中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1502-1507.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2217
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
骨水泥间隔器表面微观形貌改变对诱导膜内成骨因子表达的影响
李树源1,周琦石2,李 悦2,林知毅3,周宏亮1,申 震1,胡 柽1,杨佳宝1
- 1广州中医药大学第一临床医学院,广东省广州市 510405;2广州中医药大学第一附属医院一骨科,广东省广州市 510405;3广州市番禺区中医院,广东省广州市 511400
Effects of changes in surface morphology of bone cement spacer on the expression of bone growth factor in induced membrane
Li Shuyuan1, Zhou Qishi2, Li Yue2, Lin Zhiyi3, Zhou Hongliang1, Shen Zhen1, Hu Cheng1, Yang Jiabao1
- 1The First Clinical Medical College, Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 2First Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 510405, Guangdong Province, China; 3Panyu Hospital of Chinese Medicine, Guangzhou 511400, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥:为临床上常用的骨科植入材料,具有很大的抗压能力,抗压缩能力为97 MPa,也具有良好的生物相容性。1987年Galibert等首次报道用聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥来治疗椎体血管瘤,并将此技术称之为经皮椎体成形。1970年Buchholz首次应用载抗生素骨水泥控制关节感染,目前以聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥作为抗生素的缓释载体被广泛应用于人工全髋关节置换及骨髓炎的治疗。
转化生长因子β1:是具有多种功能的蛋白多肽,是“转化生长因子β超家族”成员之一,大量存在于骨组织与血小板中,可以刺激间充质干细胞的增殖、分化,并抑制间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞分化,也促进成骨细胞、成软骨细胞的增殖及细胞外基质的合成,诱导膜内成骨和软骨内成骨。
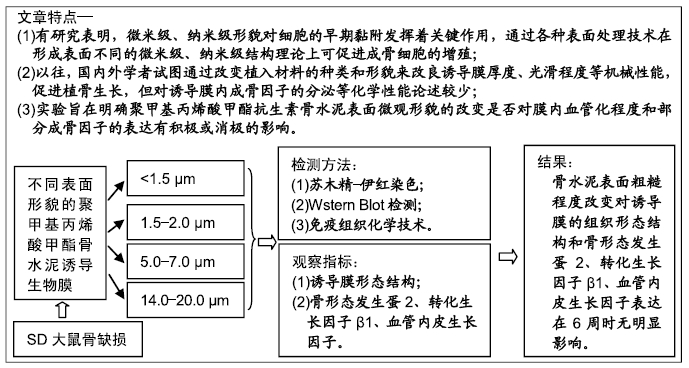
背景:目前国内外学者试图通过改变植入材料的种类和形貌、改良诱导膜厚度、光滑程度等机械化学性能来促进植骨生长。
目的:比较大鼠股骨骨缺损处不同表面粗糙程度聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥形成的诱导膜在膜内血管化程度和部分成骨因子表达的差异。
方法:取48只雄性SD大鼠(购自广州中医药大学实验动物中心)建立大鼠临界尺寸股骨缺损模型,按随机数字表法分为A、B、C、D组,分别在股骨骨缺损处植入表面粗糙度<1.5 µm、1.5-2.0 µm、5.0-7.0 µm、14.0-20.0 µm的聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥占位器。植入6周大鼠体内诱导膜形成后取出骨水泥周围的诱导膜,苏木精-伊红染色观察诱导膜病理组织形态结构变化,采用Western Blot印迹方法和免疫组织化学染色法对诱导膜中骨形态发生蛋白2、转化生长因子β1、血管内皮生长因子蛋白进行定量和定性分析。实验获得广州中医药大学动物实验伦理委员会批准,批准号:20181101006。
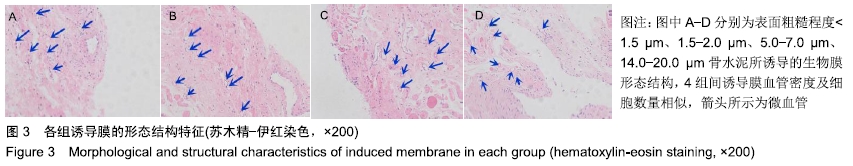
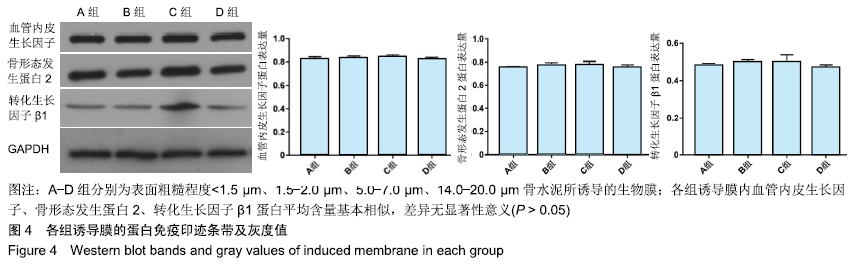
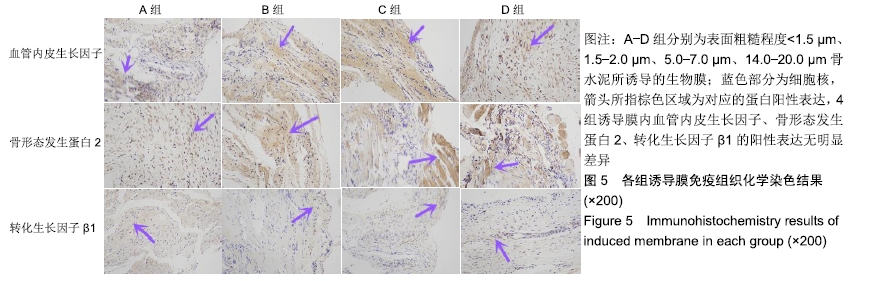
结果与结论:①苏木精-伊红染色显示,4种表面粗糙程度不同的骨水泥均可以形成较为规则的诱导膜,4组诱导膜之间血管化程度和细胞的数量大体相似;②Western Blot印迹检测显示,各组诱导膜内骨形态发生蛋2、转化生长因子β1、血管内皮生长因子蛋白平均含量基本相似(P > 0.05);③免疫组织化学染色显示,各组诱导膜内骨形态发生蛋2、转化生长因子β1、血管内皮生长因子蛋白阳性表达基本相似(P > 0.05);④结果表明,骨水泥表面粗糙程度改变对诱导膜的组织形态结构和骨形态发生蛋2、转化生长因子β1、血管内皮生长因子表达在6周时无明显影响。
ORCID: 0000-0003-1405-0765(李树源)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: