中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (15): 2394-2399.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3798
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
髋关节置换中短柄假体置入位置差别的力学分析
李咏壑1,王献抗2,孟 昱2,刘 璐2,张春秋1,叶金铎1
- 1天津市先进机电系统设计与智能控制重点实验室,机电工程国家级实验教学示范中心,天津理工大学机械工程学院,天津市 300384;2天津市骨植入物界面功能化与个性研究企业重点实验室,嘉思特华剑医疗器材(天津)有限公司,天津市 300190
Mechanical analysis on the position difference of short-stemmed prosthesis in hip arthroplasty
Li Yonghe1, Wang Xiankang2, Meng Yu2, Liu Lu2, Zhang Chunqiu1, Ye Jinduo1
- 1Tianjin Key Laboratory of Advanced Electromechanical System Design and Intelligent Control, National Experimental Teaching Demonstration Center of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, School of Mechanical Engineering, Tianjin University of Technology, Tianjin 300384, China; 2Key Laboratory of Tianjin Bone Implant Interface Functionalization and Personality Research Enterprise, Just Huajian Medical Device(Tianjin) Co., Ltd., Tianjin 300190, China
摘要:
文题释义:
髋关节置换:通过用模拟人体髋关节结构的假体置换病损的关节来达到消除髋关节病痛、恢复关节功能目的的手术,是人工髋关节成形术中最常用的方法,已经发展成为治疗髋关节疾病的重要方法。
短柄假体:常见的股骨柄根据长短可以分为短柄假体和中长柄假体,长久以来中长假体柄一直占据市场的主要份额,但随着微创理念的发展,短柄假体被提出,其具有手术截骨量少、手术方便、便于翻修的独特优势,成为髋关节置换假体的新选择。
背景:近年来,全髋关节置换的应用使大多患者初期都获得了满意的疗效,但临床上全髋置换后的并发症仍然是困扰医生和患者的一大难题,假体置入位置的优良成为评估置换效果的重要方面。
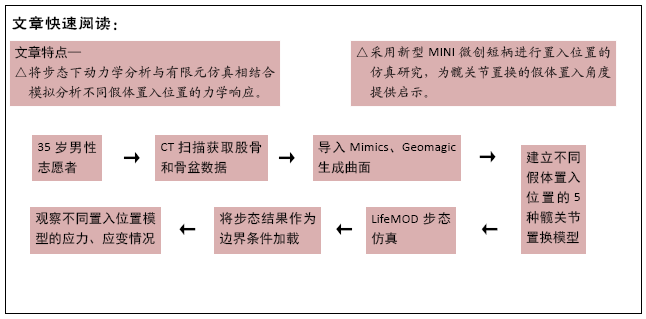
目的:探究短柄假体不同置入位置对全髋关节置换效果的影响,为临床手术实施提供启示。
方法:利用人体动力学软件进行完整周期的步态仿真,获得髋关节的承力条件;模拟短柄假体不同置入位置,即人体力线位置以及内、外偏3°,5°位置,建立其相应的全髋关节置换三维有限元模型,分析不同全髋关节置换模型中股骨、短柄的应力变化以及聚乙烯内衬的应变变化情况。
结果与结论:①步态下髋关节的关节力和角度随时间呈周期性变化,约1.17 s为一个周期,在0.4 s左右关节合力达到峰值约700 N;②无论内外偏角度的大小,股骨小转子下方以及底端外侧的应力值均高于人体力线位置时的应力,内偏比外偏对股骨应力的影响更大;③股骨短柄的最大拉压应力在人体力线位时均比内、外偏时的应力值低;④以人体力线位为参考,聚乙烯内衬的最大压应变在外偏3°时最小,为 2 198 με;其他角度时的最大压应变均比人体力线位时大,其中内偏5°时最大达到了7 348 με,是人体力线时的2.08倍,此角度下会加剧内衬的磨损;⑤提示在全髋关节置换过程中,不同假体置入位置会对股骨、假体和内衬的力学环境产生很大影响,在术中应该尽量保证假体处在与人体力线重合的位置。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2927-1184 (李咏壑)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: