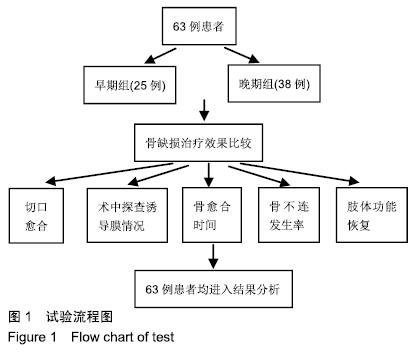
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 493-498.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1963
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 下一篇
早期与晚期行诱导膜内植骨的骨愈合效果分析
周子红1,吴永伟2,冯德宏1,赵继军1,顾三军2,许亚军2,芮永军2,殷小根3,殷渠东2
- 1无锡市人民医院骨科,江苏省无锡市 214000;2无锡市骨科医院骨科,江苏省无锡市 214062;3无锡市张渚人民医院骨科,江苏省无锡市 214231
Bone healing effects of early-stage versus late-stage bone grafting within induced membrane
Zhou Zihong1, Wu Yongwei2, Feng Dehong1, Zhao Jijun1, Gu Sanjun2, Xu Yajun2, Rui Yongjun2, Yin Xiaogen3, Yin Qudong2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Wuxi People’s Hospital, Wuxi 214000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Wuxi Orthopedics Hospital, Wuxi 214062, Jiangsu Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Zhangzhu People’s Hospital, Wuxi 214231, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
诱导膜技术:是修复骨缺损,尤其是感染性骨缺损的有效方法。手术分二个阶段,第一阶段手术是在骨缺损部位填塞骨水泥,由于异物反应刺激周围软组织形成伪膜,伪膜逐渐增厚成为诱导膜;第二阶段手术是切开诱导膜取出骨水泥填塞物,在诱导膜内植入松质骨等植骨材料,并缝合诱导膜。第二阶段手术时间因骨缺损部位是否感染和感染何时得到控制而不同。
诱导膜包裹松质骨植骨修复骨缺损的机制:一方面是诱导膜具有机械性的隔离和包裹作用;另一方面诱导膜是生物膜,具有生物性成骨活性。诱导膜厚度可达1 mm左右,比正常骨膜更厚,外层主要为纤维组织,具有机械性隔离纤维组织长入骨缺损部位作用。
背景:对于骨缺损的治疗,早期与晚期阶段行诱导膜内植骨修复的骨愈合效果可能存在差异。
目的:探讨早期与晚期阶段行诱导膜内植骨修复骨缺损的愈合效果差异和影响骨愈合的主要因素。
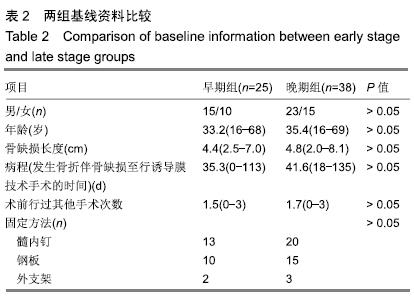
方法:选择2007年1月至2017年8月无锡市骨科医院和无锡市人民医院行诱导膜技术治疗的63例胫骨骨缺损患者,其中男38例,女25例,年龄16-69岁,按骨水泥填塞后诱导膜内植骨时机不同分为2组:早期组(n=25)在骨水泥填塞后6-8周诱导膜内植骨,晚期组(n=38)在骨水泥填塞后10-12周诱导膜内植骨。随访评估两组骨缺损愈合与患肢功能恢复情况,分析发生延迟愈合和骨不连的原因。试验获得无锡市人民医院和无锡市骨科医院医学伦理委员会审批(LW2019001)。
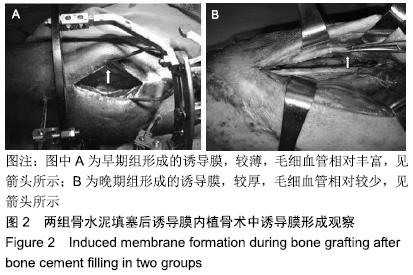
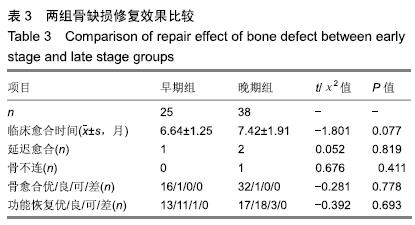
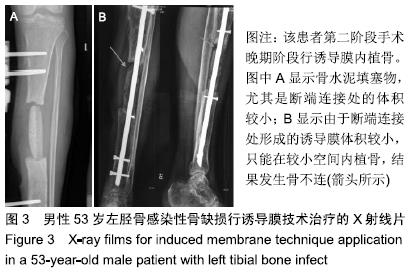
结果与结论:①63例患者均顺利完成骨移植手术,术中发现早期组形成的诱导膜较薄、毛细血管相对较多,而晚期组形成的诱导膜通常较厚、毛细血管相对较少;②63例获得16-50个月随访;早期组伤口或切口一期愈合22例,延期愈合3例;晚期组伤口或切口一期愈合34例,延期愈合2例,二期愈合2例;③早期组延迟愈合1例,无骨不连病例,临床愈合时间5.0-12.0个月,平均6.64个月;晚期组延迟愈合2例,骨不连1例,临床愈合时间5.0-16.0个月,平均7.42个月;两组骨缺损愈合时间、骨不连发生情况比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);④早期组患肢功能恢复:优13例、良11例、可1例,晚期组患肢功能恢复:优17例、良18例、可3例,两组患肢功能恢复情况比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);⑤结果表明,不同时期行诱导膜内植骨对骨缺损骨愈合时间有一定影响,但影响较小,对愈合率无影响,而诱导膜体积和完整性、植骨质量和数量及断端稳定性等其它因素对骨缺损骨愈合,尤其是愈合率的影响更大。ORCID: 0000-0002-7347-1773(周子红)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: