中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (22): 3561-3566.doi: 10.12307/2023.360
• 骨科植入物相关基础实验 Basic experiments of orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
川芎嗪对大鼠脊髓损伤后铁代谢的影响
范 筱1,2,3,陶经纬1,蒋昇源1,邓博文1,穆晓红1
- 1北京中医药大学东直门医院,北京市 100700;2北京中医药大学,北京市 100029;3青岛市市立医院,山东省青岛市 266011
Effect of tetramethylpyrazine on iron metabolism after spinal cord injury in rats
Fan Xiao1, 2, 3, Tao Jingwei1, Jiang Shengyuan1, Deng Bowen1, Mu Xiaohong1
- 1Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China; 2Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100029, China; 3Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266011, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
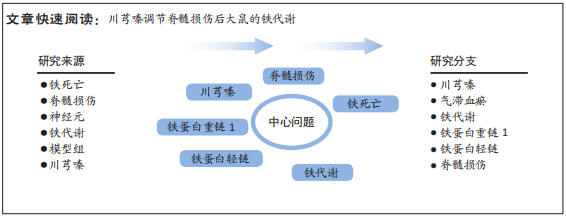
铁死亡:是一种铁依赖性的,区别于细胞凋亡、细胞坏死、细胞自噬的新型细胞程序性死亡方式。铁死亡的主要机制是在二价铁或酯氧合酶的作用下,催化细胞膜上高表达的不饱和脂肪酸,发生脂质过氧化,从而诱导细胞死亡;此外,还表现为抗氧化体系(谷胱甘肽系统)的调控核心酶GPX4的降低。脊髓损伤:由创伤暴力作用于脊柱,引起脊柱骨折、脱位,从而导致脊髓和马尾神经受损,损伤平面以下肢体出现运动功能、感觉功能、神经反射以及括约肌功能障碍的严重中枢神经系统损伤。
背景:铁代谢紊乱是导致脊髓损伤后神经细胞铁死亡的重要病理因素,不利于脊髓损伤修复。川芎嗪作为行气活血中药川芎的有效活性成分单体,被证实对脊髓损伤具有良好的抗炎、抗脂质过氧化反应以及神经保护作用,需进一步明确其促进脊髓损伤修复的作用机制。
目的:研究川芎嗪对大鼠脊髓损伤后铁代谢的调节作用,探讨其改善脊髓损伤的相关机制。
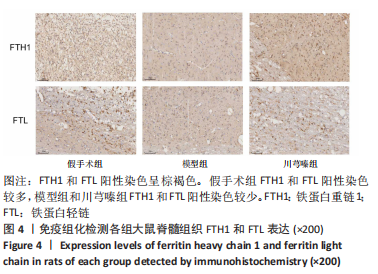
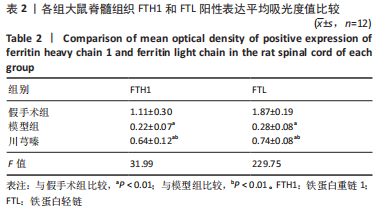
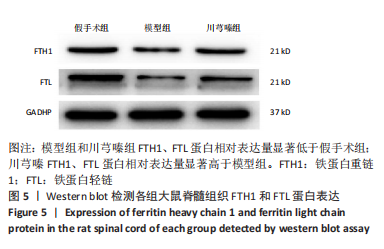
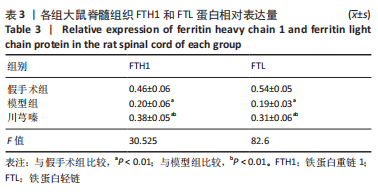
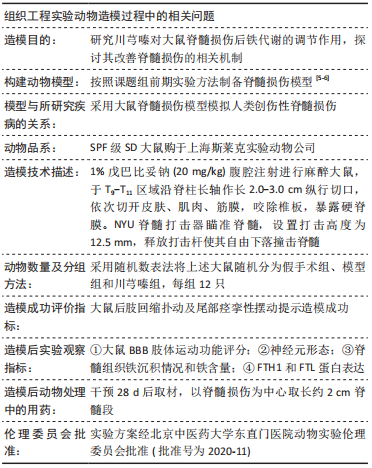
方法:将36只SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组和川芎嗪组,每组12只;假手术组仅行椎板切除术,术后给予生理盐水腹腔注射;模型组和川芎嗪组制备脊髓损伤模型,术后分别给予生理盐水和川芎嗪腹腔注射,术后4周取材。采用BBB肢体运动功能评分评价大鼠肢体运动功能,尼氏染色观察神经元形态,普鲁士染色观察脊髓组织铁沉积,铁检测试剂盒检测脊髓组织铁含量,免疫组化检测铁蛋白重链1和铁蛋白轻链表达,Western blot检测铁蛋白重链1和铁蛋白轻链的蛋白表达量。
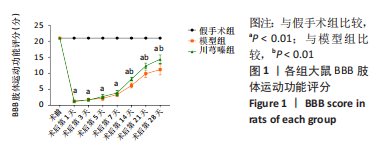
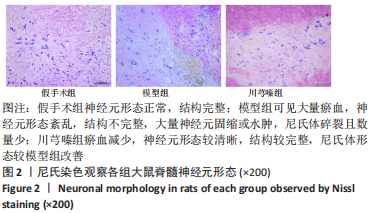
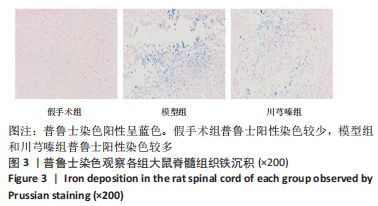
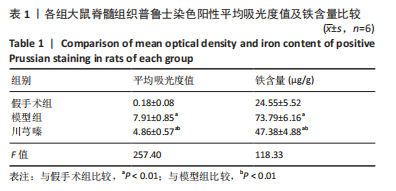
结果与结论:①模型组和川芎嗪组大鼠各个时间点BBB评分显著低于假手术组(P < 0.01),自术后第14天,川芎嗪组大鼠BBB评分显著高于模型组(P < 0.01);②尼氏染色结果显示,假手术组神经元形态结构正常,模型组可见大量瘀血,神经元形态结构紊乱,川芎嗪组瘀血较少,神经元形态结构较模型组改善;③普鲁士染色结果显示,假手术组铁沉积较少,模型组和川芎嗪组铁沉积较多;普鲁士染色阳性平均吸光度值模型组和川芎嗪组显著大于假手术组(P < 0.01),川芎嗪组显著小于模型组(P < 0.01);④铁含量检测结果显示,模型组和川芎嗪组显著多于假手术组(P < 0.01),川芎嗪组显著少于模型组(P < 0.01);⑤免疫组化染色结果显示,铁蛋白重链1和铁蛋白轻链阳性表达平均吸光度值模型组和川芎嗪组显著小于假手术组(P < 0.01),川芎嗪组显著大于模型组(P < 0.01);⑥Western blot检测结果显示,铁蛋白重链1蛋白和铁蛋白轻链蛋白的相对表达量模型组和川芎嗪组显著少于假手术组(P < 0.01),川芎嗪组显著多于模型组(P < 0.01);⑦结果说明,川芎嗪通过调控铁蛋白重链1和铁蛋白轻链的表达而调节脊髓损伤后铁代谢紊乱,从而发挥神经保护作用,促进脊髓损伤大鼠肢体运动功能恢复。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5147-6701 (范筱)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: