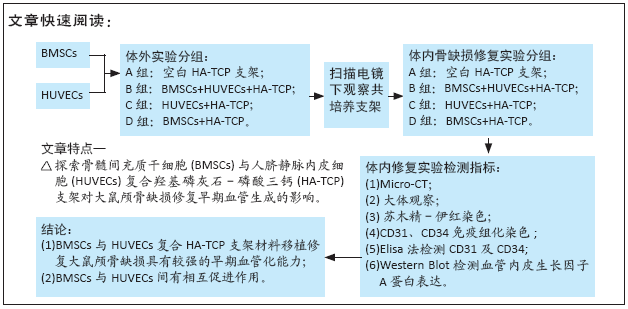
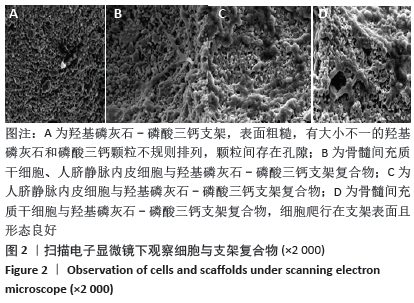
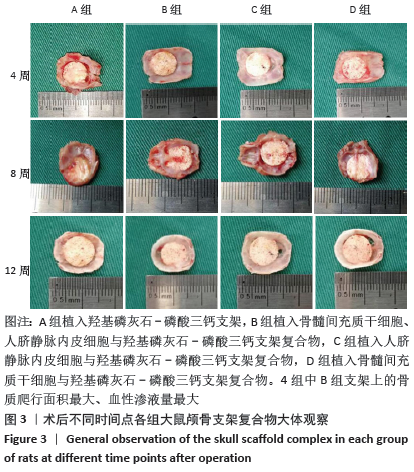
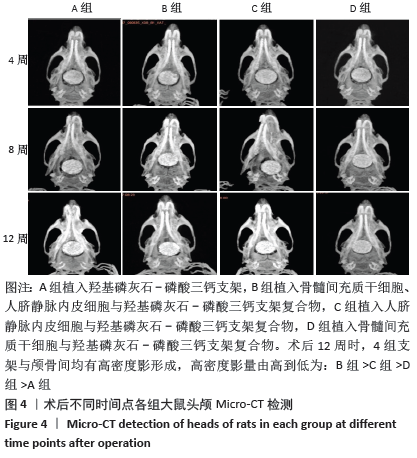
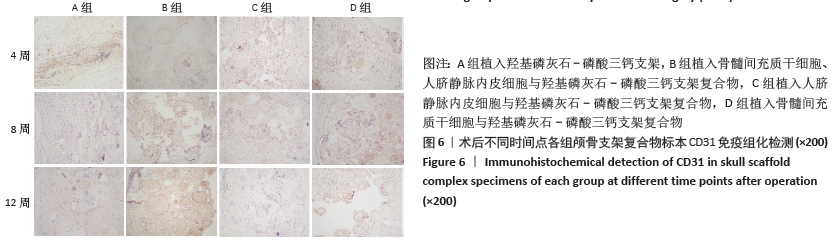
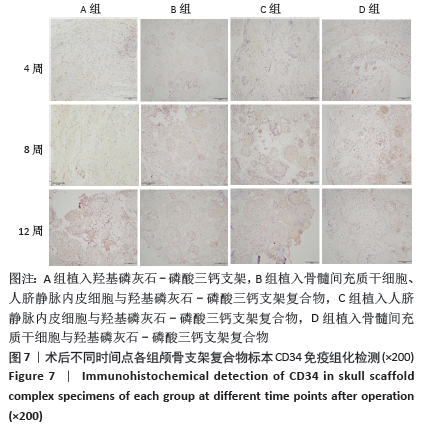
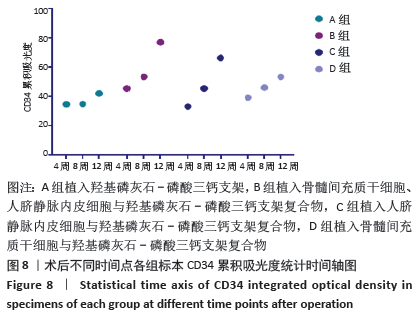
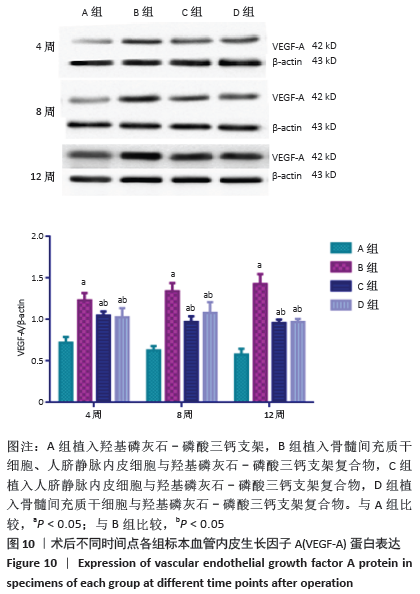
[1] PEARSON RG, BHANDARI R, QUIRK RA, et al. Recent Advances in Tissue Engineering. J Long Term Eff Med Implants. 2017;27(2-4):199-231.
