中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 566-571.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2206
• 纳米生物材料 nanobiomaterials • 上一篇 下一篇
磁性靶向纳米粒体外多模态成像及对肝星状细胞的靶向作用
李 璇1,鲁 敏2,李明星1,敖 梦3,4,唐琳梅1,曾 祯1,胡经纬1,黄志强1,宣吉晴1
- 1西南医科大学附属第一医院超声科;2重庆医科大学附属第三医院放射科;3重庆医科大学超声影像学研究所;4重庆医科大学附属第二医院超声科
In vitro multi-modal imaging of magnetic targeted nanoparticles and their targeting effect on hepatic stellate cells
Li Xuan1, Lu Min2, Li Mingxing1, Ao Meng3, 4, Tang Linmei1, Zeng Zhen1, Hu Jingwei1, Huang Zhiqiang1, Xuan Jiqing1
- 1Department of Ultrasound, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University; 2Department of Radiology, The Third Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University; 3Institute of Ultrasound Imaging, Chongqing Medical University; 4Department of Ultrasound, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University
摘要:
文题释义:
多模态成像:随着分子影像学的飞速发展,多模态成像改变了传统单一的成像方式,联合超声、CT、MRI、光声及SPECT等各自独特的成像优势,只使用一种对比剂即可获得多种模态增强显影,同时得到疾病的解剖学、分子学及功能学信息。这对疾病的诊断、受检者的健康及减少医疗资源浪费都有重要意义。
寻靶:通过对微泡外壳进行改建,将特异性配体结合或连接到微泡表面,这些微泡可通过血液循环聚到特定的病变组织上,并长时间停留于靶组织或靶器官,从而达到使病变组织在影像中得到特异性的标记增强或局部靶向治疗作用的目的。
背景:近来年,分子成像结合医学影像技术和靶向分子探针逐渐成为研究的热点,其相互结合能够在分子水平对靶组织进行观察,从而实现对疾病的发生、发展实时无创成像。
目的:制备载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒探针,探讨其体外超声/CT/MRI成像效果,观察其体外对大鼠肝星状细胞的靶向能力。
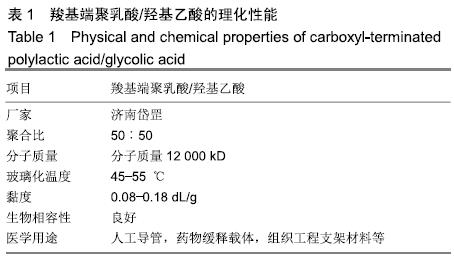
方法:以高分子材料聚乳酸/羟基乙酸作为外壳、含有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列环八肽作为配体,通过双步乳化法制备包载磁性颗粒和全氟辛溴烷的载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒cRGD-PLGA-Fe3O4-PFOB,检测其理化性质。将载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒以双蒸水稀释为不同质量浓度的混悬液,体外观察其超声、CT、MRI显影效果。通过碳二亚胺法连接精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列肽与载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒,验证载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒的精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列连接情况和体外靶向能力。细胞毒性实验测定不同质量浓度载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒对大鼠肝细胞BRL-3A的毒性作用。
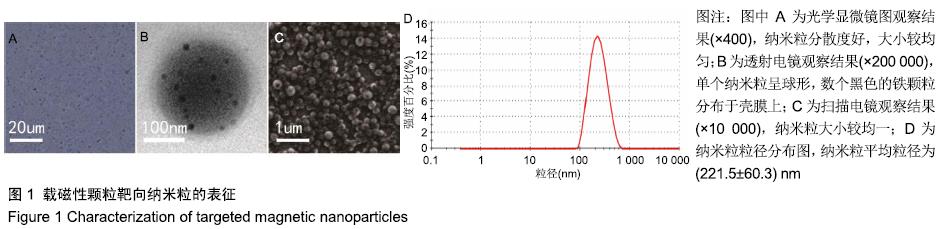
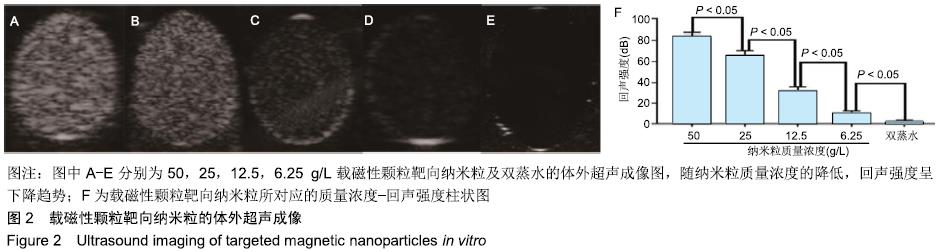
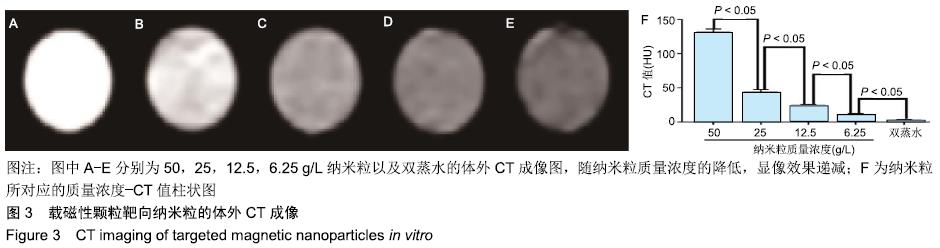
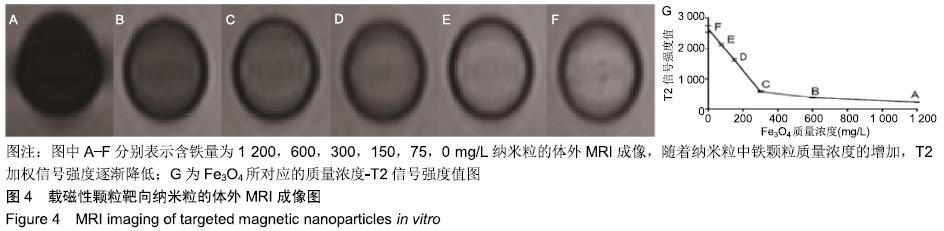
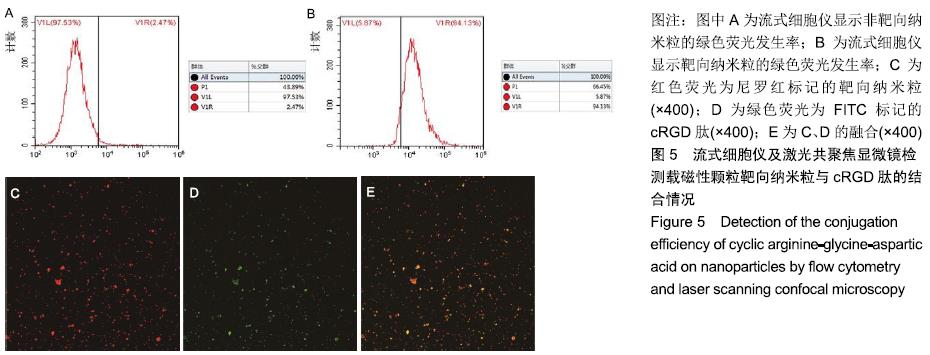
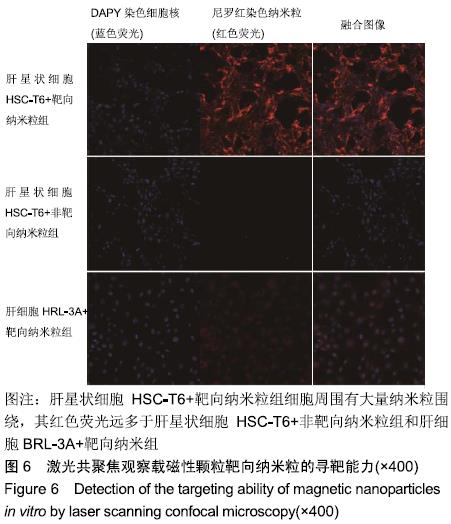
结果与结论:①载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒分散度好,大小较均匀,单个纳米粒呈球形,数个黑色的铁颗粒分布于壳膜上,平均粒径为(221.5±60.3) nm,Fe3O4包封率为38%;②随着载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒质量浓度的降低,样品的超声回声强度、CT值均逐渐降低;随着纳米粒中Fe3O4颗粒质量浓度的增加,MRI T2加权信号强度逐渐降低;③流式细胞仪检测显示,含有精氨酸-甘氨酸-天冬氨酸序列环八肽与载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒的连接率为94.13%;体外靶向实验显示,大部分载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒聚集于大鼠肝星状细胞细胞HSC-T6周围;④不同质量浓度的载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒对大鼠肝细胞BRL-3A活力无影响;⑤结果表明,载磁性颗粒靶向纳米粒探针不仅能作为多模态显像剂用于超声、CT、MRI,且在体外实验中对大鼠肝星状细胞有较强的靶向能力,对肝纤维化的早期诊断具有重大应用潜力。ORCID: 0000-0001-8470-8548(李璇)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: