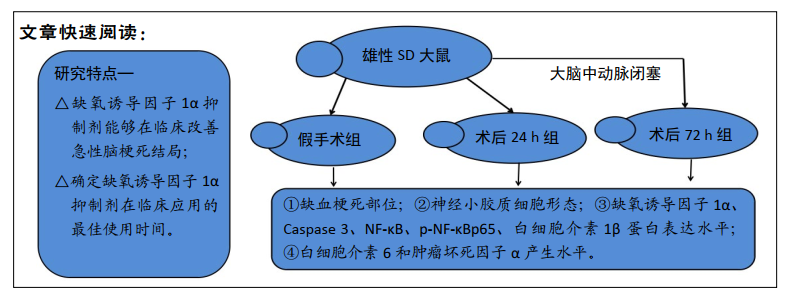
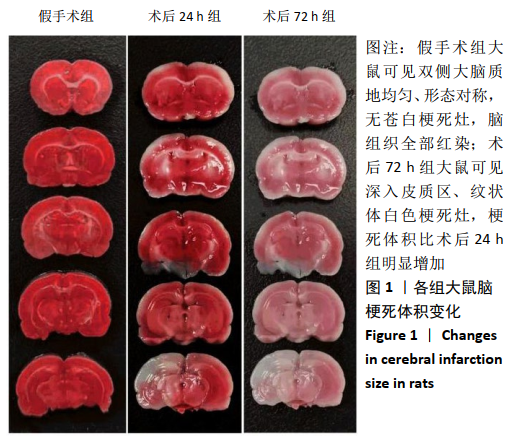
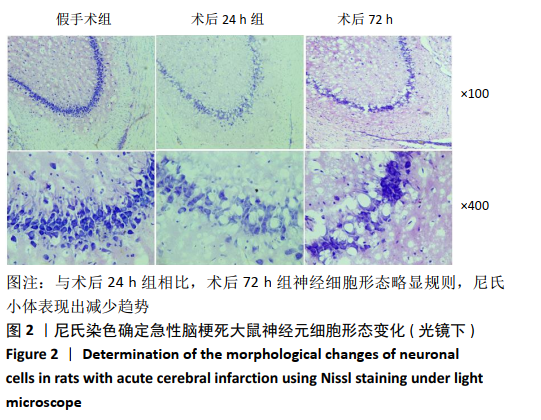
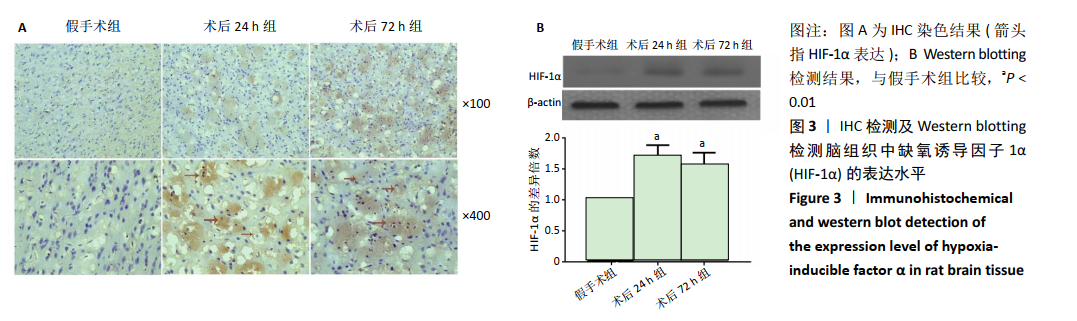
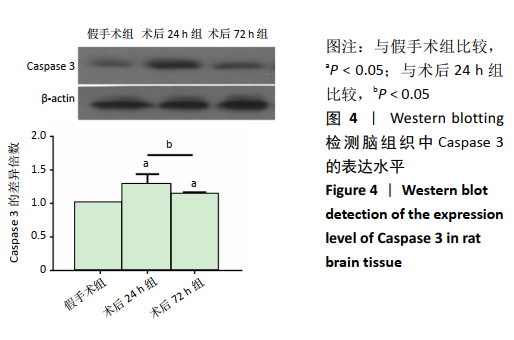
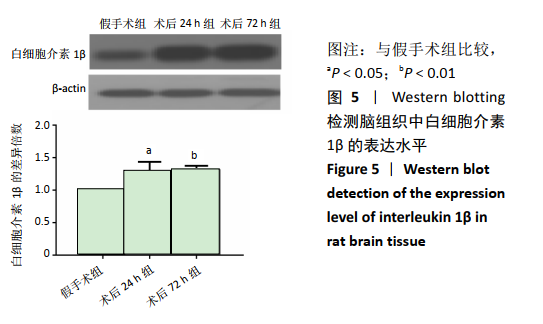
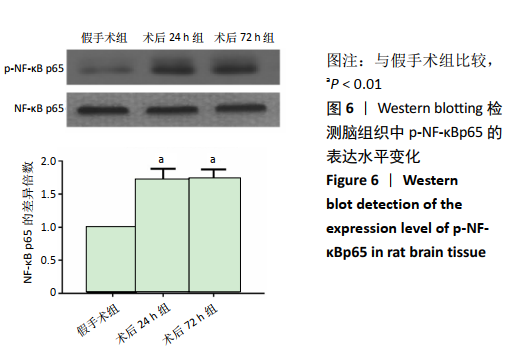
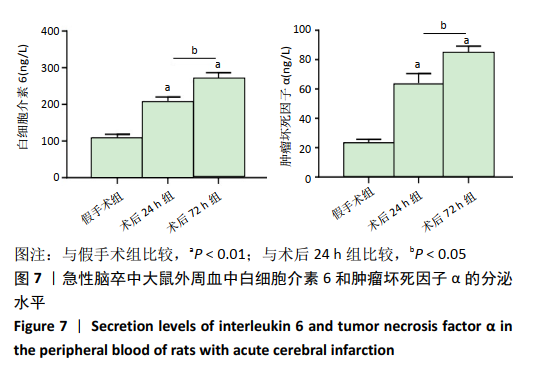
[1] GJERDE G, NAESS H. Risk factor burden predicts long-term mortality after cerebral infarction. Acta Neurol Scand. 2014;129(3):173-177.
[2] HATTORI A, TAKAMOCHI K, KITAMURA Y, et al. Risk factor analysis of cerebral infarction and clinicopathological characteristics of left upper pulmonary vein stump thrombus after lobectomy. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2019;67(2): 247-253.
[3] IKEDA K, SAWADA M, MORIOKA H, et al. Clinical Profile and Changes of Serum Lipid Levels in Epileptic Patients after Cerebral Infarction. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2017;26(3):644-649.
[4] LIAO SJ, GONG Q, CHEN XR, et al. Netrin-1 rescues neuron loss by attenuating secondary apoptosis in ipsilateral thalamic nucleus following focal cerebral infarction in hypertensive rats. Neuroscience. 2013;231:225-232.
[5] MO Z, TANG C, LI H, et al. Eicosapentaenoic acid prevents inflammation induced by acute cerebral infarction through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Life Sci. 2020;242:117133.
[6] HAO MQ, XIE LJ, LENG W, et al. Trim47 is a critical regulator of cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through regulating apoptosis and inflammation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;515(4):651-657.
[7] BAI S, SUN Y, WU L, et al. Tripotolide ameliorates inflammation and apoptosis induced by focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2016;45(5):493-500.
[8] SINGH N, SHARMA G, MISHRA V. Hypoxia inducible factor-1: its potential role in cerebral ischemia. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2012;32(4):491-507.
[9] NIU X, LI S, ZHENG S,et al. Hypoxia-induced brain cell damage in male albino wistar rat. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2018;25(7):1473-1477.
[10] CHEN W, OSTROWSKI RP, OBENAUS A, et al. Prodeath or prosurvival: two facets of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in perinatal brain injury. Exp Neurol. 2009;216(1):7-15.
[11] BEDERSON JB, PITTS LH, TSUJI M, et al. Rat middle cerebral artry occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of neurologic examination. Stroke, 1998;95(1):78-84.
[12] CI X, XING C, ZHANG B, et al. KLF5 inhibits angiogenesis in PTEN deficient prostate cancer by attenuating AKT activation and subsequent HIF-1a accumulation. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:91.
[13] 张洁琼,张向楠.缺氧诱导因子-1α ( HIF-1α)在脑缺氧损伤血脑屏障破坏中的作用[J].西北国防医学杂志,2015,36(12):818-821.
[14] 武孝刚,刘家传,王金标,等.颅脑损伤大鼠皮质HIF-1α和GLUT-3的表达及意义[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2015,20(1):37-40.
[15] LIU X, DING H, LI X, et al. Hypercapnia Exacerbates the Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption Via Promoting HIF-1a Nuclear Translocation in the Astrocytes of the Hippocampus: Implication in Further Cognitive Impairment in Hypoxemic Adult Rats. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(7):1674-1689.
[16] AL-UBAIDI FL, SCHULTZ N, EGEVAD L, et al. Castration Therapy of Prostate Cancer Results in Downregulation of HIF-1α Levels. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;82(3):1243-1248.
[17] GUO Y. Role of HIF-1a in regulating autophagic cell survival during cerebral ischemia reperfusion in rats. Oncotarget. 2017;8(58):98482-98494.
[18] RYOU MG, CHOUDHURY GR, LI W, et al. Methylene blue-induced neuronal protective mechanism against hypoxia-reoxygenation stress. Neuroscience. 2015; 301:193-203.
[19] HELTON R, CUI J, SCHEEL JR, et al. Brain-specific knock-out of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha reduces rather than increases hypoxic-ischemi damage. J Neurosci. 2005;25(16):4099-4107.
[20] 张磊,刘家传,杨艳艳,等.缺氧预处理对创伤性脑损伤大鼠脑组织HIF-1α、VEGF表达的影响[J]. 安徽医科大学学报,2014,49(4):447-451.
[21] LIU R, LIAO XY, PAN MX, et al. Glycine Exhibits neuroprotective effects in ischemic stroke in rats through the inhibition of M1 micro- glial polarization via the NF-kappaB p65 /Hif-1alpha signaling path- way. J Immunol. 2019;202(6):1704-1714.
[22] SAAD MAE, FAHMY MIM, AL-SHORBAGY M, et al. Nateglinide Exerts Neuroprotective Effects via Downregulation of HIF-1alpha/TIM-3 Inflammatory Pathway and Promotion of Caveolin-1 Expression in the Rat’s Hippocampus Subjected to Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Inflammation. 2020; 43(2):401-416.
[23] YANG Z, ZHONG LN, ZHONG SH, et al. Hypoxia induces microglia autophagy and neural inflammation injury in focal cerebral ischemia model. Exp Mol Pathol. 2015;98:219 -224.
[24] YANG Z, ZHAO TZ, ZOU YJ, et al. Hypoxia Induces autophagic cell death through hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in microglia. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96509.
[25] HOU Y, WANG J, FENG J. The neuroprotective effects of curcumin are associated with the regulation of the reciprocal function between autophagy and HIF-1alpha in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:1135-1144.
[26] OU LC, YEH SH, GEAN PW, et al. Selective inhibition of early-but not-late-experssed HIF-1 alpha is neuroprotective in rats after focal ischemic brain damage. Brain Pathol. 2011;21:249 -262.
[27] SCHAIBLE EV, WINDSCHÜGL J, BOBKIEWICZ W, et al. 2-Methoxyestra-diol confers neuroprotection and inhibits a maladaptive HIF-1α response after traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neurochem. 2014;129:940 -954.
[28] ZHANG Z, YAO L, YANG J, et al. PI3K/Akt and HIF-1 signaling pathway in hypoxia-ischemia (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(4):3547-3554.
[29] SEMENZA GL. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) pathway. Sci STKE. 2007; 2007(407):cm8
[30] MCGETTRICK AF, O’NEILL LAJ. The Role of HIF in Immunity and Inflammation.Cell Metab. 2020;32(4):524-536.
[31] Yu LM, Zhang WH, Han XX, et al. Hypoxia-Induced ROS Contribute to Myoblast Pyroptosis during Obstructive Sleep Apnea via the NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:4596368.
[32] Jiang Y, Zhu Y, Wang X,et al. Temporal regulation of HIF-1 and NF-kappaB in hypoxic hepatocarcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 2015;6(11):9409-9419.
[33] Zou YM, Hu GY, Zhao XQ, et al. Hypoxia-induced autophagy contributes to radioresistance via c-Jun-mediated Beclin1 expression in lung cancer cells. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2014;34:761-767.
[34] Taylor CT. Interdependent roles for hypoxia inducible factor and nuclear factor-kappaB in hypoxic inflammation. J Physiol. 2008;586(17):4055-4059.
[35] Lei R, Li J, Liu F, et al. HIF-1alpha promotes the keloid development through the activation of TGF-beta/Smad and TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB pathways. Cell Cycle. 2019;18(23):3239-3250.
[36] 毛汉丁,程岗,刘帅,等. 舱室内爆震伤后 HIF-1α、NF-κB在犬脑和肺组织的表达及其相关性[J]. 中华神经外科疾病研究杂志,2018,17(4):314-318.
[37] Yin W, Ma L, Zhang J, et al. The migration of neural progenitor cell mediated by SDF-1 is NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha dependent upon hypoxia. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013;19(3):145-153.
[38] Yu LM, Zhang WH, Han XX, et al. Hypoxia-Induced ROS Contribute to Myoblast Pyroptosis during Obstructive Sleep Apnea via the NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha Signaling Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:4596368.
[39] Rius J, Guma M, Schachtrup C, et al. NF-kappaB links innate immunity to the hypoxic response through transcriptional regulation of HIF-1alpha. Nature. 2008;453(7196):807-811.
[40] Fallah J, Rini BI. HIF Inhibitors: Status of Current Clinical Development. Curr Oncol Rep. 2019;21(1):6.
[41] Li Y, Sui H, Jiang C, et al. Dihydroartemisinin Increases the Sensitivity of Photodynamic Therapy Via NF-kappaB/HIF-1alpha/VEGF Pathway in Esophageal Cancer Cell in vitro and in vivo. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):2035-2045. |