中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1508-1514.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2218
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
超临界二氧化碳萃取的猪松质骨
罗旭江1,2,鲜 海1,彭礼庆1,2,沈 师1,2,张 彬1,2,高 超2,王振勇2,眭 翔2,黄靖香2,韩 刚2,刘舒云2,郭全义2,鲁晓波1
- 1西南医科大学附属医院骨与关节外科,四川省泸州市 646000;2中国人民解放军总医院骨科研究所,骨科再生医学北京市重点实验室,全军骨科战创伤重点实验室,北京市 100853
Extraction of porcine cancellous bone by supercritical carbon dioxide
Luo Xujiang1, 2, Xian Hai1, Peng Liqing1, 2, Shen Shi1, 2, Zhang Bin1, 2, Gao Chao2, Wang Zhenyong2, Sui Xiang2, Huang Jingxiang2, Han Gang2, Liu Shuyun2, Guo Quanyi2, Lu Xiaobo1
- 1Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, Sichuan Province, China; 2Institute of Orthopedics, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing Key Lab of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedics, Key Laboratory of Musculoskeletal Trauma & War Injuries, PLA, Beijing 100853, China
摘要:
文题释义:
超临界二氧化碳:任何一种物质都存在3种相态,即气相、液相、固相,其中液、气两相相界面消失的点叫超临界点。二氧化碳(CO2)因性质稳定、无毒,临界点容易达到而被广泛应用。
松质骨:主要分布于长骨的两端、短骨、扁骨及不规则骨的内部,由骨小梁互相交织构成,其骨密度低于皮质骨,富有弹性,松质骨结构有助于维持骨骼形态,抵抗压力。松质骨高度多孔,可以促进气体交换、营养和代谢废物扩散,能够引导自体干细胞爬行进入缺损区域,加快血管长入,促进骨重建。
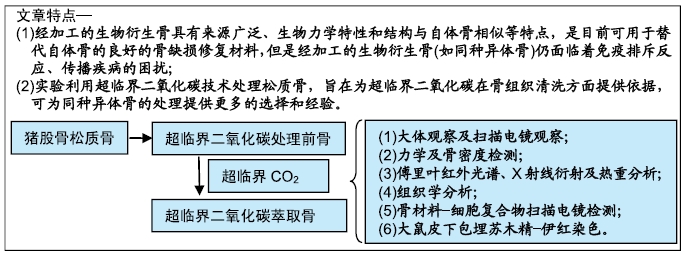
背景:近年来国外使用超临界流体进行生物材料处理的研究较多,但是超临界流体应用于骨组织清洗的研究少见,国内相关报道更少。
