| [1] Oda S, Otsuki S, Kurokawa Y, et al. A new method for meniscus repair using type I collagen scaffold and infrapatellar fat pad. J Biomater Appl. 2015;29(10): 1439-1448. [2] Doryab A, Amoabediny G, Salehi-Najafabadi A, et al. Advances in pulmonary therapy and drug development: Lung tissue engineering to lung-on-a-chip. Biotechnol Adv. 2016; 34(5):588-596. [3] Wu J, Ravikumar P, Nguyen KT, et al. Lung protection by inhalation of exogenous solubilized extracellular matrix. PLoS One. 2017;12(2):e0171165. [4] 孙良,李丕宝,栾保华,等.脱细胞基质软骨支架的制备[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(16):2494-2499.[5] 吕志刚,徐列明.丹参酚酸B的药理研究概况[J].医学研究杂志, 2008,37(8):114-116.[6] 李克明,付桂香.丹参中丹酚酸B的药理研究进展[J].中日友好医院学报,2008,22(6):366-377.[7] 刘宾,张蔓菁,夏纬,等.反复冻融与超高压处理制备脱细胞组织工程血管支架的实验研究[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志,2009, 20(12):761-764.[8] 刘宾,李菲,张蔓菁,等.超声空化法对脱细胞血管支架组织结构及生物力学特性影响的实验研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志, 2015, 26(12):755-759.[9] 赵艳红,杨强,彭江,等.新型脱细胞骨基质材料的组织学结构及其细胞相容性观察[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2013,27(7): 781-785.[10] 杰永生,綦惠,陈磊,等.脱蛋白联合冷冻干燥法制备异种骨的实验研究[J].中国医药生物技术,2013,8(5):331-335.[11] 刘昊,张永刚,郭全义,等.新型脱细胞骨基质-壳聚糖骨组织工程支架的制备及性能评价[J].军医进修学院学报,2011,32(6): 616-619.[12] 夏建春,米立国,高英,等.NaOH消蚀法制备胎儿脱细胞真皮基质的研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2005,23(4):409-412.[13] 彭希亮,张玉红,倪文琼.脂肪组织来源干细胞构建皮肤复合组织修复创面缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(1):8-12.[14] 李一平.冠状动脉粥样硬化型心脏病发病机制的代谢组学初步探索及优化冠状动脉粥样硬化型心脏病介入治疗的临床研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,中国医学科学院,清华大学医学部,北京协和医学院中国医学科学院.2017.[15] 李晓玉,廉东波,肖萌萌,等.脱细胞血管基质管状支架用于猪胆管损伤修复的实验研究[J].中华普通外科杂志,2018,33(2): 152-155.[16] 刘俊,张晓膺.纳米APS外膜肝素化内膜小口径组织工程血管的实验研究[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版),2017,37(3):337-343.[17] 邵擎东,汪铮,李宇飞,等.部分间质血管-脱细胞骨基质-壳聚糖支架在促进兔桡骨骨折愈合中的作用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2017, 34(1):97-101.[18] 陶然岑,郭光伟.丹参酚酸B后处理脱细胞猪心脏瓣膜的形态学及生物力学研究[J].中国现代医生,2011,49(22):13-14,28.[19] 陈晓波,吴英锋,段红永,等.不同方法制备脱细胞血管基质的比较[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2011,5(20):6098-6101.[20] 付炜,薛继鑫,何晓敏,等.应用血管脱细胞基质膜片构建组织工程血管的初步研究[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2012,6(22): 7090-7094.[21] 刘国锋,何志娟,杨大平,等.生物酶连续消化法对犬颈总动脉脱细胞基质材料生物力学的影响研究[J].中国美容医学,2010,19(7): 996-999.[22] Zhang J, Huang X, Wang L. Sheep acellular dermal matrix microparticle transplant for wound in rats. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2018;43(7):711-717. [23] Kong X, Kong C, Wen S, et al. The use of heparin, bFGF, and VEGF 145 grafted acellular vascular scaffold in small diameter vascular graft. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018. doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.34160. [24] Lee JW, Park JY, Park SH, et al. Cross-linked electrospun cartilage acellular matrix/poly(caprolactone-co-lactide-co- glycolide) nanofiber as an antiadhesive barrier. Acta Biomater. 2018;74:192-206.[25] de Resende DRB, Greghi SLA, Siqueira AF, et al. Acellular dermal matrix allograft versus free gingival graft: a histological evaluation and split-mouth randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig. 2018. doi: 10.1007/s00784-018-2470-6.[26] Moyer HR, Hart AM, Yeager J, et al. A Histological Comparison of Two Human Acellular Dermal Matrix Products in Prosthetic-Based Breast Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2017;5(12):e1576. [27] Bohá? M, Danišovi? ?, Koller J, et al. What happens to an acellular dermal matrix after implantation in the human body? A histological and electron microscopic study. Eur J Histochem. 2018;62(1):2873.[28] 肖玲芳,张卫芳,龚志成.丹酚酸B的心血管药理研究进展[J].中南医学科学杂志,2015,43(1):90-94.[29] 方宁涛,孙洪亮,谢尚喆,等.十二烷基肌氨酸钠法制备带瓣管道支架及其生物学性能分析[J].中华胸心血管外科杂志,2007,23(4): 260-262.[30] 史振宇,张祥满,陈枫,等.聚己内酯-碳酸亚乙酯和血管内皮生长因子静电混纺支架的构建及其生物学性能[J].复旦学报(医学版), 2015,42(1):50-56. |
.jpg)
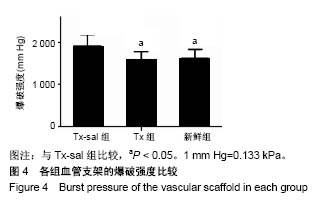
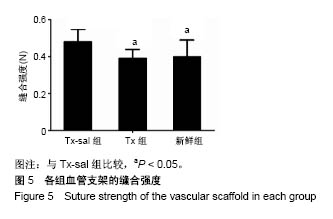
.jpg)