| [1]Kwan PO, Tredget EE. Biological Principles of Scar and Contracture. Hand Clin. 2017;33(2):277-292.[2]Alster TS,Tanzi EL.Hypertrophic scars and keloids: etiology and management. Am J Clin Dermatol.2003; 4(4):235-243.[3]Butzelaar L, Ulrich MMW, Mink vd MAB, et al.Currently known risk factors for hypertrophic skin scarring: A review. J Plast Reconstr Aes.2016; 69(2):163-169.[4]Butzelaar L, Soykan EA, Garre F, et al. Going into surgery: Risk factors for hypertrophic scarring. Wound Repair Regen. 2015; 23(4):531-537.[5]Matheny RW,Adamo ML.Current Perspectives on Akt Akt-ivation and Akt-ions.Exp Biol Med.2009; 234(11): 1264-1270.[6]Patel P, Sekiguchi Y, Oh KH, et al. Smad3-dependent and -independent pathways are involved in peritoneal membrane injury. Kidney Int.2010;77(4):319-328.[7]Baimei L, Yang L, Li W, et al. RNA-seq-based analysis of the hypertrophic scarring with and without pressure therapy in a Bama minipig model. Sci Rep-UK.2018; 8(1): 11831-11841.[8]农晓琳,邓凌,李佳荃,等. bFGF、TGFβ1在人皮肤病理性瘢痕不同时期的表达及意义[J].广西医科大学学报, 2010, 27(2): 180-183.[9]周鹏军,王琼,李张军,等. 光动力疗法对兔耳增生性瘢痕组织中MMP-9,MMP-13和TIMP-1的影响[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2013,27(9):877-880.[10]蔡景龙.现代瘢痕学[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,1999.[11]Deitch EA, Wheelahan TM, Rose MP, et al. Hypertrophic burn scars: analysis of variables. J Trauma.1983;23(10): 895-898.[12]Beldon P. Abnormal scar formation in wound healing. Nursing Times.2000;96(10):44-45.[13]Bayat A, McGrouther DA, Ferguson MW. Skin scarring. Brit Med J.2003;326(7380): 88-92.[14]Kwan PO, Tredget EE. Biological principles of scar and contracture. Hand Clinics.2017; 33(2): 277-292.[15]Slemp AE, Kirschner RE. Keloids and scars: a review of keloids and scars, their pathogenesis, risk factors, and management. Curr Opin Pediatr.2006;18(4): 396-402.[16]Niessen FB, Spauwen PH, Schalkwijk J, et al. On the nature of hypertrophic scars and keloids: a review [J]. Plast Reconstr Surg.1999; 104(5): 1435-1458.[17]Ehrlich HP, Desmoulière A, Diegelmann RF, et al. Morphological and immunochemical differences between keloid and hypertrophic scar. Am J Pathol.1994;145(1): 105-113.[18]Schneider M, Meites E, Daane SP. Keloids: Which treatment is best for your patient?.J Fam Practice. 2013; 62(5):227-33.[19]南美兰,金哲虎,金承龙.4-HPR对瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞ProcollagenⅠ、MMP-1及信号通路P13K/Akt的影响[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2018,32(3):245-251.[20]Jalali M, Bayat A.Current use of steroids in management of abnormal raised skin scars.Am Surgeon.2007; 5(3):175-180.[21]Leventhal D, Furr M, Reiter D. Treatment of Keloids and Hypertrophic Scars: A Meta-analysis and Review of the Literature. Arch Facial Plast Surg.2006; 8(6):362-368.[22]李荟元,鲁开化,郭树忠.新编瘢痕学[M].西安:第四军医大学出版社, 2003.[23]van der Veer WM, Bloemen MC, Ulrich MM, et al. Potential cellular and molecular causes of hypertrophic scar formation. Burns, 2009, 35(1):15-29.[24]王配合. γδT细胞、IGF-1及Akt与增生性瘢痕相关研究[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学,2011.[25]陈伟,付小兵,孙同柱,等.增生性瘢痕中磷酸化 P38 丝裂原活化蛋白激酶和 c-Jun蛋白的表达特征及其与瘢痕形成的关系[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2003, 17(5):379-381.[26]Lin N, Moroi Y, Uchi H, et al. Significance of the expression of phosphorylated-STAT3, -Akt, and -ERK1/2 in several tumors of the epidermis. J Dermatol Sci.2007;48(1):71-73.[27]刘剑毅,李世荣. PI3K/AKT 信号通路在CTGF促人增生性瘢痕成纤维细胞转分化中的作用[J].中国美容医学杂志, 2008, 17(3): 395-397.[28]Paterno J, Vial IN, Wong VW, et al. Akt-mediated mechanotransduction in murine fibroblasts during hypertrophic scar formation. Wound Repair Regen, 2011, 19(1): 49-58.[29]An G,Liang SZ,Sheng CH,et al.Upregulation of microRNA-205 suppresses vascular endothelial growth factor expression-mediated PI3K/Akt signaling transduction in human keloid fibroblasts. Eep Biol Med.2017;242(3):1-11.[30]Lee JP, Li YC, Chen HY, et al. Protective effects of luteolin against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury involves inhibition of MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in neutrophils.Acta Pharmacologica Sinica.2010; 31(7):831-838.[31]Hu XL, Wang HT, Liu JQ, et al. The role of ERK and JNK signaling in connective tissue growth factor induced extracellular matrix protein production and scar formation. Arch Dermatol Res.2013; 305(5):433-445.[32]Lee SJ,Namkoong S,Kim YM,et al.Fractalkine stimulates angiogenesis by activating the Raf/MEK/ERK-and PI3K/Akt/eNOS-dependent signal pathways .AmJ Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2006;291(6):2836-2846[33]Bullard LE,Qi X,Penn JS. Role for extracellular signal-responsive kinase -1 and -2 in retinal angiogenesis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2003; 44(4):1722-1731.[34]任萱,林莉萍,丁健.微管抑制剂C9抑制新生血管生成的作用机制[J].中国新药杂志, 2011,20(17):1703-1710[35]王芳,唐旭华,周晖. 分子靶向抗肿瘤药物的皮肤不良反应及处理[J]. 中华皮肤科杂志,2016,49(7):519-523.