目的:评估超临界二氧化碳萃取技术处理猪股骨松质骨的有效性及对骨生物学性能的影响。
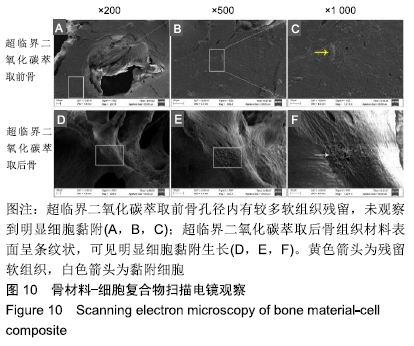
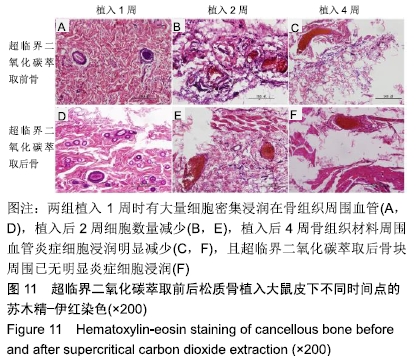
方法:分别制备超临界二氧化碳萃取前(对照组)及萃取后猪股骨骨块(实验组),检测两组骨密度、微观结构、最大抗压强度、弹性模量、骨组织组成成分、胶原含量与组织学分析。将骨髓间充质干细胞分别接种于两组骨块上,培养1 d后,扫描电镜观察材料骨小梁微孔结构及骨材料-细胞复合物中细胞黏附及生长情况。将两组骨块分别植入SD大鼠皮下,术后1,2,4周组织学观察皮下包埋炎症反应。动物实验方案已经解放军总医院伦理委员会批准。
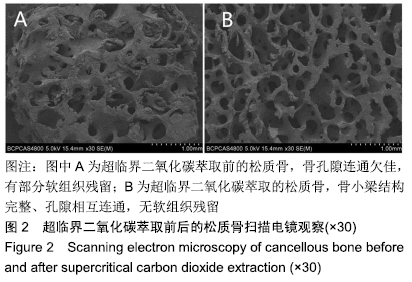
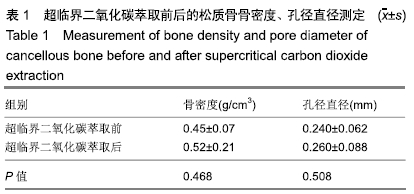
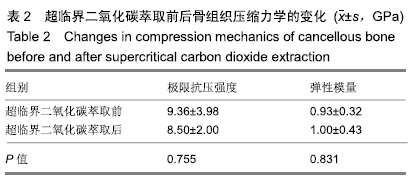
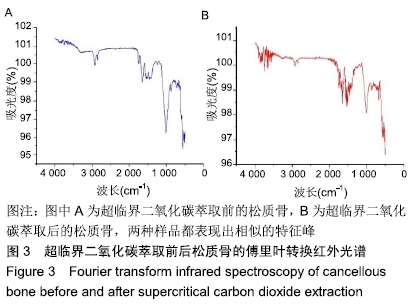
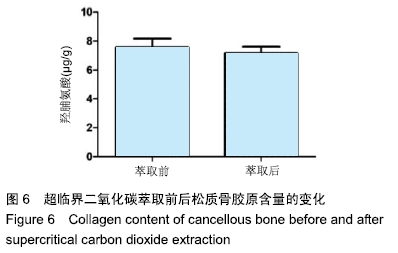
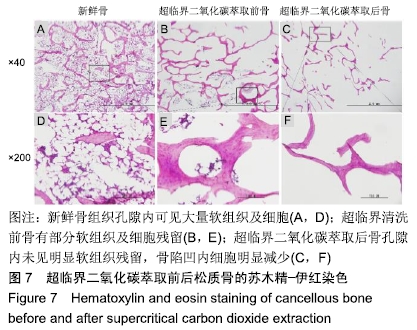
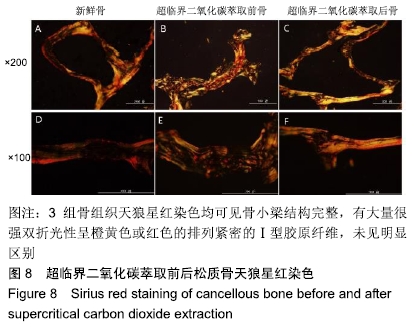
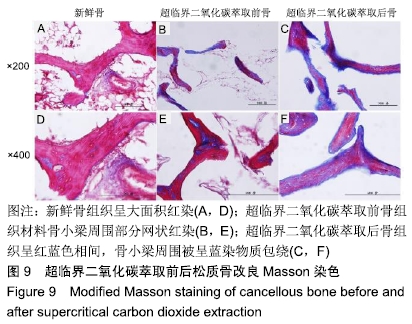
结果与结论:①两组材料孔径大小、骨密度、最大抗压强度、弹性模量、胶原含量比较差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05);②扫描电镜显示,对照组材料孔隙连通欠佳,有软组织残留;实验组材料孔隙相互连通、结构完整;③傅里叶红外光谱及X射线衍射分析显示,两组骨组织材料具有相似的吸收峰及衍射峰,热重分析显示超临界二氧化碳萃取可减少骨组织水分含量;④苏木精-伊红染色显示实验组骨无软组织残留,骨陷凹内细胞残留明显减少,对照组有软组织及细胞残留;天狼星红及改良Masson染色显示实验组骨胶原结构完整,胞质成分减少,对照组胞质成分残留明显;⑤扫描电镜显示,对照组骨无明显细胞黏附,实验组骨可见明显细胞黏附生长;⑥实验组骨组织植入皮下的血管周围炎症反应明显轻于对照组骨组织;⑦结果表明,超临界二氧化碳萃取技术是一种有效、环保的骨组织处理技术,在不影响其胶原结构及含量、力学性能的基础上,能够有效去除猪股骨松质骨细胞及软组织,保留骨孔隙结构完整,增加细胞黏附及生长,有效减低炎性排斥反应。
ORCID: 0000-0003-4451-4815(罗旭江)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: