| [1]赵长霖,彭琦,谢汉平.ECM,MMP与角膜结构和角膜损伤修复[J].国际眼科杂志,2006,6(1):173-177.[2]Zeng Y, Yang J, Huang K, et al. A comparison of biomechanical properties between human and porcine cornea. J Biomech. 2001;34(4): 533-537.[3]Nguyen TD, Jones RE, Boyce BL. A nonlinear anisotropic viscoelastic model for the tensile behavior of the corneal stroma. J Biomech Eng. 2008;130(4):041020. [4]Elsheikh A, Alhasso D. Mechanical anisotropy of porcine cornea and correlation with stromal microstructure. Exp Eye Res. 2009;88(6): 1084-1091. [5]田磊.在体角膜生物力学测量方法的建立与临床应用及京尼平兔角膜交联的初步研究[D].北京:解放军医学院,2014.[6]Raiskup F, Spoerl E. Corneal crosslinking with riboflavin and ultraviolet A. I. Principles. Ocul Surf. 2013;11(2):65-74. [7]Wittig-Silva C, Chan E, Islam FM, et al. A randomized, controlled trial of corneal collagen cross-linking in progressive keratoconus: three-year results. Ophthalmology. 2014;121(4):812-821. [8]Zhou L, Sawaguchi S, Twining SS, et al. Expression of degradative enzymes and protease inhibitors in corneas with keratoconus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1998;39(7):1117-1124.[9]金敏,李君文,王忠彦.微生物胶原酶研究进展[J].氨基酸和生物资源,2003, 25(1):3-8.[10]Ravanti L, Heino J, López-Otín C, et al. Induction of collagenase-3 (MMP-13) expression in human skin fibroblasts by three-dimensional collagen is mediated by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1999;274(4):2446-2455.[11]Mandl I. Collagenase. Science. 1970;169(3951):1234-1238.[12]Barrett AJ, Knight CG, Brown MA, et al. A continuous fluorimetric assay for clostridial collagenase and Pz-peptidase activity. Biochem J. 1989; 260(1):259-263.[13]Gonulalan EM, Nemutlu E, Demirezer LO. A new perspective on evaluation of medicinal plant biological activities: The correlation between phytomics and matrix metalloproteinases activities of some medicinal plants. Saudi Pharm J. 2019;27(3):446-452.[14]Nascimento GG, Baelum V, Timo Sorsa T, et al. Salivary levels of MPO, MMP-8 and TIMP-1 are associated with gingival inflammation response patterns during experimental gingivitis. Cytokine. 2019;115:135-141.[15]Hernández M, Gamonal J, Salo T, et al. Reduced expression of lipopolysaccharide-induced CXC chemokine in Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced experimental periodontitis in matrix metalloproteinase-8 null mice. J Periodontal Res. 2011;46(1):58-66. [16]Åström P, Juurikka K, Hadler-Olsen ES, et al. The interplay of matrix metalloproteinase-8, transforming growth factor-β1 and vascular endothelial growth factor-C cooperatively contributes to the aggressiveness of oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2017;117(7):1007-1016.[17]Vandenbroucke RE, Dejonckheere E, Van Lint P, et al. Matrix metalloprotease 8-dependent extracellular matrix cleavage at the blood-CSF barrier contributes to lethality during systemic inflammatory diseases. J Neurosci. 2012;32(29):9805-9816.[18]Sakimoto T, Ohnishi T, Ishimori A. Simultaneous study of matrix metalloproteinases, proinflammatory cytokines, and soluble cytokine receptors in the tears of noninfectious corneal ulcer patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2014;252(9):1451-1456. [19]Du GL, Chen WY, Li XN, et al. Induction of MMP?1 and ?3 by cyclical mechanical stretch is mediated by IL?6 in cultured fibroblasts of keratoconus. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(6):3885-3892. [20]Robert MC, Arafat SN, Spurr-Michaud S, et al. Tear Matrix Metalloproteinases and Myeloperoxidase Levels in Patients With Boston Keratoprosthesis Type I. Cornea. 2016;35(7):1008-1014.[21]Maymon E, Romero R, Pacora P, et al. Human neutrophil collagenase (matrix metalloproteinase 8) in parturition, premature rupture of the membranes, and intrauterine infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2000; 183(1):94-99.[22]Gutiérrez-Fernández A, Inada M, Balbín M, et al. Increased inflammation delays wound healing in mice deficient in collagenase-2 (MMP-8). FASEB J. 2007;21(10):2580-2591.[23]Rohini G, Murugeswari P, Prajna NV, et al. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-8, MMP-9) and the tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMP-1, TIMP-2) in patients with fungal keratitis. Cornea. 2007;26(2):207-211.[24]Hanemaaijer R, Sorsa T, Konttinen YT, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-8 is expressed in rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Regulation by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and doxycycline. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(50):31504-31509.[25]Bian F, Wang C, Tukler-Henriksson J, et al. MMP-8 Is Critical for Dexamethasone Therapy in Alkali-Burned Corneas Under Dry Eye Conditions. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(11):2506-2516. [26]金鑫,刘素素,贺司宇,等.基质金属蛋白酶-8对角膜基质胶原的作用研究[J].重庆医学,2017,46(30):4187-4189.[27]汪倩,王琳琳,张妍,等.角膜生物力学特性的测量方法研究现状[J].国际眼科杂志,2016,16(10):1840-1846.[28]张海霞,李林,张昆亚,等.兔眼角膜生物力学特性的年龄相关性[J].医用生物力学,2014,29(3):271-275.[29]Zhang H, Khan MA, Zhang D, et al. Corneal Biomechanical Properties after FS-LASIK with Residual Bed Thickness Less Than 50% of the Original Corneal Thickness. J Ophthalmol. 2018;2018:2752945. [30]张海霞,张迪,秦晓,等.角膜生物力学特性研究进展[J].科技导报,2018, 36(13):23-29.[31]Wang X, Li X, Chen W, et al. Effects of ablation depth and repair time on the corneal elastic modulus after laser in situ keratomileusis. Biomed Eng Online. 2017;16(1):20. [32]Liu X, Wang L, Ji J, et al. A mechanical model of the cornea considering the crimping morphology of collagen fibrils. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55(4):2739-2746. [33]赵云阁,欧尔比特•安尼瓦尔,祝诚.细胞外基质与基质金属蛋白酶[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,1999,26(3):223-227.[34]王晓君,陈维毅,李晓娜,等.周期性机械拉伸对兔角膜成纤维细胞MMP-2/ TIMP-2及TGF-β1表达的影响[J].太原理工大学学报,2012,43(6):770-774.[35]黄丽,项敏泓,张兴儒.基质金属蛋白酶及其抑制剂在眼表疾病发病机制研究中的进展[J].国际眼科纵览,2017,41(1):32-37.[36]Bian F, Wang C, Tukler-Henriksson J, et al. MMP-8 Is Critical for Dexamethasone Therapy in Alkali-Burned Corneas Under Dry Eye Conditions. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231(11):2506-2516. [37]唐维强,柳林.基质金属蛋白酶与角膜病变[J].国际眼科杂志,2004,4(1): 120-124.[38]Wang A, Chen W, He R, et al. Experimental study on corneal biomechanical properties of rabbit eye after LASIK. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2009;26(2):323-326.[39]王红燕,肖博,楚艳华,等.微创核黄素-紫外线A巩膜胶原交联对巩膜生物力学强度的增强作用及安全性[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2018,36(2):96.[40]Zheng X, Wang Y, Zhao Y, et al. Experimental Evaluation of Travoprost-Induced Changes in Biomechanical Behavior of Ex-Vivo Rabbit Corneas. Curr Eye Res. 2018. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2018.1516781. [Epub ahead of print][41]Elsheikh A, Wang D, Pye D. Determination of the modulus of elasticity of the human cornea. J Refract Surg. 2007;23(8):808-818.[42]Qiao J, Li H, Tang Y, et al. A rabbit model of corneal Ectasia generated by treatment with collagenase type II. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018;18(1):94. [43]Rose JS, Eldrina J, Joshua A, et al. Objective quantification of corneal haziness using anterior segment optical coherence tomography. J Curr Ophthalmol. 2017;30(1):54-57. [44]Meek KM, Knupp C. Corneal structure and transparency. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015;49:1-16. [45]Scietti L, Chiapparino A, De Giorgi F, et al. Molecular architecture of the multifunctional collagen lysyl hydroxylase and glycosyltransferase LH3. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):3163.[46]Hong CW, Sinha-Roy A, Schoenfield L, et al. Collagenase-mediated tissue modeling of corneal ectasia and collagen cross-linking treatments. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53(4):2321-2327. [47]Wang X, Huang Y, Jastaneiah S, et al. Protective Effects of Soluble Collagen during Ultraviolet-A Crosslinking on Enzyme-Mediated Corneal Ectatic Models. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0136999. [48]乔静,李海丽,宋文静,等.Ⅱ型胶原酶构建兔角膜离体扩张模型[J].中华眼视光学与视觉科学杂志,2016,18(5):275-279. |
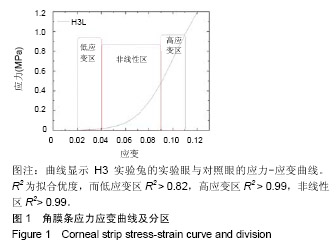
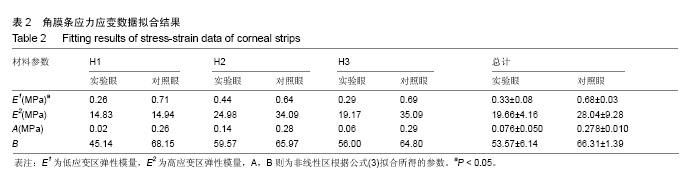
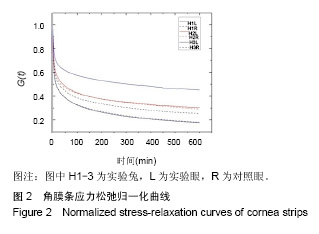
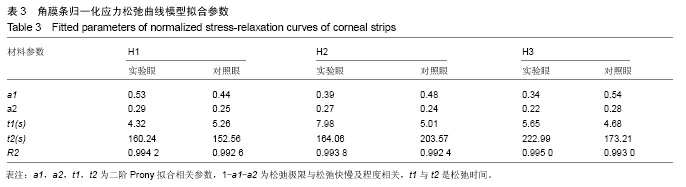
.jpg)
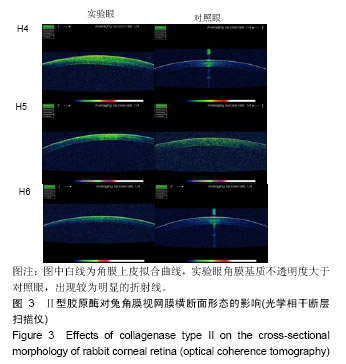
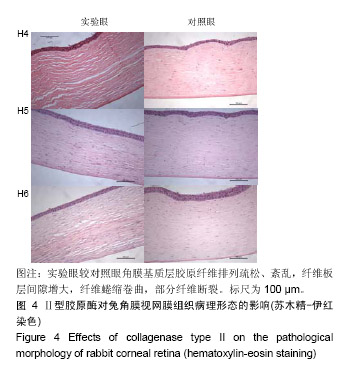


.jpg)