内蒙古医科大学,1基础医学院人体解剖学教研室,2数字医学中心,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010059;3内蒙古医科大学研究生院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010010
Digital measurements of the anatomical parameters of pedicle-rib unit screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae of preschoolers
He Yujie1, Wang Haiyan1, Li Zhijun1, 2, Li Xiaohe1, Cai Yongqiang1, 2, Dai Lina1, Xu Yangyang3, Wang Yidan3, Xu Xuebin3
- 1Department of Anatomy of Basic Medical School, 2Center of Digital Medicine, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010059, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 3Graduate School, Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010010, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
文题释义:
学龄期儿童:从入小学到青春期发育开始之前为学龄期,一般指6或7-12岁。在经历过第1次生长高速期(出生到3岁)后,此时身高及体质量为稳定生长期,除生殖系统外,其他系统器官发育均接近成人水平。大脑皮质理解、分析,认知能力增强,社会心理进一步发育,在小学的教育影响下,学龄期儿童的认识、观察、注意、记忆、想象、思维、语言等方面不断发展。从11-12岁女孩便开始进入青春期,男孩进入青春期的时间则相对晚一两年。
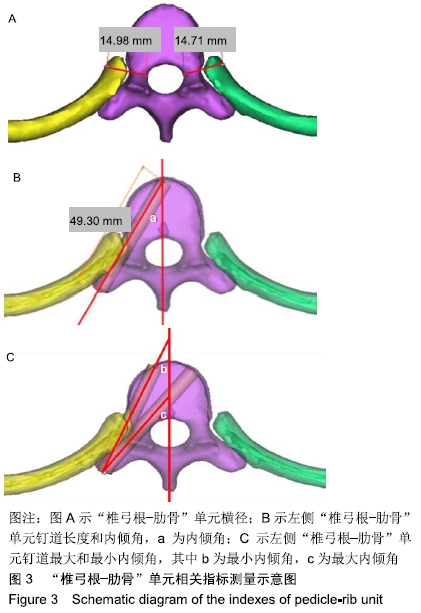
椎弓根-肋骨单元:椎弓根与其外侧自前向后的肋椎关节、肋骨头、肋横突关节和肋横突韧带共同构成“椎弓根-肋骨”单元。第1,11,12肋头只与其相对应椎体的肋凹及椎间盘相关节;第2-9肋骨的肋头位于上下两个椎体之间;第10肋头有的也和相邻的两椎体相关节;上7个肋骨的肋结节与相应的胸椎横突尖前面的肋凹相关节;第8-10肋结节较近于肋骨的下缘,与相应的胸椎横突尖的上缘相关节;第11,12肋与胸椎存在有肋椎关节,无肋横突关节。
背景:经椎弓根螺钉内固定已广泛应用于腰椎,且在胸椎中固定的应用已逐渐被接受。但由于考虑到上胸椎椎弓根狭窄,特别是在T3-T9之间,椎弓根置钉几乎都会穿破皮质伤及邻近重要结构的风险,为避免出现严重的并发症,有学者提出经肋横突关节和肋椎关节至椎体的椎弓根外入路,之后又有人设计了类似的进钉方法,提供足够不穿出肋骨的安全路径。目前,现有的研究多集中于成人中、上胸椎。
目的:测量学龄期儿童胸椎经椎弓根-肋骨单元螺钉内固定的相关解剖参数,探讨其在不同年龄段、不同性别之间的发育规律和形态特征,为临床提供理论依据。
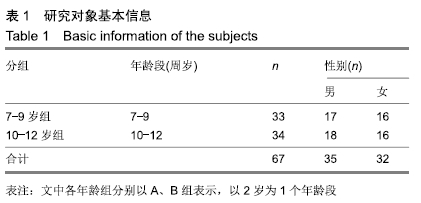
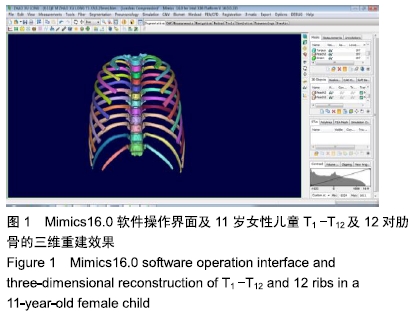
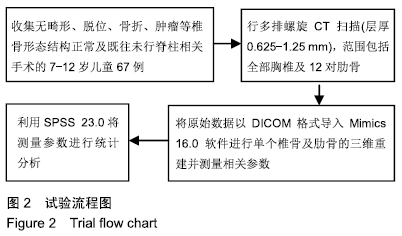
方法:选择7-12岁学龄期儿童胸椎67例,无骨质破坏、肿瘤、畸形、退变、骨折等脊柱疾患及既往无脊柱相关手术病史,行螺旋CT扫描后三维重建,观测椎弓根-肋骨单元的形态结构,测量其横径、长度、内倾角及经椎弓根-肋骨单元置钉安全角度范围并进行统计分析,探讨其在解剖学上置钉的可行性。所有儿童的监护人对试验方案均知情同意,且得到医院伦理委员会批准。
