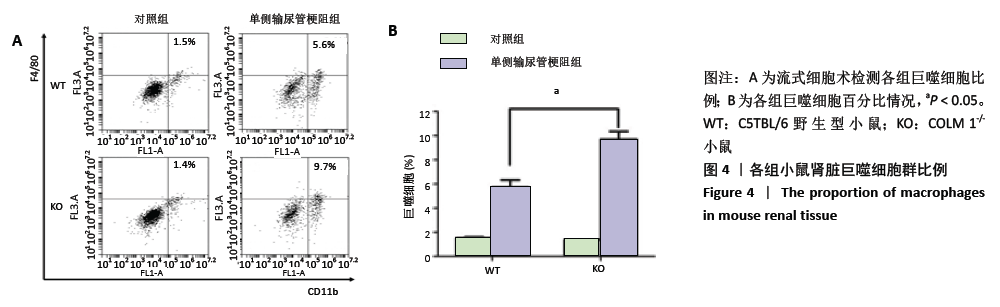
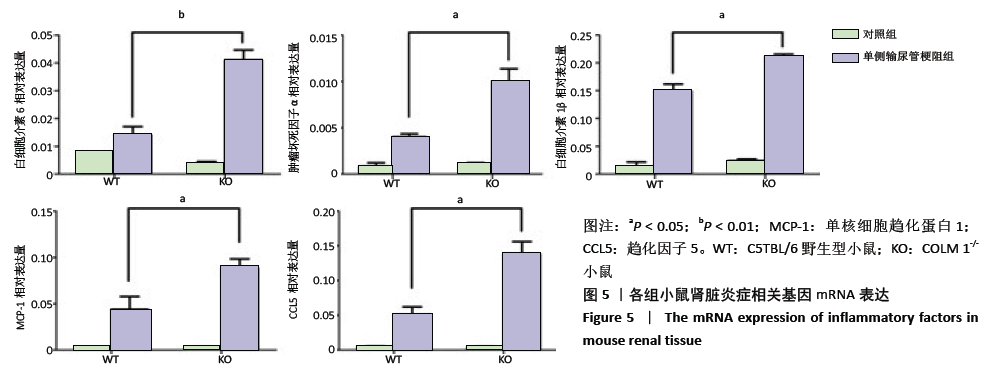
[1] HUMPHREYS BD. Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2018;80:309-326.
[2] WEBSTER AC, NAGLER EV, MORTON RL, et al. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2017;389(10075):1238-1252.
[3] ROMAGNANI P, REMUZZI G, GLASSOCK R, et al. Chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17088.
[4] RUIZ-ORTEGA M, RAYEGO-MATEOS S, LAMAS S, et al. Targeting the progression of chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16:269-288.
[5] NOGUEIRA A, PIRES MJ, OLIVEIRA PA. Pathophysiological mechanisms of renal fibrosis: a review of animal models and therapeutic strategies. In Vivo. 2017;31(1):1-22.
[6] CHEVALIER RL, FORBES MS, THORNHILL BA. Ureteral obstruction as a model of renal interstitial fibrosis and obstructive nephropathy. Kidney International. 2009;75(11):1145-1152.
[7] KLADNEY RD, BULLA GA, GUO L, et al. GP73, a novel Golgi-localized protein upregulated by viral infection. Gene. 2000;249(1-2):53-65.
[8] JIANG K, LI W, ZHANG Q, et al. GP73 N-glycosylation at Asn144 reduces hepatocellular carcinoma cell motility and invasiveness. Oncotarget. 2016;7(17):23530-23541.
[9] HU L, YAO W, WANG F, et al. GP73 is upregulated by Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) infection and enhances HCV secretion. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(3): e90553.
[10] YANG L, LUO P, SONG Q, et al. DNMT1/miR-200a/GOLM1 signaling pathway regulates lung adenocarcinoma cells proliferation. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;99:839-847.
[11] ALLAM MA, ELTIBY DM, NASSAR Y, et al. Studying the value of golgi protein 73 as a serum marker in hepatocellular carcinoma versus alfa feto protein. Nature and Science. 2016;14(1):126-129.
[12] KOJIMA S, ENOKIDA H, YOSHINO H, et al. The tumor-suppressive microRNA-143/145 cluster inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting GOLM1 in prostate cancer. J Hum Genet. 2014;59(2):78-87.
[13] YANG S, ZENG C, FANG X, et al, Hepatitis B virus upregulates GP73 expression by activating the HIF-2α signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2018; 15(4):5264-5270.
[14] YE Q, ZHU W, ZHANG J, et al. GOLM1 modulates EGFR/RTK cell-surface recycling to drive hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:444-458.
[15] LIU Y, ZHANG X, ZHOU S, et.al. Knockdown of Golgi phosphoprotein 73 blocks the trafficking of matrix metalloproteinase‐2 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and inhibits cell invasion. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(4): 2399-2409.
[16] YANG X, WEI C. LIU N, et al. GP73, a novel TGF-β target gene, provides selective regulation on Smad and non-Smad signaling pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019;1866(4):588-597.
[17] ZHANG X, ZHU C, WANG T, et al. GP73 represses host innate immune response to promote virus replication by facilitating MAVS and TRAF6 degradation. PLoS Pathogens. 2017;13(4):e1006321.
[18] LIU Y, LIEWEN H, MARKULY M, et al. A review of GOLPH2, an oncogenic protein and novel therapeutic options for GOLPH2 driven tumours. J Translat Sci. 2019;6:1-4.
[19] YANG H, LIU G, LIU B, et al. GP73 promotes invasion and metastasis of bladder cancer by regulating the epithelial–mesenchymal transition through the TGF‐β1/Smad2 signalling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2018; 22(3):1650-1665.
[20] XU R, JI J, ZHANG X, et al. PDGFA/PDGFR α-regulated GOLM1 promotes human glioma progression through activation of AKT. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36(1):193.
[21] DING X, DENG G, LIU J, et al. GOLM1 silencing inhibits the proliferation and motility of human glioblastoma cells via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Brain Res. 2019;1717:117-126.
[22] YAN G, RU Y, WU K, GOLM1 promotes prostate cancer progression through activating PI3K‐AKT‐mTOR signaling. Prostate. 2018;78(3): 166-177.
[23] LI XM, CAO LL. Identification of GOLM1 as a Positively Regulator of Tumor Metastasis by Regulating MMP13 in Gastric Carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2019;26(4):421-430.
[24] ZHANG W, KIM H, LV J, et al. Golgi phosphoprotein 2 is a novel regulator of IL-12 production and macrophage polarization. J Immunol. 2018;200(4):1480-1488.
[25] LIU Y. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7(12):684-696.
[26] PILLING D, FAN T, HUANG D, et al. Identification of markers that distinguish monocyte-derived fibrocytes from monocytes, macrophages, and fibroblasts. PLoS One. 2009;4(10):e7475.
[27] DISTLER JHW, GYÖRFI A, RAMANUJAM M, et al. Shared and distinct mechanisms of fibrosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15:705-730.
[28] NOGUEIRA A, PORES MJ, OLIVEIRA P. Pathophysiological mechanisms of renal fibrosis: a review of animal models and therapeutic strategies. In Vivo. 2017;31(1):1-22.
[29] BLACK LM, LEVER JM, AGARWAL A. Renal Inflammation and Fibrosis: A Double-edged Sword. J Histochem Cytochem. 2019;67(9):663-681.
[30] HUEN SC, Cantley LG. Macrophages in Renal Injury and Repair. Annu Rev Physiol. 2017;79:449-469.
[31] KLUTH DC. Pro-resolution properties of macrophages in renal injury. Kidney Int. 2007;72(3):234-236.
[32] Huang L, Wang AM, Hao Y, et al. Macrophage Depletion Lowered Blood Pressure and Attenuated Hypertensive Renal Injury and Fibrosis. Front Physiol. 2018;9:473.
[33] MARTÍNEZ-KLIMOVA E, APARICIO-TREJO OE, TAPIA E, et al. Unilateral ureteral obstruction as a model to investigate fibrosis-attenuating treatments. Biomo- lecules. 2019;9(4):141.
[34] TANG PM, NIKOLIC-PATERSON DJ, LAN H. Macrophages: versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019; 15(3):144-158.
[35] LU H, WU L, LIU L.Quercetin ameliorates kidney injury and fibrosis by modulating M1/M2 macrophage polarization. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018;154:203-212.
[36] Sato Y, Yanagita M. Immune cells and inflammation in AKI to CKD progression.Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2018;315:F1501-F1512.
[37] LV W, BOOZ GW, WANG Y, et al. Inflammation and renal fibrosis: recent developments on key signaling molecules as potential therapeutic targets. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;820:65-76.
[38] GRANDE MT, PÉREZ-BARRIOCANAL F, LÓPEZ-NOVOA JM. Role of inflammation in túbulo-interstitial damage associated to obstructive nephropathy.J Inflamm (Lond). 2010;7:19.
[39] LIANG H, XU F, WEN X, et al.Interleukin-33 signaling contributes to renal fibrosis following ischemia reperfusion. Eur J Pharmacol. 2017;812:18-27.
[40] MAEL-AININ M, ABED A, CONWAY SJ, et al. Inhibition of periostin expression protects against the development of renal inflammation and fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25(8):1724-1736.
[41] WRIGHT LM, YONG S, PICKEN MM, et al. Decreased survival and hepato-renal pathology in mice with c-terminally truncated GP73 (GOLPH2).Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2009;2(1):34-47.
|