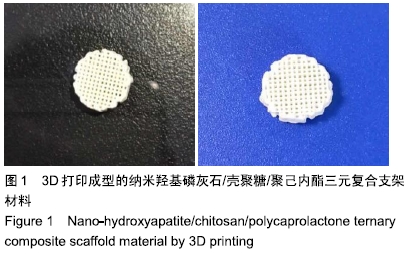
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1496-1501.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2238
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印成型纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/聚己内酯三元复合支架材料的构建及表征
余和东1,张 丽1,夏凌云1,毛 敏1,倪小兵1,冷卫东1,罗 杰2
- 十堰市太和医院(湖北医药学院附属医院),1口腔医学中心,2神经外科,湖北省十堰市 442000
Construction and characterization of nano-hydroxyapatite/chitosan/polycaprolactone composite scaffolds by 3D printing
Yu Hedong1, Zhang Li1, Xia Lingyun1, Mao Min1, Ni Xiaobing1, Leng Weidong1, Luo Jie2
- 1Stomatological
Center, 2Department of Neurosurgery, Taihe Hospital (Affiliated
Hospital of Hubei University of Medicine), Shiyan 442000, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
组织工程骨:将体外培养的功能相关的种子细胞种植于天然的或人工合成的支架材料内,加入生长因子体外培养一段时间,将他们移植到体内,促进组织修复和骨再生的人工骨。组织工程骨形成的3要素为:支架材料、成骨细胞、生长因子。
生物陶瓷:生物表面活性陶瓷通常含有羟基,还可做成多孔性,生物组织可长入并同其表面发生牢固的键合;生物吸收性陶瓷的特点是能部分吸收或者全部吸收,在生物体内能诱发新生骨的生长。生物活性陶瓷具有骨传导性,它作为一个支架,成骨在其表面进行;还可作为多种物质的外壳或填充骨缺损。生物陶瓷有羟基磷灰石陶瓷、磷酸三钙陶瓷等。
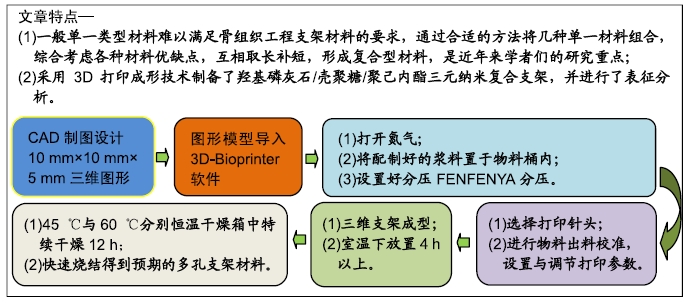
背景:目前常用的骨缺损修复支架材料种类较多,但单一类型材料难以满足骨组织工程支架材料的要求,通过合适的方法将几种单一材料组合形成复合型材料,综合考虑各种材料优缺点,是近年来学者们的研究重点。
目的:构建纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/聚己内酯三元复合支架材料,并作表征分析研究。
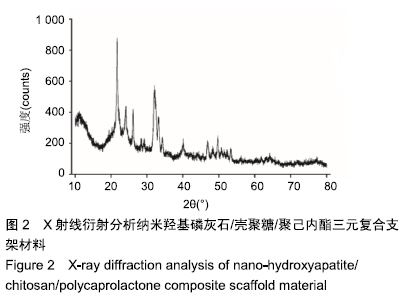
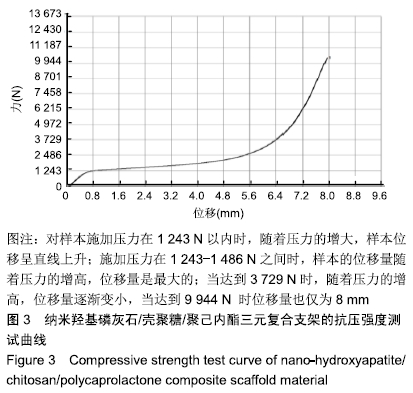
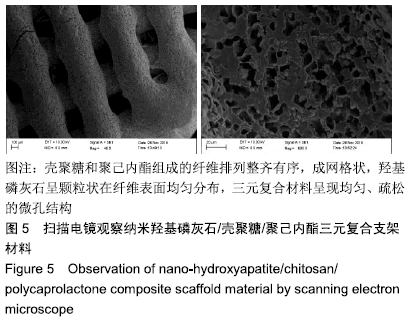
方法:采用3D打印成型技术制备纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/聚己内酯多孔三元复合支架材料,从X射线衍射分析、吸水率、抗压强度、体外降解性能、孔径分析、扫描电镜分析等多个维度对支架材料进行表征研究。
结果与结论:①X射线衍射分析显示,纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/聚己内酯多孔三元复合支架的晶型峰图与羟基磷灰石粉末衍射标准卡片类似,表明该三元复合支架是通过物理作用相互结合的,不影响羟基磷灰石的生物学功能;②三元复合支架的吸水率为18.28%,亲水性好,支架可承受的最大压力为1 415 N,其体外降解速率与成骨速率相当;③显微镜下可见三元复合支架的内孔为方形,孔径250 µm,孔径大小均匀、分布有致;④扫描电镜下三元复合支架可见,壳聚糖和聚己内酯组成的纤维排列整齐有序,成网格状, 羟基磷灰石呈颗粒状在纤维表面均匀分布,三元复合材料呈现均匀、疏松的微孔结构;⑤结果表明,通过3D打印成型技术可成功制备纳米羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖/聚己内酯三元复合支架材料,其具有适度的抗压强度、一定的孔隙率、适宜的降解速度和吸水率,能为修复骨缺损的奠定基础。
ORCID: 0000-0002-6321-9160(余和东)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: