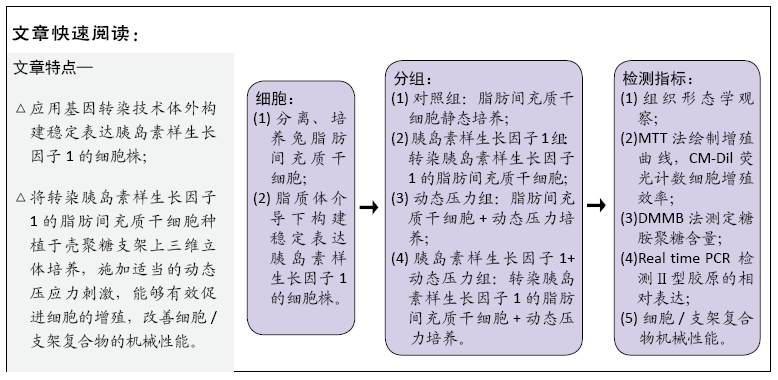
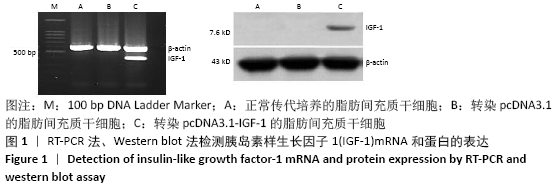
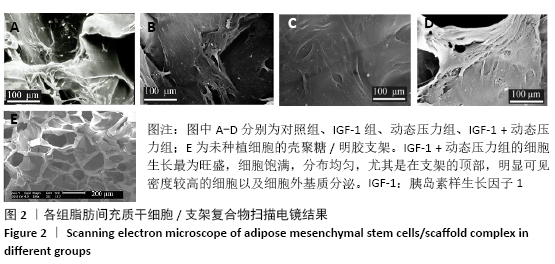
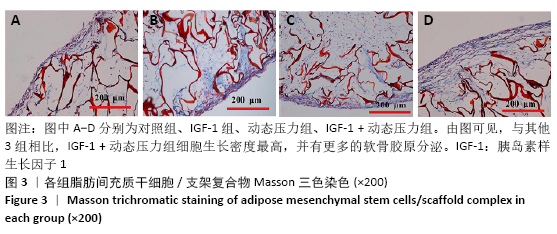
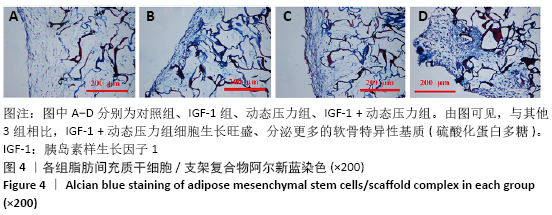
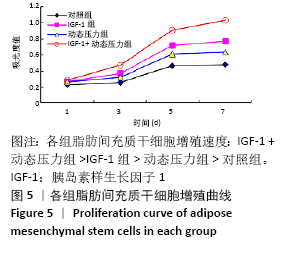
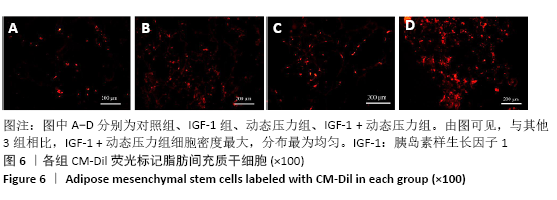
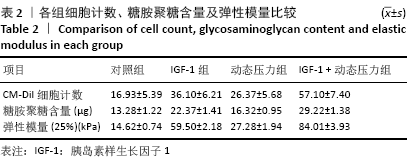
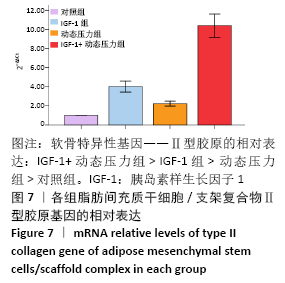
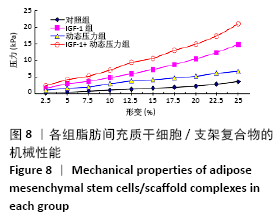
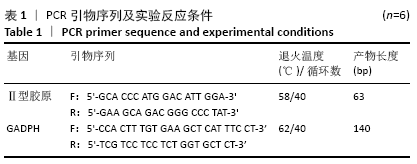
[1] ROSADI I, KARINA K, ROSLIANA I, et al. In vitro study of cartilage tissue engineering using human adipose-derived stem cells induced by platelet-rich plasma and cultured on silk fibroin scaffold. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019; 10(1):369.
[2] BONASSAR LJ, GRODZINSKY AJ, FRANK EH, et al. The effect of dynamic compression on the response of articular cartilage to insulin-like growth factor-I. J Orthop Res. 2001;19(1):11-17.
[3] BRYANT SJ, NICODEMUS GD, VILLANUEVA I. Designing 3D photopolymer hydrogels to regulate biomechanical cues and tissue growth for cartilage tissue engineering. Pharm Res. 2008;25(10):2379-2386.
[4] YANG J, ZHANG Y, ZANG G, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells improve erectile function partially through the secretion of IGF-1, bFGF, and VEGF in aged rats. Andrology. 2018;6(3):498-509.
[5] OH SJ, CHOI KU, CHOI SW, et al. Comparative Analysis of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells and Their Secretome for Auricular Cartilage Regeneration. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:8595940.
[6] ROBALLO KCS, DA SILVEIRA JC, BRESSAN FF, et al. Neurons-derived extracellular vesicles promote neural differentiation of ADSCs: a model to prevent peripheral nerve degeneration. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):11213.
[7] MORSCHEID S, REY-RICO A, SCHMITT G, et al. Therapeutic Effects of rAAV-Mediated Concomittant Gene Transfer and Overexpression of TGF-β and IGF-I on the Chondrogenesis of Human Bone-Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(10):2591.
[8] 杨强,丁晓明,徐宝山,等.取向性丝素蛋白支架复合脂肪干细胞体外构建组织工程软骨[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(12):1235-1242.
[9] AN C, CHENG Y, YUAN Q, et al. IGF-1 and BMP-2 induces differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells into chondrocytes-like cells. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38(4):1647-1654.
[10] 张传辉,杨军,李建军.调控脂肪间充质干细胞成软骨分化基因Sox-9和低氧诱导因子1α的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(45):6766-6773.
[11] WANG X, ZHANG J, CUI W, et al. Composite Hydrogel Modified by IGF-1C Domain Improves Stem Cell Therapy for Limb Ischemia. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(5):4481-4493.
[12] 赵永亮,冯军宇,王刚,等.周期性动态压力对海藻酸钠培养间充质干细胞成软骨分化的作用[J/CD].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2016,10(4): 413-418.
[13] OKUBO R, ASAWA Y, WATANABE M, et al. Proliferation medium in three-dimensional culture of auricular chondrocytes promotes effective cartilage regeneration in vivo. Regen Ther. 2019;11:306-315.
[14] SAWATJUI N, LIMPAIBOON T, SCHROBBACK K, et al. Biomimetic scaffolds and dynamic compression enhance the properties of chondrocyte- and MSC-based tissue-engineered cartilage. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018; 12(5):1220-1229.
[15] 张传辉,杨军,李建军,等.兔脂肪干细胞体外构建组织工程软骨:负载胰岛素样生长因子1基因的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(28):5131-5135.
[16] PRAXENTHALER H, KRÄMER E, WEISSER M, et al. Extracellular matrix content and WNT/β-catenin levels of cartilage determine the chondrocyte response to compressive load. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018; 1864(3):851-859.
[17] 张云松,高建华,鲁峰,等.荧光活性染料DiI标记人脂肪干细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(15):2897-2899.
[18] 王一兵,张芮,冯永强,等.羰花青荧光染料示踪在大鼠胚胎皮肤成纤维细胞移植中的应用[J].中华医学杂志,2009,89(14):986-989.
[19] AZIZ AH, ECKSTEIN K, FERGUSON VL, et al. The effects of dynamic compressive loading on human mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis in the stiff layer of a bilayer hydrogel. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(6):946-959.
[20] 余晓明,孟昊业,孙振,等.生物反应器中的力学刺激促进组织工程软骨再生[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(2):185-190.
[21] ANDERSON DE, JOHNSTONE B. Dynamic Mechanical Compression of Chondrocytes for Tissue Engineering: A Critical Review. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2017;5:76.
[22] KOZHEMYAKINA E, LASSAR AB, ZELZER E. A pathway to bone: signaling molecules and transcription factors involved in chondrocyte development and maturation. Development. 2015;142(5):817-831.
[23] CHEN CH, KUO CY, CHEN JP. Effect of Cyclic Dynamic Compressive Loading on Chondrocytes and Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Co-Cultured in Highly Elastic Cryogel Scaffolds. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(2):370.
[24] JIMI E, FEI H, NAKATOMI C. NF-κB Signaling Regulates Physiological and Pathological Chondrogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6275.
[25] YAN C, WANG Y, SHEN XY, et al. MicroRNA regulation associated chondrogenesis of mouse MSCs grown on polyhydroxyalkanoates. Biomaterials. 2011;32(27): 6435-6444.
[26] AKIYAMA H. Transcriptional regulation in chondrogenesis by Sox9. Clin Calcium. 2011;21(6):845-851.
[27] 李昆朋,张雯,李忠,等.动态压应力促进软骨前体干细胞Sox9 和细胞外基质表达[J].中华生物医学工程杂志,2016,22(3):189-193.
[28] ZHANG Y, TANG CL, CHEN WJ, et al. Dynamic compression combined with exogenous SOX-9 promotes chondrogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in PLGA scaffold. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015;19(14):2671-2678.
|