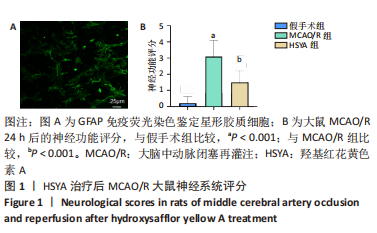
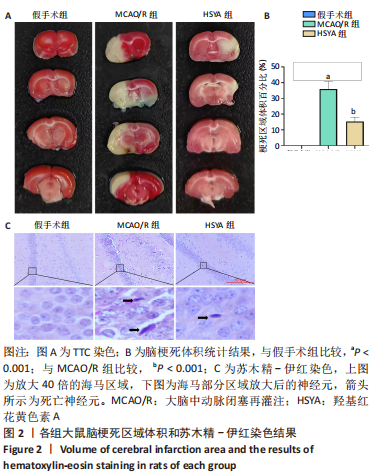
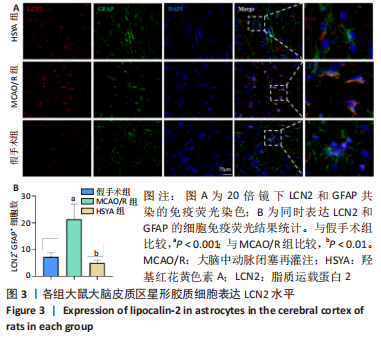
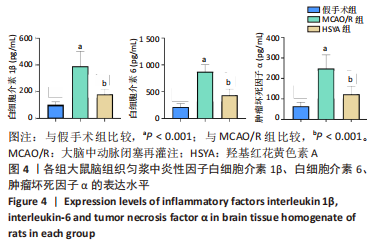
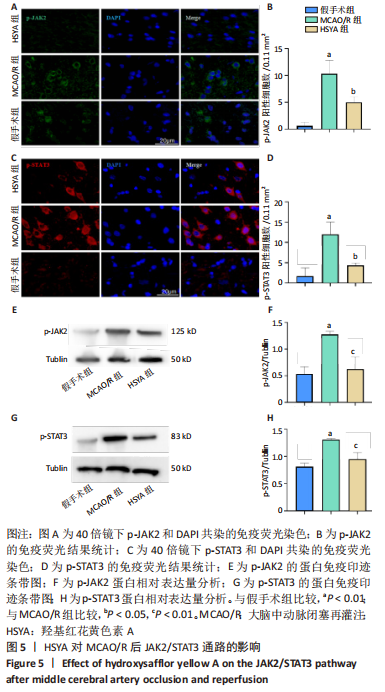
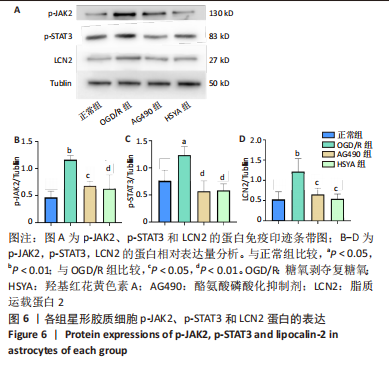
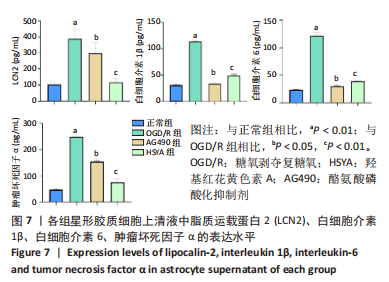
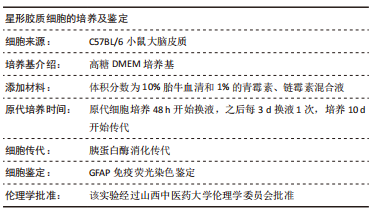
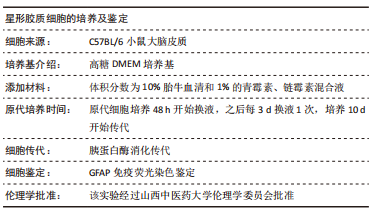
[1] BARTHELS D, DAS H. Current advances in ischemic stroke research and therapies. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020;1866(4):165260.
[2] ANRATHER J, IADECOLA C. Inflammation and Stroke: An Overview. Neurotherapeutics. 2016;13(4):661-670.
[3] SOFRONIEW MV. Astrocyte Reactivity: Subtypes, States, and Functions in CNS Innate Immunity. Trends Immunol. 2020;41(9):758-770.
[4] PEKNY M, WILHELMSSON U, TATLISUMAK T, et al. Astrocyte activation and reactive gliosis-A new target in stroke? Neurosci Lett. 2019;689:45-55.
[5] SUK K. Lipocalin-2 as a therapeutic target for brain injury: An astrocentric perspective. Prog Neurobiol. 2016;144:158-172.
[6] KEHRER JP. Lipocalin-2: pro- or anti-apoptotic? Cell Biol Toxicol. 2010;26(2):83-89.
[7] CHAKRABORTY S, KAUR S, GUHA S, et al. The multifaceted roles of neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) in inflammation and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012; 1826(1):129-169.
[8] XU WX, ZHANG J, HUA YT, et al. An Integrative Pan-Cancer Analysis Revealing LCN2 as an Oncogenic Immune Protein in Tumor Microenvironment. Front Oncol. 2020;10:605097.
[9] LIU R, WANG J, CHEN Y, et al. NOX activation in reactive astrocytes regulates astrocytic LCN2 expression and neurodegeneration. Cell Death Dis. 2022;13(4):371.
[10] WAN T, ZHU W, ZHAO Y, et al. Astrocytic phagocytosis contributes to demyelination after focal cortical ischemia in mice. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):1134.
[11] LUO C, ZHOU S, YIN S, et al. Lipocalin-2 and Cerebral Stroke. Front Mol Neurosci. 2022; 15:850849.
[12] WU ZL, CIALLELLA JR, FLOOD DG, et al. Comparative analysis of cortical gene expression in mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27(3):377-386.
[13] MARQUES F, RODRIGUES AJ, SOUSA JC, et al. Lipocalin 2 is a choroid plexus acute-phase protein. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2008;28(3):450-455.
[14] ZHAO N, XU X, JIANG Y, et al. Lipocalin-2 may produce damaging effect after cerebral ischemia by inducing astrocytes classical activation. J Neuroinflammation. 2019;16(1): 168.
[15] AGASHE RP, LIPPMAN SM, KURZROCK R. JAK: Not Just Another Kinase. Mol Cancer Ther. 2022;21(12):1757-1764.
[16] O’CALLAGHAN JP, KELLY KA, VANGILDER RL, et al. Early activation of STAT3 regulates reactive astrogliosis induced by diverse forms of neurotoxicity. PLoS One. 2014;9(7): e102003.
[17] OKADA S, NAKAMURA M, KATOH H, et al. Conditional ablation of Stat3 or Socs3 discloses a dual role for reactive astrocytes after spinal cord injury. Nat Med. 2006; 12(7):829-834.
[18] WU M, WANG L, LI F, et al. Resveratrol Downregulates STAT3 Expression and Astrocyte Activation in Primary Astrocyte Cultures of Rat. Neurochem Res. 2020;45(2):455-464.
[19] LI H, ZHANG Q, ZHANG G. Signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 activation is mediated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor and L-type voltage-gated Ca2+ channel during cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 2003;345(1):61-64.
[20] HRISTOVA M, ROCHA-FERREIRA E, FONTANA X, et al. Inhibition of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) reduces neonatal hypoxic-ischaemic brain damage. J Neurochem. 2016;136(5):981-994.
[21] ZHANG X, SHEN D, FENG Y, et al. Pharmacological Actions, Molecular Mechanisms, Pharmacokinetic Progressions, and Clinical Applications of Hydroxysafflor Yellow A in Antidiabetic Research. J Immunol Res. 2021;2021:4560012.
[22] CHEN S, SUN M, ZHAO X, et al. Neuroprotection of hydroxysafflor yellow A in experimental cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via metabolic inhibition of phenylalanine and mitochondrial biogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 2019;19(4):3009-3020.
[23] SUN Y, XU DP, QIN Z, et al. Protective cerebrovascular effects of hydroxysafflor yellow A (HSYA) on ischemic stroke. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;818:604-609.
[24] 戴纪恒.基于SIRT1-HIF-1α-VEGFA信号转导通路探讨羟基红花黄色素A调控血管新生保护氧糖剥夺/复糖复氧损伤大鼠脑微血管内皮细胞[D].合肥:安徽中医药大学,2020.
[25] 戚智锋,师文娟,闫峰,等.羟基红花黄色素A对脑缺血-再灌注大鼠星形胶质细胞活性的影响[J].中国脑血管病杂志,2013,10(9):488-491.
[26] 田京伟,傅风华,蒋王林,等.羟基红花黄色素A对脑缺血所致大鼠脑线粒体损伤的保护作用[J].药学学报,2004,39(10):774-777.
[27] PAN H, XU Y, CAI Q, et al. Effects of β-Asarone on Ischemic Stroke in Middle Cerebral Artery Occlusion Rats by an Nrf2-Antioxidant Response Elements (ARE) Pathway-Dependent Mechanism. Med Sci Monit. 2021;27:e931884.
[28] 曹水娟.羟基红花黄色素A促大鼠局灶性脑缺血后血管新生作用的分子基础初探[D].北京:中国协和医科大学,2007.
[29] 韩光远,刘可心,魏汝恒,等.羟基红花黄色素A对糖氧剥夺/复糖复氧后星形胶质细胞保护作用及其机制研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2022,38(3):275-281.
[30] DOWLATI A, NETHERY D, KERN JA. Combined inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor and JAK/STAT pathways results in greater growth inhibition in vitro than single agent therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004;3(4):459-463.
[31] ASCHNER M. Immune and inflammatory responses in the CNS: modulation by astrocytes. Toxicol Lett. 1998;102-103:283-287.
[32] IADECOLA C, BUCKWALTER MS, ANRATHER J. Immune responses to stroke: mechanisms, modulation, and therapeutic potential. J Clin Invest. 2020;130(6):2777-2788.
[33] WEI R, SONG L, MIAO Z, et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Exerts Neuroprotective Effects via HIF-1α/BNIP3 Pathway to Activate Neuronal Autophagy after OGD/R. Cells. 2022; 11(23):3726.
[34] JANG E, KIM JH, LEE S, et al. Phenotypic polarization of activated astrocytes: the critical role of lipocalin-2 in the classical inflammatory activation of astrocytes. J Immunol. 2013;191(10):5204-5219.
[35] ZHU H, JIAN Z, ZHONG Y, et al. Janus Kinase Inhibition Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke Injury and Neuroinflammation Through Reducing NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via JAK2/STAT3 Pathway Inhibition. Front Immunol. 2021;12:714943.
[36] YU L, LIU Z, HE W, et al. Hydroxysafflor Yellow A Confers Neuroprotection from Focal Cerebral Ischemia by Modulating the Crosstalk Between JAK2/STAT3 and SOCS3 Signaling Pathways. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2020;40(8):1271-1281. |