[36]Shetlar MR, Shetlar CL, Hendricks L, et al. The use of athymic nude mice for the study of human keloids. Exp Biol Med.1985; 179(4): 549-552.[37]Kischer CW, Pindur J, Shetlar MR, et al. Implants of hypertrophic scars and keloids into the nude (athymic) mouse: viability and morphology. J Trauma.1989; 29(5): 672-677.[38]Morris DE, Wu L, Zhao LL, et al. Acute and chronic animal models for excessive dermal scarring: quantitative studies. Plast Reconstr Surg.1997;100(3): 674-681.[39]李荟元,刘建波,兰海.建立增生性瘢痕动物实验模型[J].第四军医大学学报, 1998,19: 655-657.[40]李荟元,刘建波,夏炜,等.增生性瘢痕动物实验模型的建立与应用[J].中华整形外科杂志, 2001,17(5):276-278.[41]陈俊颖. 人与巴马香猪皮肤的比较生物学研究[J].中国比较医学杂志,2006,16(5):288-290.[42]Mitra A, Leyes A, Manser K, et al. Use of Minipig Skin Biopsy Model as an Innovative Tool to Design Topical Formulation to Achieve Desired Pharmacokinetics in Humans. J Pharm Sci-US.2015; 104(5):1701-1708.[43]Bai X, He T, Liu J, et al. Loureirin B inhibits fibroblast proliferation and extracellular matrix deposition in hypertrophic scar via TGF-\r, β\r, /Smad pathway. Exp Dermatol.2015; 24(5):355-360.[44]马娜,郭瑞珍,阮媛,等.PI3K-AKT-Bcl-2抗凋亡途径与瘢痕癌癌细胞凋亡相关性探讨[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2014, 21(8):599-604.[45]李菲菲,米立国,隋鸿锦.血管内皮生长因子对皮肤血管生成影响的研究进展[J].大连医科大学学报,2009, 31(5):599-603.[46]行敏,赵凤梅,吴洁,等. CO2点阵激光联合紫草治疗增生性瘢痕临床疗效及对血清中VEGF的影响[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志, 2018,32(1):110-114.[47]李学锋,李道萍,王慧君. 小鼠皮肤创伤愈合过程中VEGF、TGF-β1、bFGF表达的免疫组织化学研究[J]. 中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志, 2003,12(4):367-371.[48]Bao P, Kodra A, Tomic-Canic M, et al. The Role of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Wound Healing. J Surg Res. 2009;153(2):347-358[49]Labler L,Rancan M,Mica L,et al.Vacuum-assisted closure therapy increases local interleukin-8 and vascular endothelial growth factor levels in traumatic wounds.J Trauma Nurs.2009; 66(66): 749-757[50]Erba P, Ogawa R, Ackermann M, et al. Angiogenesis in wounds treated by microdeformational wound therapy. Ann Surg.2011; 253(2): 402-409.[51]Zhu KQ, Engrav LH, Armendariz R, et al. Changes in VEGF and nitric oxide after deep dermal injury in the female, red Duroc pig—further similarities between female, Duroc scar and human hypertrophic scar. Burns.2005; 31(1):0-10.[52]刘晓彤,沈若武,卞明心,等.大鼠创伤皮肤组织VEGF、PDGF和bFGF表达及意义[J].青岛大学医学院学报, 2016,52(2): 209-211. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
PI3K/AKT信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3Ks)信号参与体内细胞的增殖、分化、凋亡和葡萄糖转运等多种生理功能,近年来发现IA型PI3K和下游分子蛋白激酶B(PKB或Akt)组成的信号途径与人类皮肤瘢痕组织形成的关系密切。
MEK/ERK信号通路:胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinase,ERK)是丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)家族的一员,它的信号传递途径是涉及调节细胞生长、发育及分裂的信号网络的核心,其基本的信号传递步骤遵循Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK途径。
文题释义:
PI3K/AKT信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3Ks)信号参与体内细胞的增殖、分化、凋亡和葡萄糖转运等多种生理功能,近年来发现IA型PI3K和下游分子蛋白激酶B(PKB或Akt)组成的信号途径与人类皮肤瘢痕组织形成的关系密切。
MEK/ERK信号通路:胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinase,ERK)是丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)家族的一员,它的信号传递途径是涉及调节细胞生长、发育及分裂的信号网络的核心,其基本的信号传递步骤遵循Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK途径。.jpg) 文题释义:
PI3K/AKT信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3Ks)信号参与体内细胞的增殖、分化、凋亡和葡萄糖转运等多种生理功能,近年来发现IA型PI3K和下游分子蛋白激酶B(PKB或Akt)组成的信号途径与人类皮肤瘢痕组织形成的关系密切。
MEK/ERK信号通路:胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinase,ERK)是丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)家族的一员,它的信号传递途径是涉及调节细胞生长、发育及分裂的信号网络的核心,其基本的信号传递步骤遵循Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK途径。
文题释义:
PI3K/AKT信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3Ks)信号参与体内细胞的增殖、分化、凋亡和葡萄糖转运等多种生理功能,近年来发现IA型PI3K和下游分子蛋白激酶B(PKB或Akt)组成的信号途径与人类皮肤瘢痕组织形成的关系密切。
MEK/ERK信号通路:胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinase,ERK)是丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)家族的一员,它的信号传递途径是涉及调节细胞生长、发育及分裂的信号网络的核心,其基本的信号传递步骤遵循Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK途径。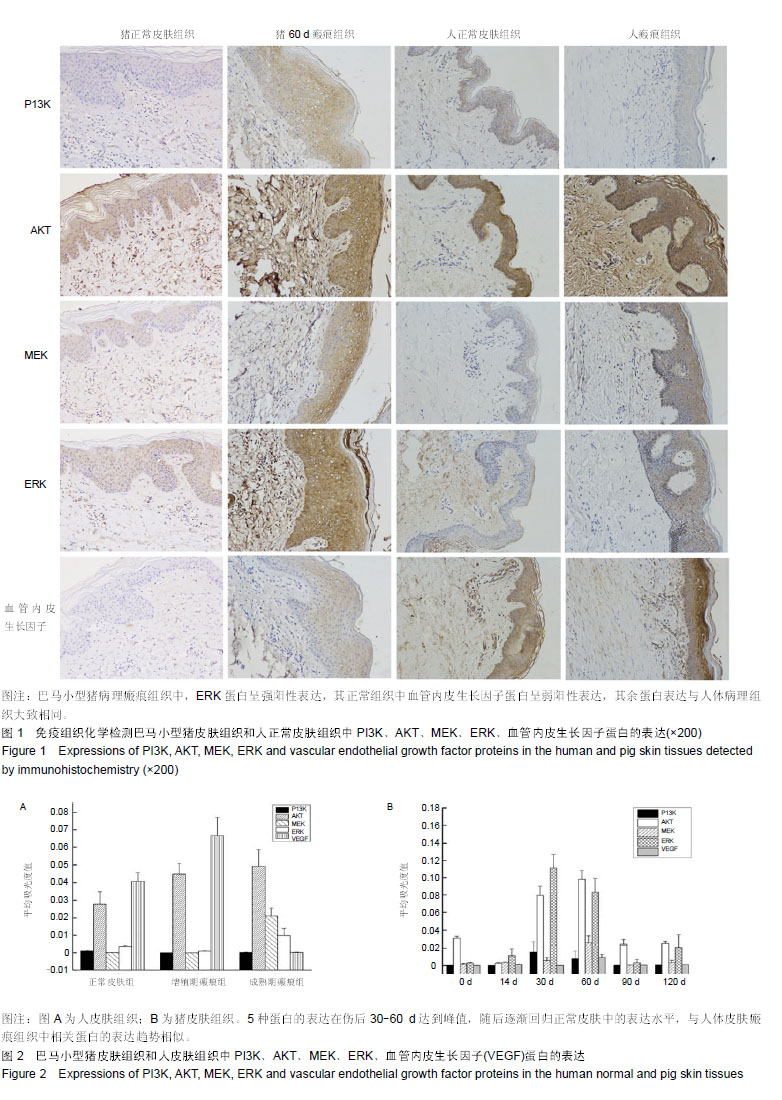
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
PI3K/AKT信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3Ks)信号参与体内细胞的增殖、分化、凋亡和葡萄糖转运等多种生理功能,近年来发现IA型PI3K和下游分子蛋白激酶B(PKB或Akt)组成的信号途径与人类皮肤瘢痕组织形成的关系密切。
MEK/ERK信号通路:胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinase,ERK)是丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)家族的一员,它的信号传递途径是涉及调节细胞生长、发育及分裂的信号网络的核心,其基本的信号传递步骤遵循Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK途径。
文题释义:
PI3K/AKT信号通路:磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3Ks)信号参与体内细胞的增殖、分化、凋亡和葡萄糖转运等多种生理功能,近年来发现IA型PI3K和下游分子蛋白激酶B(PKB或Akt)组成的信号途径与人类皮肤瘢痕组织形成的关系密切。
MEK/ERK信号通路:胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinase,ERK)是丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MAPK)家族的一员,它的信号传递途径是涉及调节细胞生长、发育及分裂的信号网络的核心,其基本的信号传递步骤遵循Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK途径。