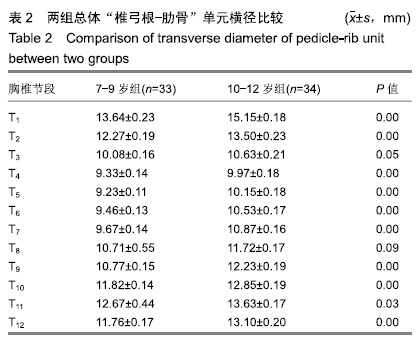
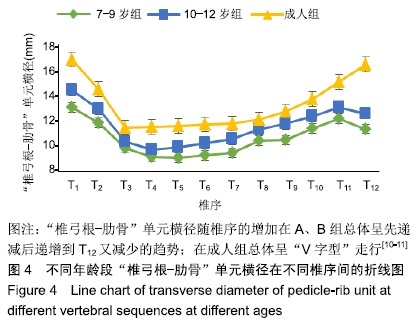
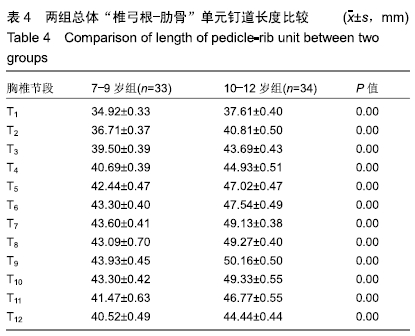
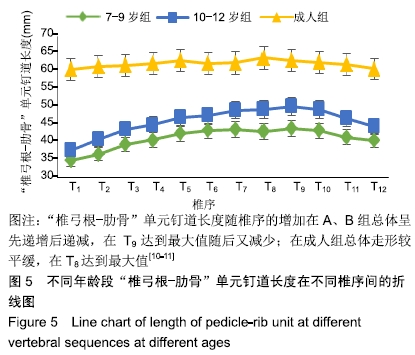
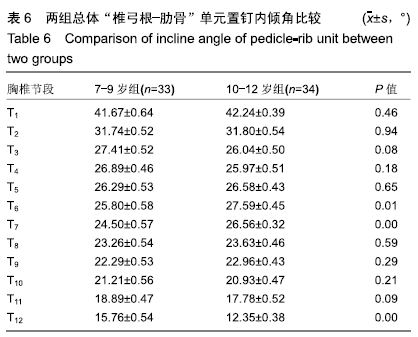
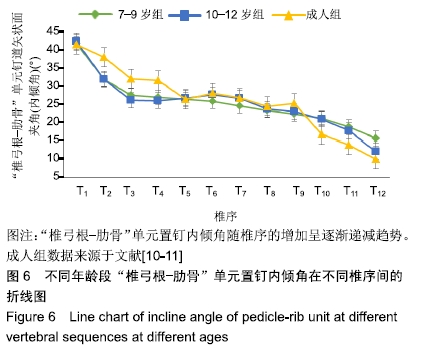
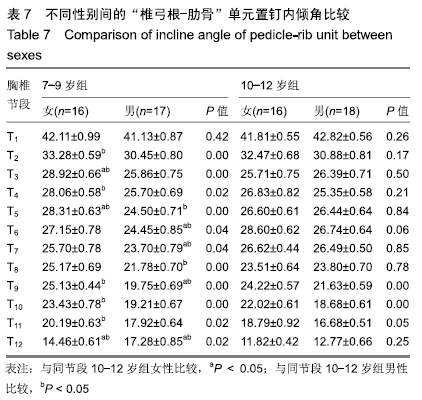
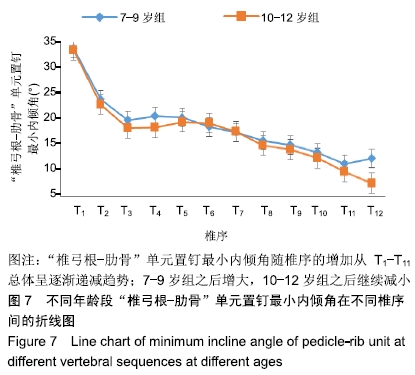
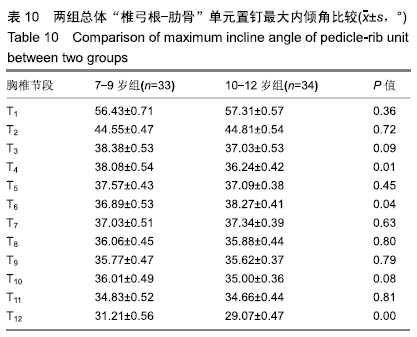
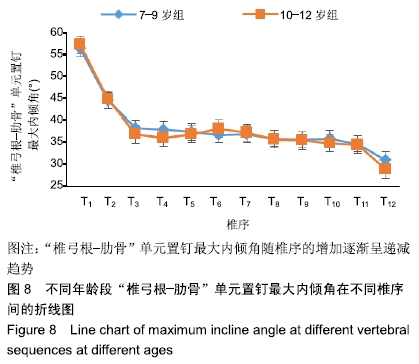
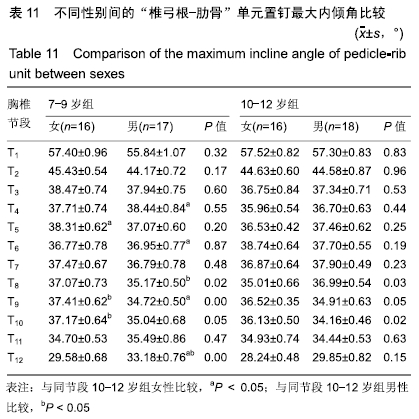
结果与结论:①胸椎“椎弓根-肋骨”单元横径随年龄增加而增大,随椎序的增加呈先减少后增加的趋势,同年龄组内男性大于女性;②经“椎弓根-肋骨”单元钉道长度在不同年龄组中差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),随年龄的增长出现明显增高趋势,随椎序的增加呈先增后减趋势;③经“椎弓根-肋骨”单元置钉最小和最大内倾角得出安全角度范围为18°-25°,其中置钉安全范围最大位于T1,其次为T10,最小位于T4和T5;④由此可见,胸椎经椎弓根-肋骨单元置钉安全角度范围儿童较成人窄,在行椎弓根-肋骨单元置钉时若参照成人的标准可能会引起严重的神经血管损伤,需根据术前CT结果进行个体化置钉。ORCID: 0000-0002-1977-3180(和雨洁)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: