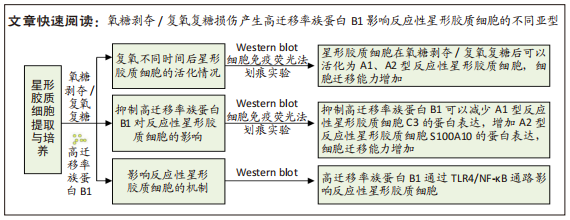
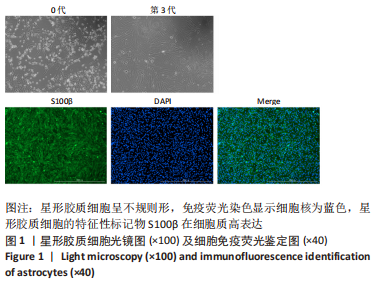
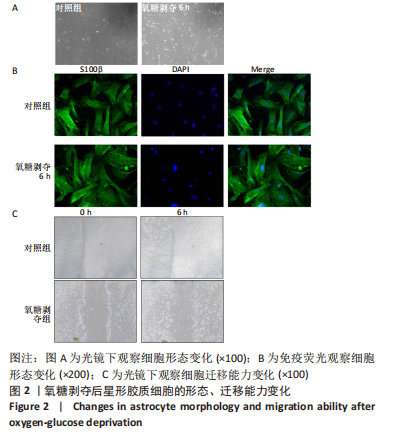
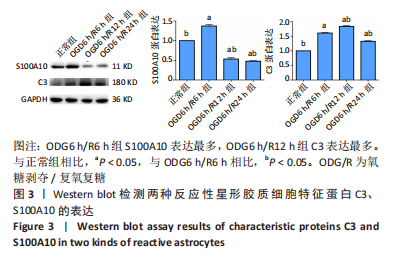
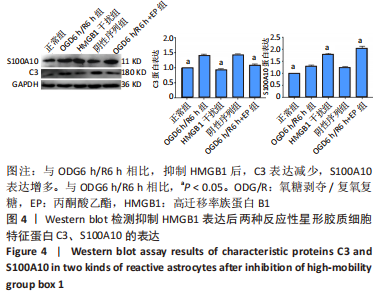
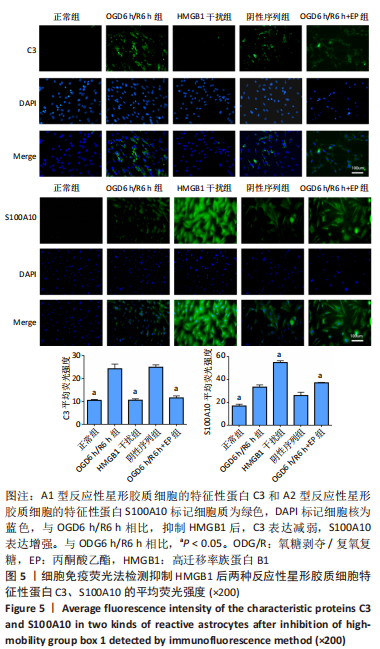
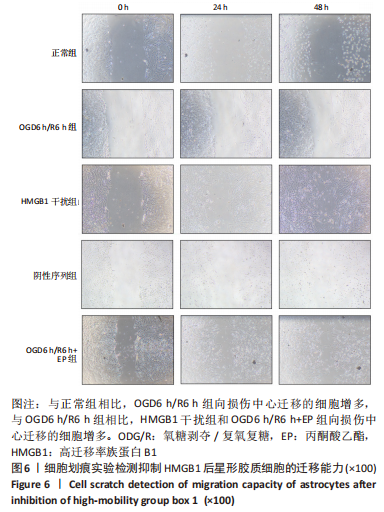
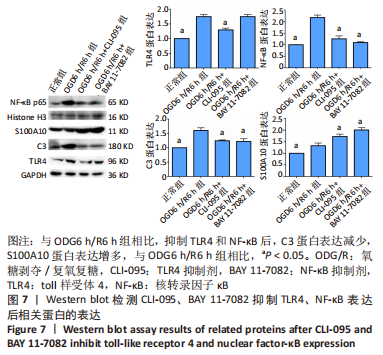
[1] DAVID G, MOHAMMADI S, MARTIN AR, et al. Traumatic and nontraumatic spinal cord injury: pathological insights from neuroimaging. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(12):718-731.
[2] THURET S, MOON LD, GAGE FH. Therapeutic interventions after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7(8):628-643.
[3] ALIZADEH A, DYCK SM, KARIMI-ABDOLREZAEE S. Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury: An Overview of Pathophysiology, Models and Acute Injury Mechanisms. Front Neurol. 2019;10:282.
[4] MONJE M. Spinal Cord Injury - Healing from Within. N Engl J Med. 2021; 384(2):182-184.
[5] VON LEDEN RE, YAUGER YJ, KHAYRULLINA G, et al. Central Nervous System Injury and Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidase: Oxidative Stress and Therapeutic Targets. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34(4):755-764.
[6] ESCARTIN C, GALEA E, LAKATOS A, et al. Reactive astrocyte nomenclature, definitions, and future directions. Nat Neurosci. 2021; 24(3):312-325.
[7] LIDDELOW SA, GUTTENPLAN KA, CLARKE LE, et al. Neurotoxic reactive astrocytes are induced by activated microglia. Nature. 2017;541(7638): 481-487.
[8] CARTER SF, HERHOLZ K, ROSA-NETO P, et al. Astrocyte Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease. Trends Mol Med. 2019;25(2):77-95.
[9] LI L,LI Y,HE B, et al. HSF1 is involved in suppressing A1 phenotype conversion of astrocytes following spinal cord injury in rats.J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18:205.
[10] ZAMANIAN JL, XU L, FOO LC, et al. Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J Neurosci. 2012;32(18):6391-6410.
[11] TAKAHASHI S, MASHIMA K. Neuroprotection and Disease Modification by Astrocytes and Microglia in Parkinson Disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022;11(1):170.
[12] LI X, LI M, TIAN L, et al. Reactive Astrogliosis: Implications in Spinal Cord Injury Progression and Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; 2020:9494352.
[13] HARA M, KOBAYAKAWA K, OHKAWA Y, et al. Interaction of reactive astrocytes with type I collagen induces astrocytic scar formation through the integrin-N-cadherin pathway after spinal cord injury. Nat Med. 2017;23(7):818-828.
[14] GUO H,FAN Z,WANG S, et al. Astrocytic A1/A2 paradigm participates in glycogen mobilization mediated neuroprotection on reperfusion injury after ischemic stroke.J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18:230.
[15] PAPATHEODOROU A, STEIN A, BANK M, et al. High-Mobility Group Box 1 (HMGB1) Is Elevated Systemically in Persons with Acute or Chronic Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. J Neurotrauma. 2017;34(3):746-754.
[16] SCAFFIDI P, MISTELI T, BIANCHI ME. Release of chromatin protein HMGB1 by necrotic cells triggers inflammation. Nature. 2002;418(6894): 191-195.
[17] FAN H, TANG HB, CHEN Z, et al. Inhibiting HMGB1-RAGE axis prevents pro-inflammatory macrophages/microglia polarization and affords neuroprotection after spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2020; 17(1):295.
[18] SUN L, LI M, MA X, et al. Inhibition of HMGB1 reduces rat spinal cord astrocytic swelling and AQP4 expression after oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation via TLR4 and NF-κB signaling in an IL-6-dependent manner. J Neuroinflammation. 2017;14(1):231.
[19] BRAMBILLA R, BRACCHI-RICARD V, HU WH, et al. Inhibition of astroglial nuclear factor kappaB reduces inflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury. J Exp Med. 2005;202(1):145-156.
[20] LIU J, ZHANG S, FAN X, et al. Dexmedetomidine Preconditioning Ameliorates Inflammation and Blood-Spinal Cord Barrier Damage After Spinal Cord Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Down-Regulation High Mobility Group Box 1-Toll-Like Receptor 4-Nuclear Factor κB Signaling Pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(2):E74-E81.
[21] ZHANG Y, MENG T, CHEN J, et al. miR-21a-5p Promotes Inflammation following Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury through Upregulation of Neurotoxic Reactive Astrocyte (A1) Polarization by Inhibiting the CNTF/STAT3/Nkrf Pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(11):2795-2810.
[22] KISUCKÁ A, BIMBOVÁ K, BAČOVÁ M, et al. Activation of Neuroprotective Microglia and Astrocytes at the Lesion Site and in the Adjacent Segments Is Crucial for Spontaneous Locomotor Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury. Cells. 2021;10(8):1943.
[23] 吕聪,孙麟,冯皓宇,等.减少氧糖剥夺/复氧后脊髓星形胶质细胞凋亡:抑制高迁移率族蛋白B1/核转录因子κB通路的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(33):5353-5359.
[24] 宋君来,李满,孙麟,等.抑制高迁移率族蛋白1减轻大鼠脊髓星形胶质细胞氧糖剥夺/复氧后的损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2018, 22(28):4537-4543.
[25] WANG X,ZHANG Z,ZHU Z, et al. Photobiomodulation Promotes Repair Following Spinal Cord Injury by Regulating the Transformation of A1/A2 Reactive Astrocytes.Front Neurosci. 2021;15:768262.
[26] ZHAO HD, HUANG SQ, TANG CL, et al. Influence of electroacupuncture on locomotor function and expression of spinal HMGB1 and TLR4 in mice with spinal cord injury. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2021;46(4):259-265.
[27] WANG Q, DING Q, ZHOU Y, et al. Ethyl pyruvate attenuates spinal cord ischemic injury with a wide therapeutic window through inhibiting high-mobility group box 1 release in rabbits. Anesthesiology. 2009;110(6):1279-1286.
[28] SONG HH, SONG TC, YANG T, et al. High mobility group box 1 mediates inflammatory response of astrocytes via cyclooxygenase 2/prostaglandin E2 signaling following spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(9):1848-1855.
[29] PAUDEL YN, SHAIKH MF, CHAKRABORTI A, et al. HMGB1: A Common Biomarker and Potential Target for TBI, Neuroinflammation, Epilepsy, and Cognitive Dysfunction. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:628.
[30] NI B, CAO Z, LIU Y. Glycyrrhizin protects spinal cord and reduces inflammation in spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Neurosci. 2013;123(11):745-751.
[31] BI Y, ZHU Y, ZHANG M, et al. Effect of Shikonin on Spinal Cord Injury in Rats Via Regulation of HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kB Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(2):481-491.
[32] YUAN Y, SU Z, PU Y, et al. Ethyl pyruvate promotes spinal cord repair by ameliorating the glial microenvironment. Br J Pharmacol. 2012; 166(2):749-763.
[33] FILOUS AR, SILVER J. “Targeting astrocytes in CNS injury and disease: A translational research approach”. Prog Neurobiol. 2016;144:173-187.
[34] ESCARTIN C, GUILLEMAUD O, CARRILLO-DE SAUVAGE MA. Questions and (some) answers on reactive astrocytes. Glia. 2019;67(12):2221-2247.
[35] FAN YY, HUO J. A1/A2 astrocytes in central nervous system injuries and diseases: Angels or devils?Neurochem Int. 2021;148:105080.
[36] WANG P, LI C, LIAO G, et al. Vanillin attenuates proinflammatory factors in a tMCAO mouse model via inhibition of TLR4/NF-kB signaling pathway. Neuroscience. 2022;491:65-74.
[37] ZOU HJ, GUO SW, ZHU L, et al. Methylprednisolone Induces Neuro-Protective Effects via the Inhibition of A1 Astrocyte Activation in Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury Mouse Models. Front Neurosci. 2021;15:628917.
[38] HOU Y, WANG K, WAN W, et al. Resveratrol provides neuroprotection by regulating the JAK2/STAT3/PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway after stroke in rats. Genes Dis. 2018;5(3):245-255.
[39] NING SL, ZHU H, SHAO J, et al. MiR-21 inhibitor improves locomotor function recovery by inhibiting IL-6R/JAK-STAT pathway-mediated inflammation after spinal cord injury in model of rat. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(2):433-440.
[40] MORIZAWA YM, HIRAYAMA Y, OHNO N, et al. Author Correction: Reactive astrocytes function as phagocytes after brain ischemia via ABCA1-mediated pathway. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):1598.
[41] MA M, LI H, WU J, et al. Roles of Prokineticin 2 in Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury via Regulation of Phenotype Polarization in Astrocytes. Mol Neurobiol. 2020;57(9):3744-3758.
[42] ZHANG L, GUO K, ZHOU J, et al. Ponesimod protects against neuronal death by suppressing the activation of A1 astrocytes in early brain injury after experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurochem. 2021;158(4):880-897. |