中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (23): 3680-3685.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1313
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
干预Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对硬皮病模型小鼠皮肤组织纤维化及上皮间质转化的影响
刘金娟1,杨宏发2,李勇坚1,陈艳明1
- (南华大学附属第二医院,1皮肤性病科,2心血管内科,湖南省衡阳市 421001)
Effects of the intervention of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway on skin tissue fibrosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in mouse models of scleroderma
Liu Jinjuan1, Yang Hongfa2, Li Yongjian1, Chen Yanming1
- (1Department of Dermatology & Sexually Transmitted Diseases, 2Department of Cardiovasology, the Second Hospital of University of South China, Hengyang 421001, Hunan Province, China)
摘要:
.jpg) 文题释义:
Wnt信号通路:1982年在小鼠乳腺癌发现了Wnt基因,由于此基因激活依赖小鼠乳腺癌相关病毒基因的插入,因此,当时被命名为Int1基因,之后的研究表明,Int1基因在小鼠正常胚胎发育中起重要作用,相当于果蝇的无翅(Wingless)基因,可控制胚胎的轴向发育。此后大量研究提示了Int1基因在神经系统胚胎发育中的重要性,因此将Wingless与Int1结合,称为Wnt基因。人Wnt基因定位于12q13.在胚胎发育中,Wnt基因调控的重要信号传导系统即为Wnt通路,是一类广泛存在于无脊椎和脊椎动物中且进化上高度保守的信号通路,在机体发育、生长、疾病、衰老及死亡等生理病理过程中具有至关重要的作用。研究已证实,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路广泛参与心、肺、肝、肾等器官纤维化疾病的发病过程。
羟脯氨酸:是胶原中特有的氨基酸,是胶原组织的主要成分之一,约占胶原氨基酸总量的13%。利用其是胶原所特有的特点,通过分析羟脯氨酸含量,可以了解机体胶原蛋白代谢情况。
文题释义:
Wnt信号通路:1982年在小鼠乳腺癌发现了Wnt基因,由于此基因激活依赖小鼠乳腺癌相关病毒基因的插入,因此,当时被命名为Int1基因,之后的研究表明,Int1基因在小鼠正常胚胎发育中起重要作用,相当于果蝇的无翅(Wingless)基因,可控制胚胎的轴向发育。此后大量研究提示了Int1基因在神经系统胚胎发育中的重要性,因此将Wingless与Int1结合,称为Wnt基因。人Wnt基因定位于12q13.在胚胎发育中,Wnt基因调控的重要信号传导系统即为Wnt通路,是一类广泛存在于无脊椎和脊椎动物中且进化上高度保守的信号通路,在机体发育、生长、疾病、衰老及死亡等生理病理过程中具有至关重要的作用。研究已证实,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路广泛参与心、肺、肝、肾等器官纤维化疾病的发病过程。
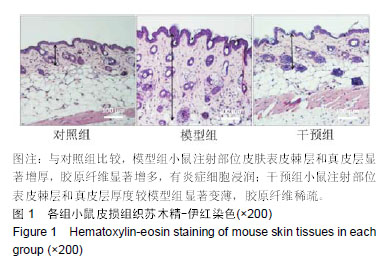
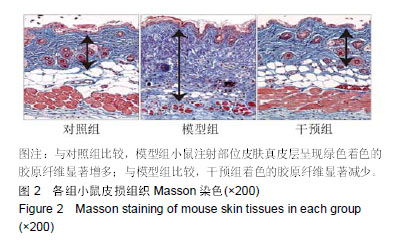
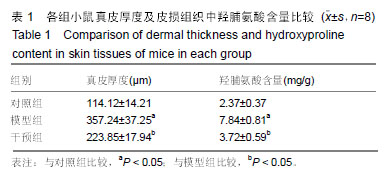
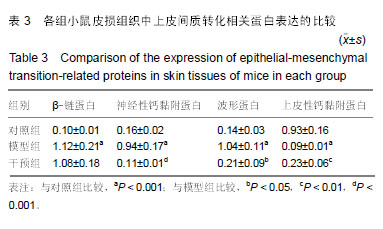
羟脯氨酸:是胶原中特有的氨基酸,是胶原组织的主要成分之一,约占胶原氨基酸总量的13%。利用其是胶原所特有的特点,通过分析羟脯氨酸含量,可以了解机体胶原蛋白代谢情况。摘要 背景:研究证实,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在系统性硬化症的发生发展中起着重要作用,然而有关抑制Wnt/β-catenin抑制患者皮损信号是否改善硬皮病的报道较少。 目的:探究抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对硬皮病小鼠皮肤组织纤维化及上皮间质转化的影响。 方法:选取雌性BALB/c小鼠24只,购自长沙市天勤生物技术有限公司。实验方案经南华大学动物实验伦理委员会批准。随机将24只BALB/c小鼠均分为3组:对照组背部皮下注射生理盐水;模型组和干预组采用背部注射博来霉素500 mg/L建立硬皮病小鼠模型;干预组同时腹腔注射5 mg/kg的IGC-001(Wnt/ β-catenin信号通路抑制剂),1次/d,连续注射4周。麻醉后取各组小鼠背部注射区皮肤,采用苏木精-伊红和Masson染色,观察皮损组织病理学变化、胶原纤维分布和真皮厚度;采用水解法检测皮损组织羟脯氨酸含量;Western blot检测皮损组织中β-链蛋白(β-catenin)、Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、纤维链接蛋白、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、上皮性钙黏附蛋白、波形蛋白和神经性钙黏附蛋白的表达。 结果与结论:①博来霉素连续皮下注射4周后,模型组大鼠注射区域真皮层明显增厚、胶原纤维明显增多;干预组真皮层较模型组明显变薄,胶原纤维明显减少;②与对照组比较,模型组皮损组织中羟脯氨酸含量及Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、纤维链接蛋白、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、波形蛋白、神经性钙黏蛋白和β-链蛋白表达量显著增加(均P < 0.05),上皮性钙黏附蛋白表达显著降低(P < 0.05);与模型组比较,干预组皮损组织中羟脯氨酸含量及Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、纤维链接蛋白、α-平滑肌肌动蛋白、波形蛋白和神经性钙黏蛋白表达量显著降低(均P < 0.05),上皮性钙黏附蛋白表达显著增加(P < 0.05),β-链蛋白表达无显著性变化(P > 0.05);③结果说明,抑制Wnt/β-catenin信号通路可抑制硬皮病小鼠皮肤组织纤维化,其机制可能与抑制皮肤组织上皮间质转化有关。
中图分类号:


.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
Wnt信号通路:1982年在小鼠乳腺癌发现了Wnt基因,由于此基因激活依赖小鼠乳腺癌相关病毒基因的插入,因此,当时被命名为Int1基因,之后的研究表明,Int1基因在小鼠正常胚胎发育中起重要作用,相当于果蝇的无翅(Wingless)基因,可控制胚胎的轴向发育。此后大量研究提示了Int1基因在神经系统胚胎发育中的重要性,因此将Wingless与Int1结合,称为Wnt基因。人Wnt基因定位于12q13.在胚胎发育中,Wnt基因调控的重要信号传导系统即为Wnt通路,是一类广泛存在于无脊椎和脊椎动物中且进化上高度保守的信号通路,在机体发育、生长、疾病、衰老及死亡等生理病理过程中具有至关重要的作用。研究已证实,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路广泛参与心、肺、肝、肾等器官纤维化疾病的发病过程。
羟脯氨酸:是胶原中特有的氨基酸,是胶原组织的主要成分之一,约占胶原氨基酸总量的13%。利用其是胶原所特有的特点,通过分析羟脯氨酸含量,可以了解机体胶原蛋白代谢情况。
文题释义:
Wnt信号通路:1982年在小鼠乳腺癌发现了Wnt基因,由于此基因激活依赖小鼠乳腺癌相关病毒基因的插入,因此,当时被命名为Int1基因,之后的研究表明,Int1基因在小鼠正常胚胎发育中起重要作用,相当于果蝇的无翅(Wingless)基因,可控制胚胎的轴向发育。此后大量研究提示了Int1基因在神经系统胚胎发育中的重要性,因此将Wingless与Int1结合,称为Wnt基因。人Wnt基因定位于12q13.在胚胎发育中,Wnt基因调控的重要信号传导系统即为Wnt通路,是一类广泛存在于无脊椎和脊椎动物中且进化上高度保守的信号通路,在机体发育、生长、疾病、衰老及死亡等生理病理过程中具有至关重要的作用。研究已证实,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路广泛参与心、肺、肝、肾等器官纤维化疾病的发病过程。
羟脯氨酸:是胶原中特有的氨基酸,是胶原组织的主要成分之一,约占胶原氨基酸总量的13%。利用其是胶原所特有的特点,通过分析羟脯氨酸含量,可以了解机体胶原蛋白代谢情况。