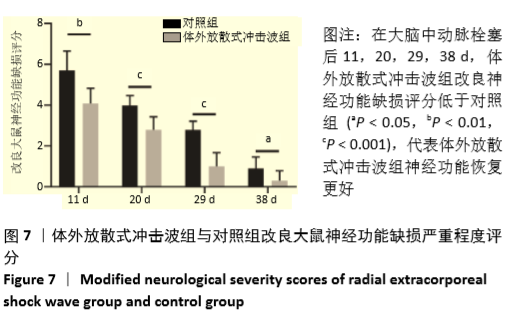
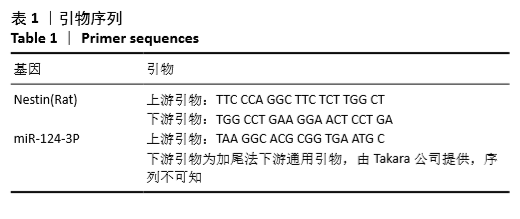
[1] WRITING GROUP MEMBERS, MOZAFFARIAN D, BENJAMIN EJ, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2016 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2016;133(4):e38-360.
[2] GUZIK A, BUSHNELL C. Stroke Epidemiology and Risk Factor Management.Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2017;23(1, Cerebrovascular Disease):15-39.
[3] PRABHAKARAN S, RUFF I, BERNSTEIN RA. Acute stroke intervention: a systematic review. JAMA. 2015;313(14):1451-1462.
[4] PHIPPS MS, CRONIN CA. Management of acute ischemic stroke. BMJ. 2020;368: l6983.
[5] LI C, RUSAK Z, HORVATH I, et al. Implementation and Validation of Engagement Monitoring in an Engagement Enhancing Rehabilitation System. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng. 2017;25(6):726-738.
[6] SUN K, LAI EC. Adult-specific functions of animal microRNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2013;14(8):535-548.
[7] DOETSCH F. A niche for adult neural stem cells. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2003;13(5): 543-550.
[8] SANDQUIST EJ, SAKAGUCHI DS. Adult neural stem cell plasticity. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(2):256-257.
[9] MARLIER Q, VERTENEUIL S, VANDENBOSCH R, et al. Mechanisms and Functional Significance of Stroke-Induced Neurogenesis. Front Neurosci. 2015;9:458.
[10] THORED P, ARVIDSSON A, CACCI E, et al. Persistent production of neurons from adult brain stem cells during recovery after stroke. Stem Cells. 2006;24(3):739-747.
[11] MING GL, SONG H. Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron. 2011;70(4):687-702.
[12] KOKAIA Z, LINDVALL O. Stem cell repair of striatal ischemia. Prog Brain Res. 2012; 201:35-53.
[13] CULLEY DJ, BOYD JD, PALANISAMY A, et al. Isoflurane decreases self-renewal capacity of rat cultured neural stem cells. Anesthesiology. 2011;115(4):754-763.
[14] HUANG L, WANG G. The Effects of Different Factors on the Behavior of Neural Stem Cells. Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:9497325.
[15] 徐廷胜,李钊.气压弹道式体外冲击波设备在骨肌系统疾病治疗中的应用[J].医疗装备,2012,25(3):19-20.
[16] KERTZMAN P, CSÁSZÁR NBM, FURIA JP, et al. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy is efficient and safe in the treatment of fracture nonunions of superficial bones: a retrospective case series. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):164.
[17] LANGENDORF EK, KLEIN A, DREES P, et al. Exposure to radial extracorporeal shockwaves induces muscle regeneration after muscle injury in a surgical rat model. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(6):1386-1397.
[18] MALLIAROPOULOS N, THOMPSON D, MEKE M, et al. Individualised radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy (rESWT) for symptomatic calcific shoulder tendinopathy: a retrospective clinical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017; 18(1):513.
[19] ATTHAKOMOL P, MANOSROI W, PHANPHAISARN A, et al. Comparison of single-dose radial extracorporeal shock wave and local corticosteroid injection for treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome including mid-term efficacy: a prospective randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):32.
[20] WALEWICZ K, TARADAJ J, RAJFUR K, et al. The Effectiveness Of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy In Patients With Chronic Low Back Pain: A Prospective, Randomized, Single-Blinded Pilot Study. Clin Interv Aging. 2019;14: 1859-1869.
[21] RAABE O, SHELL K, GOESSL A, et al. Effect of extracorporeal shock wave on proliferation and differentiation of equine adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Am J Stem Cells. 2013;2(1):62-73.
[22] ZHAI L, SUN N, ZHANG B, et al. Effects of Focused Extracorporeal Shock Waves on Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Patients with Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2016;42(3):753-762.
[23] RUAN Y, ZHOU J, KANG N, et al. The effect of low-intensity extracorporeal shockwave therapy in an obesity-associated erectile dysfunction rat model. BJU Int. 2018;122(1):133-142.
[24] QI H, JIN S, YIN C, et al. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy promotes osteochondral regeneration of knee joints in rabbits. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(4): 3478-3484.
[25] ZHANG J, KANG N, YU X, et al. Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Enhances the Proliferation and Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells by Notch, PI3K/AKT, and Wnt/β-catenin Signaling. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):15321.
[26] KANG N, ZHANG J, YU X, et al. Radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy improves cerebral blood flow and neurological function in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(4):2000-2012.
[27] RINK C, KHANNA S. MicroRNA in ischemic stroke etiology and pathology. Physiol Genomics. 2011;43(10):521-528.
[28] RUPAIMOOLE R, SLACK FJ. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017;16(3):203-222.
[29] SUN Y, LUO ZM, GUO XM, et al. An updated role of microRNA-124 in central nervous system disorders: a review. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015;9:193.
[30] SHAO Q, JIANG W, JIN Y. MiR-124 effect in neurons apoptosis in newborn rat with thyroid hypofunction. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(11):14465-14471.
[31] MALMEVIK J, PETRI R, KNAUFF P, et al. Distinct cognitive effects and underlying transcriptome changes upon inhibition of individual miRNAs in hippocampal neurons. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19879.
[32] LIU FJ, LIM KY, KAUR P, et al. microRNAs Involved in Regulating Spontaneous Recovery in Embolic Stroke Model. PLoS One. 2013;8(6):e66393.
[33] WANG S, XU J, YE R, et al. Emerging roles of microRNAs in neural stem cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;9(3):234-243.
[34] ÅKERBLOM M, SACHDEVA R, BARDE I, et al. MicroRNA-124 is a subventricular zone neuronal fate determinant. J Neurosci. 2012;32(26):8879-8889.
[35] YOO AS, STAAHL BT, CHEN L, et al. MicroRNA-mediated switching of chromatin-remodelling complexes in neural development. Nature. 2009;460(7255):642-646.
[36] YANG J, ZHANG X, CHEN X, et al. Exosome Mediated Delivery of miR-124 Promotes Neurogenesis after Ischemia. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2017;7:278-287.
[37] SUN Y, GUI H, LI Q, et al. MicroRNA-124 protects neurons against apoptosis in cerebral ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013;19(10):813-819.
[38] SUN M, HOU X, REN G, et al. Dynamic changes in miR-124 levels in patients with acute cerebral infarction. Int J Neurosci. 2019;129(7):649-653.
[39] MIAO W, BAO TH, HAN JH, et al. Voluntary exercise prior to traumatic brain injury alters miRNA expression in the injured mouse cerebral cortex. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2015;48(5):433-439.
[40] 谭辉,王键,尹婷婷,等.益气活血方基于miR-124调控Wnt通路促进神经再生[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2017,37(8):1047-1053.
[41] ZHU H, WANG J, SHAO Y, et al. Catalpol may improve axonal growth via regulating miR-124 regulated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in neurons after ischemia. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7(14):306.
[42] 杨惠泉,顾倩影,彭翊倩,等.微小RNA调节缺血诱导的内源性神经再生研究进展[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2018,45(6):637-641.
[43] LONGA EZ, WEINSTEIN PR, CARLSON S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 1989;20(1):84-91.
[44] LOHSE-BUSCH H, REIME U, FALLAND R. Symptomatic treatment of unresponsive wakefulness syndrome with transcranially focused extracorporeal shock waves. NeuroRehabilitation. 2014;35(2):235-244.
[45] CHAI HT, CHEN KH, WALLACE CG, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy effectively protects brain against chronic cerebral hypo-perfusion-induced neuropathological changes. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(11):5074-5093.
[46] MENG Y, SHANG F, ZHU Y. miR-124 participates in the proliferation and differentiation of brain glioma stem cells through regulating Nogo/NgR expression. Exp Ther Med. 2019;18(4):2783-2788.
[47] SUZUKI A, YOSHIOKA H, SUMMAKIA D, et al. MicroRNA-124-3p suppresses mouse lip mesenchymal cell proliferation through the regulation of genes associated with cleft lip in the mouse. BMC Genomics. 2019;20(1):852.
[48] CHU M, CHANG Y, GUO Y, et al. Regulation and methylation of tumor suppressor miR-124 by androgen receptor in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(4): e0116197.
[49] 郑华峰,陶晶,张斌,等.MicroRNA-124抑制大鼠血管平滑肌细胞增殖及分子机研究[J].中国心血管杂志,2016,21(1):50-54.
[50] DING C, DOU M, WANG Y, et al. miR-124/IRE-1α affects renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress in renal tubular epithelial cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2020;52(2):160-167.
[51] GACOŃ J, KABŁAK-ZIEMBICKA A, STĘPIEŃ E, et al. Decision-making microRNAs (miR-124, -133a/b, -34a and -134) in patients with occluded target vessel in acute coronary syndrome. Kardiol Pol. 2016;74(3):280-288.
[52] GACOŃ J, BADACZ R, STĘPIEŃ E, et al. Diagnostic and prognostic micro-RNAs in ischaemic stroke due to carotid artery stenosis and in acute coronary syndrome: a four-year prospective study. Kardiol Pol. 2018;76(2):362-369.
[53] LIU XS, CHOPP M, ZHANG RL, et al. MicroRNA profiling in subventricular zone after stroke: MiR-124a regulates proliferation of neural progenitor cells through Notch signaling pathway. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23461.
[54] CHE QQ, HUANG T, ZHANG YD, et al. Effect of miR-124 on neuronal apoptosis in rats with cerebral infarction through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(15):6657-6664.
[55] LIU X, LI F, ZHAO S, et al. MicroRNA-124-mediated regulation of inhibitory member of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 family in experimental stroke. Stroke. 2013;44(7):1973-1980.
[56] DOEPPNER TR, DOEHRING M, BRETSCHNEIDER E, et al. MicroRNA-124 protects against focal cerebral ischemia via mechanisms involving Usp14-dependent REST degradation. Acta Neuropathol. 2013;126(2):251-265.
[57] WESTBROOK TF, HU G, ANG XL, et al. SCFbeta-TRCP controls oncogenic transformation and neural differentiation through REST degradation. Nature. 2008;452(7185):370-374.
[58] 余剑,曾进胜.表皮生长因子促进脑梗死后神经可塑性和内源性神经干细胞分化的实验研究[C].中国康复医学会第九届全国脑血管病康复学术会议论文汇编, 2005.
[59] BERNAL A, ARRANZ L. Nestin-expressing progenitor cells: function, identity and therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(12):2177-2195.
[60] JOO S, YEON KIM J, LEE E, et al. Effects of ECM protein micropatterns on the migration and differentiation of adult neural stem cells. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13043.
[61] NAKATOMI H, KURIU T, OKABE S, et al. Regeneration of hippocampal pyramidal neurons after ischemic brain injury by recruitment of endogenous neural progenitors. Cell. 2002;110(4):429-441.
[62] LI B, PIAO CS, LIU XY, et al. Brain self-protection: the role of endogenous neural progenitor cells in adult brain after cerebral cortical ischemia. Brain Res. 2010; 1327:91-102.
[63] 张敏,刘磊,吴世陶,等.神经干细胞移植治疗大鼠脑梗死的研究[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2015,18(21):11-13.
|