[2] RASHMI, PATHAK R, AMARPAL, et al. Evaluation of tissue-engineered bone constructs using rabbit fetal osteoblasts on acellular bovine cancellous bone matrix. Vet World. 2017;10(2):163-169.
[3] LEE SH, COGER RN, CLEMENS MG. Antioxidant functionality in hepatocytes using the enhanced collagen extracellular matrix under different oxygen tensions. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(10):2825-2834.
[4] MANOHARAN V, LI Q, BERTASSONI LE. Engineering Pre-vascularized Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;881:79-94.
[5] ADEL-KHATTAB D, KAMPSCULTE M, PELESKA B, et al. An intrinsic angiogenesis approach and varying bioceramic scaffold architecture affect blood vessel formation in bone tissue engineering in vivo.Key Eng Mater. 2016;720: 58-64.
[6] KASHTE S, JAISWAL AK, KADAM S. Artificial Bone via Bone Tissue Engineering: Current Scenario and Challenges. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;14(1):1-14.
[7] WANG K, LIN RZ, MELERO-MARTIN JM. Bioengineering human vascular networks: trends and directions in endothelial and perivascular cell sources. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(3):421-439.
[8] WENGER A, STAHL A, WEBER H, et al. Modulation of in vitro angiogenesis in a three-dimensional spheroidal coculture model for bone tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. 2004;10(9-10):1536-1547.
[9] WENGER A, KOWALEWSKI N, STAHL A, et al. Development and characterization of a spheroidal coculture model of endothelial cells and fibroblasts for improving angiogenesis in tissue engineering. Cells Tissues Organs. 2005;181(2):80-88.
[10] KAIGLER D, KREBSBACH PH, WEST ER, et al. Endothelial cell modulation of bone marrow stromal cell osteogenic potential. FASEB J. 2005;19(6):665-667.
[11] JEONG J, KIM JH, SHIM JH, et al. Bioactive calcium phosphate materials and applications in bone regeneration. Biomater Res. 2019;23:4.
[12] KAMALALDIN N, JAAFAR M, ZUBAIRI SI, et al. Physico-Mechanical Properties of HA/TCP Pellets and Their Three-Dimensional Biological Evaluation In Vitro. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1084:1-15.
[13] 李彪.VEGF 165基因修饰HUVECs复合BMSCs促组织工程骨血管生成的体外实验研究[D].泸州:四川医科大学,2015:1-59.
[14] YOUREK G, HUSSAIN MA, MAO JJ. Cytoskeletal changes of mesenchymal stem cells during differentiation. ASAIO J. 2007;53(2):219-228.
[15] SANTOS MI, REIS RL. Vascularization in bone tissue engineering: physiology, current strategies, major hurdles and future challenges. Macromol Biosci. 2010;10(1):12-27.
[16] RYAN JW, RYAN US. Endothelial surface enzymes and the dynamic processing of plasma substrates. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1984;26:1-43.
[17] MÁRQUEZ WH, GÓMEZ-HOYOS J, WOODCOCK S, et al. The regional microvascular density of the gluteus medius tendon determined by immunohistochemistry with CD31 staining: a cadaveric study. Hip Int. 2015;25(2):168-171.
[18] ASAHARA T, MUROHARA T, SULLIVAN A, et al. Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science. 1997;275(5302): 964-967.
[19] APTE RS, CHEN DS, FERRARA N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell. 2019;176(6):1248-1264.
[20] CARLISLE P, MARRS J, GAVIRIA L, et al. Quantifying Vascular Changes Surrounding Bone Regeneration in a Porcine Mandibular Defect Using Computed Tomography. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2019;25(12): 721-731.
[21] SCHLICKEWEI C, KLATTE TO, WILDERMUTH Y, et al. A bioactive nano-calcium phosphate paste for in-situ transfection of BMP-7 and VEGF-A in a rabbit critical-size bone defect: results of an in vivo study. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(2):15.
[22] LIAO H, ZHONG Z, LIU Z, et al. Bone mesenchymal stem cells co-expressing VEGF and BMP-6 genes to combat avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(1):954-962.
[23] CAETANO G, WANG W, MURASHIMA A, et al. Tissue Constructs with Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Treat Bone Defects in Rats. Materials (Basel). 2019;12(14):2268.
[24] HARVESTINE JN, ORBAY H, CHEN JY, et al. Cell-secreted extracellular matrix, independent of cell source, promotes the osteogenic differentiation of human stromal vascular fraction. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(24):4104-4115.
[25] AKSEL H, HUANG GT. Combined Effects of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor and Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 on Odonto/Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells In Vitro. J Endod. 2017;43(6):930-935.
[26] SAMEE M, KASUGAI S, KONDO H, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein-2 (BMP-2) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) transfection to human periosteal cells enhances osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008;108(1):18-31.
[27] BOULETREAU PJ, WARREN SM, SPECTOR JA, et al. Hypoxia and VEGF up-regulate BMP-2 mRNA and protein expression in microvascular endothelial cells: implications for fracture healing. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109(7):2384-2397.
[28] LI P, BAI Y, YIN G, et al. Synergistic and sequential effects of BMP-2, bFGF and VEGF on osteogenic differentiation of rat osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Metab. 2014;32(6):627-635.
|