中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3660-3666.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1310
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
有氧运动训练8周2型糖尿病模型大鼠骨骼肌磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B信号转导通路的变化
赵大林1,李 晶1,马 铁1,高海宁1,刘昊鹏1,张士城1,徐思彤1,肖家煜1,李一冉1,闫圣楠1,常 波1,2
- (沈阳体育学院,1运动人体科学学院,2运动生理生化教研室,辽宁省沈阳市 110102)
Changes of phosphoinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B signaling pathway in skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes rat models after 8-week aerobic exercise
Zhao Dalin1, Li Jing1, Ma Tie1, Gao Haining1, Liu Haopeng1, Zhang Shicheng1, Xu Sitong1, Xiao Jiayu1, Li Yiran1, Yan Shengnan1, Chang Bo1, 2
- (1College of Sports Human Science, 2Department of Sports Physiology and Biochemistry, Shenyang Sport University, Shenyang 110102, Liaoning Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
蛋白激酶 B(PKB):是原癌基因c-AKT的表达产物,它参与由生长因子激活的经磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)介导的信号转导过程。与许多蛋白激酶相似,PKB分子具有一特殊的AH/PH 结构域(AH/PH domain),后者能介导信号分子间的相互作用。PKB是PI3K直接的靶蛋白。PI3K 产生的脂类第二信使PI-3,4,-P2和PI-3,4,5-P3等均能与PKB和磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶(PDK)的AH/PH结构域结合,使二者转位于质膜上并活化。PDK也能使PKB磷酸化而激活,激活的 PKB又进一步激活抗细胞凋亡机制、葡萄糖代谢(糖原合成、糖酵解及葡萄糖的摄取)及蛋白质合成等过程,从而促进细胞的生长和增殖。
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。
文题释义:
蛋白激酶 B(PKB):是原癌基因c-AKT的表达产物,它参与由生长因子激活的经磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)介导的信号转导过程。与许多蛋白激酶相似,PKB分子具有一特殊的AH/PH 结构域(AH/PH domain),后者能介导信号分子间的相互作用。PKB是PI3K直接的靶蛋白。PI3K 产生的脂类第二信使PI-3,4,-P2和PI-3,4,5-P3等均能与PKB和磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶(PDK)的AH/PH结构域结合,使二者转位于质膜上并活化。PDK也能使PKB磷酸化而激活,激活的 PKB又进一步激活抗细胞凋亡机制、葡萄糖代谢(糖原合成、糖酵解及葡萄糖的摄取)及蛋白质合成等过程,从而促进细胞的生长和增殖。
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。
.jpg) 文题释义:
蛋白激酶 B(PKB):是原癌基因c-AKT的表达产物,它参与由生长因子激活的经磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)介导的信号转导过程。与许多蛋白激酶相似,PKB分子具有一特殊的AH/PH 结构域(AH/PH domain),后者能介导信号分子间的相互作用。PKB是PI3K直接的靶蛋白。PI3K 产生的脂类第二信使PI-3,4,-P2和PI-3,4,5-P3等均能与PKB和磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶(PDK)的AH/PH结构域结合,使二者转位于质膜上并活化。PDK也能使PKB磷酸化而激活,激活的 PKB又进一步激活抗细胞凋亡机制、葡萄糖代谢(糖原合成、糖酵解及葡萄糖的摄取)及蛋白质合成等过程,从而促进细胞的生长和增殖。
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。
文题释义:
蛋白激酶 B(PKB):是原癌基因c-AKT的表达产物,它参与由生长因子激活的经磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)介导的信号转导过程。与许多蛋白激酶相似,PKB分子具有一特殊的AH/PH 结构域(AH/PH domain),后者能介导信号分子间的相互作用。PKB是PI3K直接的靶蛋白。PI3K 产生的脂类第二信使PI-3,4,-P2和PI-3,4,5-P3等均能与PKB和磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶(PDK)的AH/PH结构域结合,使二者转位于质膜上并活化。PDK也能使PKB磷酸化而激活,激活的 PKB又进一步激活抗细胞凋亡机制、葡萄糖代谢(糖原合成、糖酵解及葡萄糖的摄取)及蛋白质合成等过程,从而促进细胞的生长和增殖。
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。摘要
背景:目前普遍观点是2型糖尿病患者胰岛素信号传导中的信号分子磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶和蛋白激酶B相比于健康人群均出现异常,而运动后胰岛素敏感性的改善也与骨骼肌中胰岛素信号传导系统的蛋白表达和活性增强有关。
目的:探究8周有氧运动对中龄2型糖尿病大鼠骨骼肌磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B信号转导通路的影响。
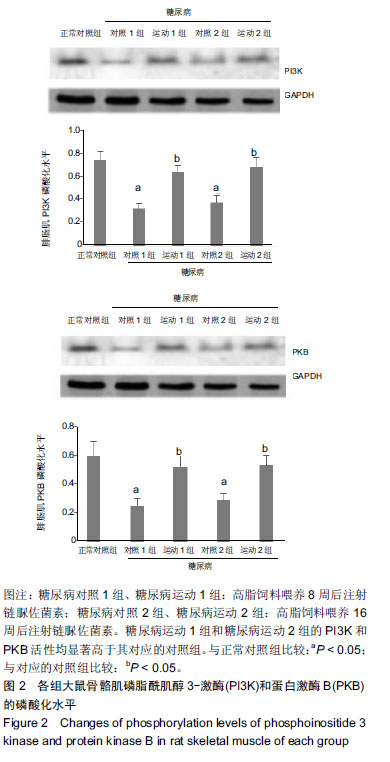
方法:10个月龄中年雌性SD大鼠75只,由成都达硕实验动物有限公司提供。实验方案经沈阳体育学院科学研究伦理委员会批准(批准号为2015006)。SD大鼠75只随机分成5组:正常对照组,给普通饲料;糖尿病对照1组、糖尿病运动1组,均于高脂饲料喂养8周后注射链脲佐菌素35 mg/kg,制备2型糖尿病模型,继续给予高脂饲料至16周;糖尿病对照2组、糖尿病运动2组,均于高脂饲料喂养16周后注射链脲佐菌素35 mg/kg,制备2型糖尿病模型;2个运动组均于第9周开始进行有氧运动,运动8周后测试血脂、血糖、胰岛素和腓肠肌磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B的蛋白表达。
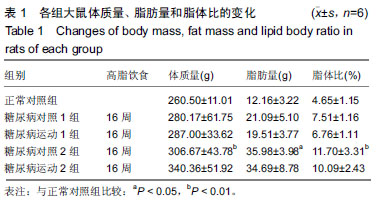
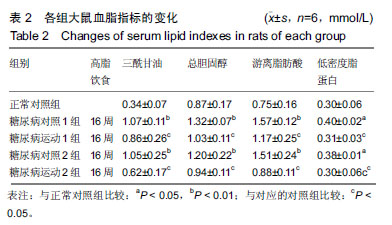
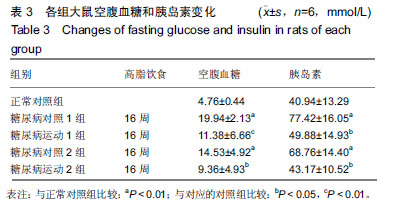
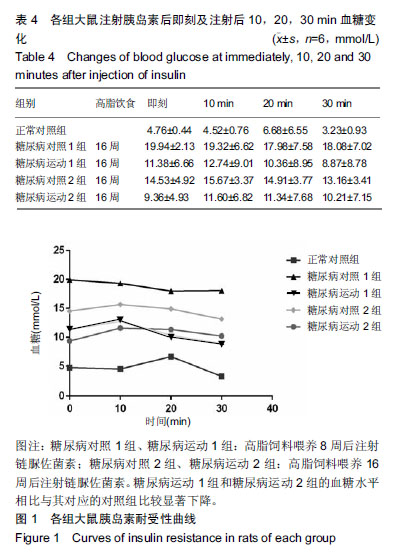
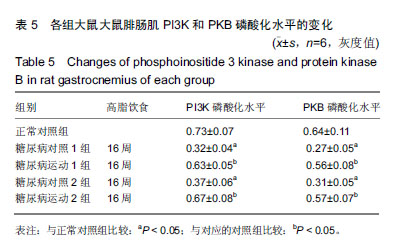
结果与结论:①8周和16周的高糖高脂饮食结合小剂量的链脲佐菌素均可引发中龄SD大鼠出现骨骼肌磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶、PK蛋白表达下降,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B信号传导发生障碍,引起脂和糖代谢紊乱,胰岛素敏感性下降,诱发2型糖尿病;②与相对应的糖尿病对照组比较,糖尿病运动1组和糖尿病运动2组的体质量有上升趋势,脂肪量和脂体比有下降趋势,三酰甘油、总胆固醇、游离脂肪酸和低密度脂蛋白值均显著降低,空腹血糖、空腹胰岛素水平显著下降,磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶和蛋白激酶B活性均显著增高;③结果说明,在诱发糖尿病前后施加运动干预,能通过增加机体能量消耗,提高骨骼肌胰岛素信号传导通路磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B磷酸化水平,增加机体胰岛素敏感性,改善脂代谢和糖代谢紊乱,最终对2型糖尿病的发生和发展起到了有效的改善/预防作用。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
蛋白激酶 B(PKB):是原癌基因c-AKT的表达产物,它参与由生长因子激活的经磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)介导的信号转导过程。与许多蛋白激酶相似,PKB分子具有一特殊的AH/PH 结构域(AH/PH domain),后者能介导信号分子间的相互作用。PKB是PI3K直接的靶蛋白。PI3K 产生的脂类第二信使PI-3,4,-P2和PI-3,4,5-P3等均能与PKB和磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶(PDK)的AH/PH结构域结合,使二者转位于质膜上并活化。PDK也能使PKB磷酸化而激活,激活的 PKB又进一步激活抗细胞凋亡机制、葡萄糖代谢(糖原合成、糖酵解及葡萄糖的摄取)及蛋白质合成等过程,从而促进细胞的生长和增殖。
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。
文题释义:
蛋白激酶 B(PKB):是原癌基因c-AKT的表达产物,它参与由生长因子激活的经磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)介导的信号转导过程。与许多蛋白激酶相似,PKB分子具有一特殊的AH/PH 结构域(AH/PH domain),后者能介导信号分子间的相互作用。PKB是PI3K直接的靶蛋白。PI3K 产生的脂类第二信使PI-3,4,-P2和PI-3,4,5-P3等均能与PKB和磷酸肌醇依赖性蛋白激酶(PDK)的AH/PH结构域结合,使二者转位于质膜上并活化。PDK也能使PKB磷酸化而激活,激活的 PKB又进一步激活抗细胞凋亡机制、葡萄糖代谢(糖原合成、糖酵解及葡萄糖的摄取)及蛋白质合成等过程,从而促进细胞的生长和增殖。
胰岛素抵抗:是指各种原因使胰岛素促进葡萄糖摄取和利用的效率下降,机体代偿性的分泌过多胰岛素产生高胰岛素血症,以维持血糖的稳定。