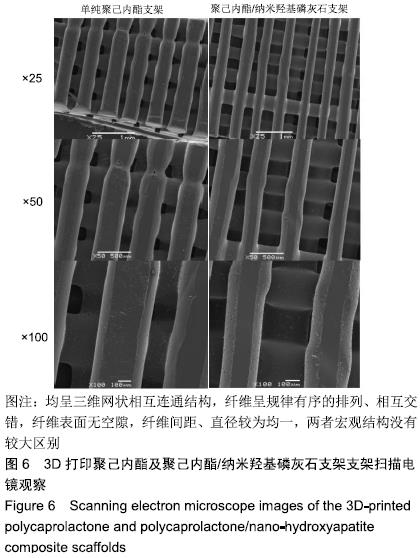
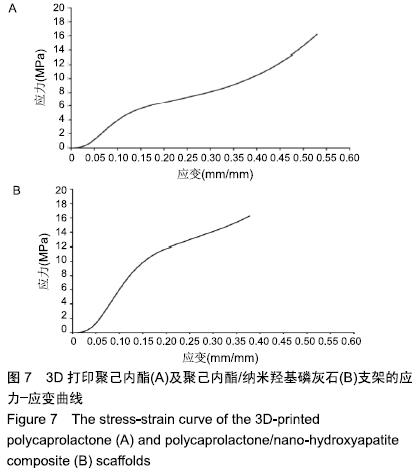
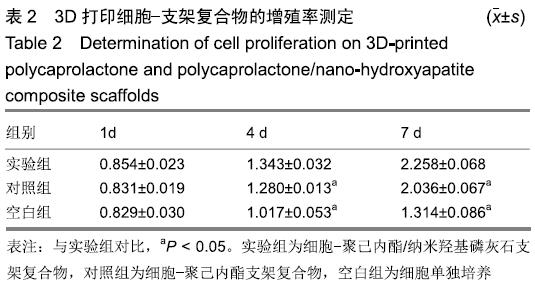
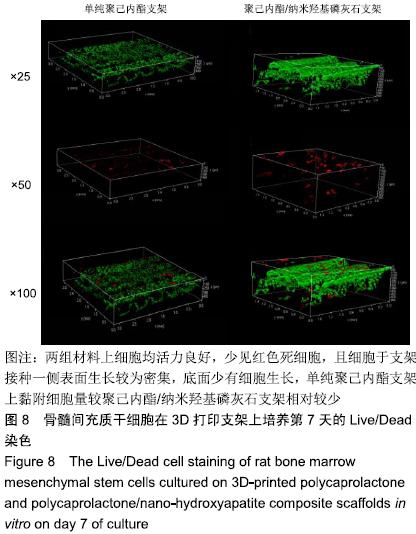
中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 589-595.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1880
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
3D打印聚己内酯/纳米羟基磷灰石复合支架与骨髓间充质干细胞的体外生物相容性
胡超然1,邱 冰1,周祝兴2,杨 洋3,李 佳3
- 1贵州省骨科医院,贵州省贵阳市 550004;2北京大学医学院,北京市 100871;3贵州医科大学,贵州省贵阳市 550001
In vitro biocompatibility of 3D printed polycaprolactone/nano-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Hu Chaoran1, Qiu Bing1, Zhou Zhuxing2, Yang Yang3, Li Jia3
- 1Guizhou Orthopedics Hospital, Guiyang 550004, Guizhou Province, China; 2Peking University Health Science Center, Beijing 100871, China; 3Guizhou Medical University, Guiyang 550001, Guizhou Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
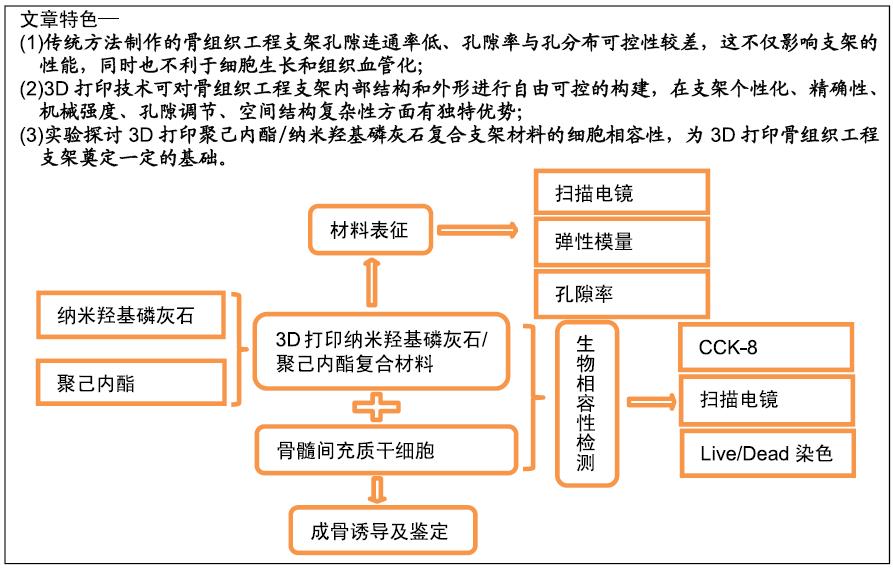
3D打印技术:是通过计算机设计3D模型,按照某一坐标轴切成无限多个剖面,然后层层打印堆叠形成一个实体的立体模型,使用3D打印技术制备的骨组织工程支架能对支架的内部结构和外形进行自由可控的构建,在支架个性化、精确性、机械强度、孔隙调节、空间结构复杂性方面有独特优势。
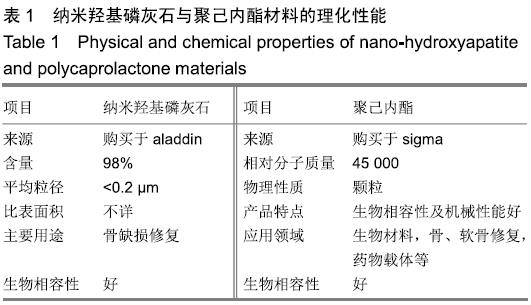
纳米羟基磷灰石/聚己内酯复合材料:羟基磷灰石是人体和动物骨骼的主要无机成分,具有良好的骨诱导性,纳米羟基磷灰石由于良好的生物相容性和骨整合能力被广泛用作骨缺损的修复材料;聚己内酯是一种已被FDA批准的生物材料,具有良好的机械性能、生物相容性及降解性。两种材料复合物的多孔结构能够为细胞生长、组织再生及血管化提供有利条件。
背景:聚己内酯/纳米羟基磷灰石复合材料是在常用骨组织工程材料基础上结合3D打印技术制备的新型复合支架材料,目前对于该复合材料的体外生物相容性研究较少。
目的:通过体外实验探讨3D打印聚己内酯/纳米羟基磷灰石复合支架材料的细胞相容性。
方法:利用3D打印技术分别制备聚己内酯及聚己内酯/纳米羟基磷灰石复合支架,表征两组材料的微观结构、孔隙率及力学性能。将大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分别接种于两组支架表面,CCK-8法检测细胞增殖率,扫描电镜和Live/Dead染色观察细胞在支架上的生长情况。
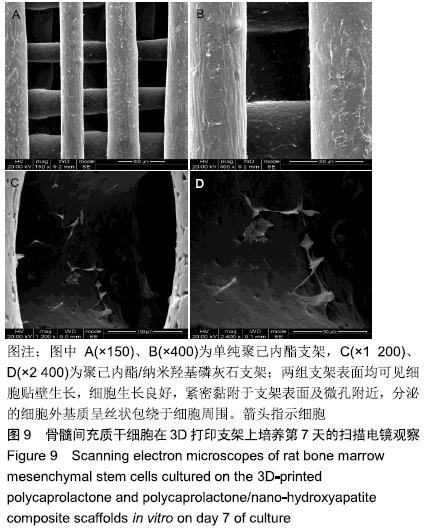
结果与结论:①两组支架均呈三维网状相互连通结构,纤维呈规律有序的排列、相互交错,纤维表面无空隙,纤维间距、直径较为均一;两组支架的孔隙率比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);复合支架的弹性模量高于单纯聚己内酯支架(P < 0.05);②两组支架表面培养1 d的细胞增殖比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),复合支架表面培养4,7 d的细胞增殖快于单纯聚己内酯支架(P < 0.05);③Live/Dead染色结果显示,两组材料均具有良好的细胞相容性,细胞活性较高,同时复合支架上的贴壁细胞更多一些;④扫描电镜显示,细胞在两种材料上生长形态良好,并紧密黏附于支架表面及微孔附近,同时可见分泌的细胞外基质呈丝状包绕于细胞周围;⑤结果表明,3D打印技术制备的聚己内酯/纳米羟基磷灰石复合支架孔隙较丰富,具备良好的力学性能,细胞相容性良好,可作为骨组织工程的支架材料。ORCID: 0000-0002-7083-6458(胡超然)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: