中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (2): 282-286.doi: 10.12307/2022.1003
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
川芎嗪改善脊髓完全横断大鼠血液流变学指标的动态观察
刘 港1,邓博文1,蒋昇源1,徐 林1,范 筱1,2,陶经纬1,张厚君1,贺 丰1,赵 毅1,穆晓红1
- 1北京中医药大学东直门医院,北京市 100700;2青岛市市立医院,山东省青岛市 266000
Tetramethylpyrazine improves hemorheological indexes in rats with complete spinal cord transection: a dynamic observation
Liu Gang1, Deng Bowen1, Jiang Shengyuan1, Xu Lin1, Fan Xiao1, 2, Tao Jingwei1, Zhang Houjun1, He Feng1, Zhao Yi1, Mu Xiaohong1
- 1Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100700, China; 2Qingdao Municipal Hospital, Qingdao 266000, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
川芎嗪:为川芎的有效活性成分之一,在治疗脊髓损伤方面具有改善微循环障碍、抑制炎症反应、调控神经细胞凋亡等作用。
血液流变学:研究范围包括血液的流动性、黏滞性、凝固性以及细胞的变形性等病理生理变化,对于疾病的诊断、预防、治疗具有重要意义。
背景:脊髓损伤后血液流变学指标的改变会引起微循环障碍,诱导组织缺血缺氧,加剧脊髓组织继发性损伤。
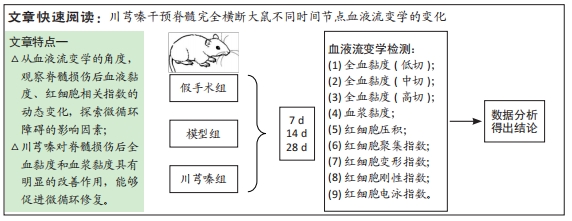
目的:观察川芎嗪干预脊髓完全横断大鼠后不同时间节点血液流变学指标的变化。
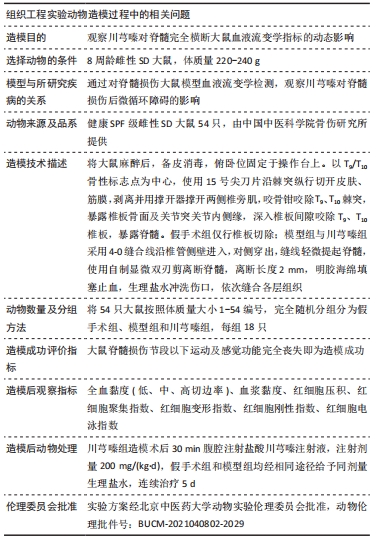
方法:将54只8周龄雌性SD大鼠随机分为假手术组、模型组、川芎嗪组,每组18只。假手术组仅行椎板切除术,模型组、川芎嗪组采用自制双刃显微剪行T10脊髓完全横断,缺损间隙2 mm,川芎嗪组在模型制备后给予200 mg/(kg·d)盐酸川芎嗪注射液腹腔注射,连续5 d。分别于造模术后7,14,28 d进行腹主动脉取血,检测全血黏度(低、中、高切边率)、血浆黏度、红细胞压积、红细胞聚集指数、红细胞变形指数、红细胞刚性指数、红细胞电泳指数。
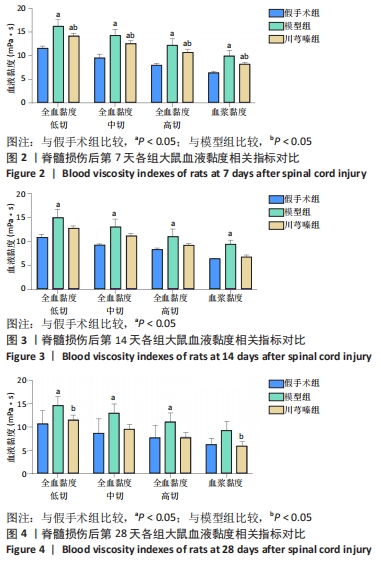
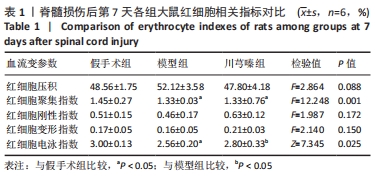
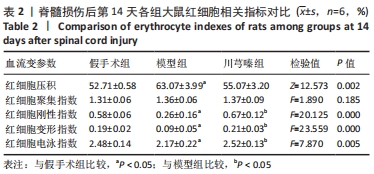
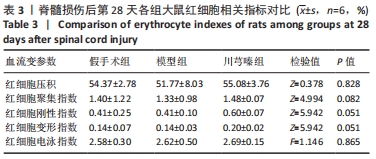
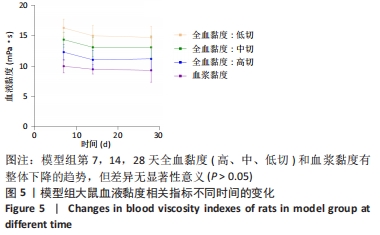
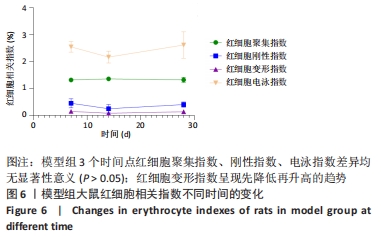
结果与结论:①脊髓损伤后第7,14,28天,模型组全血黏度(低、高、中切变率)和血浆黏度均显著高于假手术组(P < 0.05);第14天,模型组红细胞压积显著高于假手术组(P < 0.05),红细胞刚性指数、红细胞电泳指数显著低于假手术组(P < 0.05);②脊髓损伤后第7天,川芎嗪能够显著降低全血黏度(低、高、中切变率)和血浆黏度(P < 0.05);第14天川芎嗪能够升高红细胞变形指数(P < 0.05),一定程度上也能改善血液黏度相关指标,但差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);第28天川芎嗪能够显著改善全血黏度(低切)和血浆黏度(P < 0.05);③脊髓损伤后,全血黏度及血浆黏度均会升高,红细胞相关指数也会出现不同程度的变化,川芎嗪的使用能够改善早期血液流变学指标的恶化,对于改善微循环障碍具有一定的促进作用。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6014-7261(刘港)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: