中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (15): 2400-2404.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3807
• 骨科植入物 orthopedic implant • 上一篇 下一篇
多孔钽棒治疗ARCO Ⅰ-Ⅱ期非创伤性股骨头坏死后塌陷及相关因素分析
苏敬阳1,张耀杰1,曹 斌1,郝学伟1,李 晓1,韩永台2
- 1石家庄市第一医院骨科,河北省石家庄市 050000;2河北医科大学第三医院,河北省石家庄市 050000
Analysis of collapse and related factors in the treatment of ARCO I-II non-traumatic necrosis of femoral head with porous tantalum rod
Su Jingyang1, Zhang Yaojie1, Cao Bin1, Hao Xuewei1, Li Xiao1, Han Yongtai2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital of Shijiazhuang City, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China; 2Third Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
多孔钽金属:又称为“骨小梁金属”,系将纯钽以化学蒸汽沉积、渗透的方法结合到由聚亚安酯前体热降解所得到的碳骨架上,从而得到与松质骨相类似的金属多孔结构,微孔隙率可达75%-80%,孔隙直径平均约430 µm。多孔钽棒具有人类松质骨相似的弹性模量及应力传导能力,同时具有良好的细胞亲和力及组织相容性。
股骨头坏死:又称为股骨头缺血性坏死或股骨头无菌性坏死,是由不同病因破坏了股骨头血供引起骨细胞死亡及随后的修复,继而发生股骨头内骨小梁断裂,若不及时治疗,80%以上的患者将在4年内出现股骨头塌陷和骨性关节炎,5%-12%的患者需行人工全髋关节置换。
背景:多孔钽棒植入联合髓芯减压治疗早期非创伤性股骨头坏死具有较好的临床效果,但治疗后仍有股骨头塌陷病例的报道,其发生率为2%-56%。
目的:探讨多孔钽棒植入治疗ARCOⅠ-Ⅱ期非创伤性股骨头坏死后股骨头塌陷情况及其影响因素。
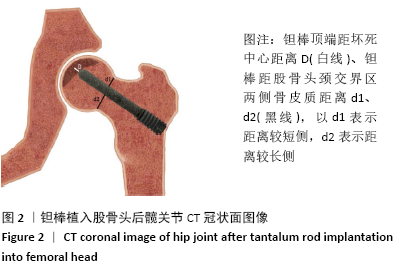
方法:回顾性分析2014年5月至2018年4月石家庄市第一医院收治的ARCOⅠ-Ⅱ期非创伤性股骨头坏死患者的病历资料,77例患者均接受多孔钽棒植入治疗,其中男58例,女19例,年龄22-58岁,术后随访观察股骨头塌陷情况。记录患者性别、年龄、股骨头坏死病因、侧别、坏死区位置、范围、ARCO分期、钽棒植入位置(钽棒顶端与坏死中心距离、钽棒与股骨头颈交界区两侧骨皮质距离比值)等临床及手术资料,对临床及手术资料进行单因素分析,采用二元多因素Logistic回归分析筛选出多孔钽棒治疗ARCOⅠ-Ⅱ期非创伤性股骨头坏死后塌陷的独立影响因素。研究获得石家庄第一医院伦理委员会批准(批准号:201403011)。
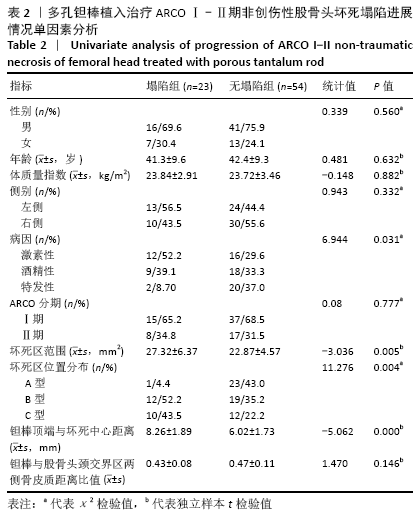
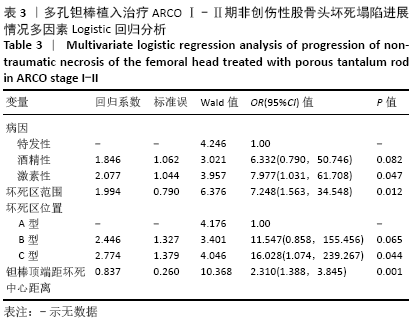
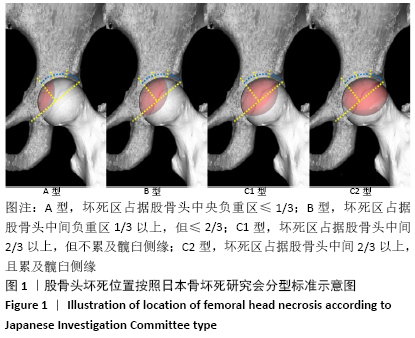
结果与结论:①77例患者术后获得3-60个月的随访,其中股骨头塌陷23例,无塌陷54例;②单因素分析显示,塌陷组与无塌陷组性别、年龄、病变侧别、ARCO分期、钽棒顶端与股骨头颈交界区两侧骨皮质距离比值差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),两组股骨头坏死病因、坏死范围、坏死位置分布及钽棒顶端与坏死中心位置距离间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);③二元多因素Logisitic回归分析显示,激素性股骨头坏死、坏死区范围、坏死区位置为C1型和钽棒顶端距坏死中心距离是影响多孔钽棒治疗ARCOⅠ-Ⅱ期非创伤性股骨头坏死后塌陷的独立影响因素[OR=7.977,95%CI(1.031,61.708),P=0.047;OR=7.248,95%CI(1.563,34.548),P=0.012;OR=16.028,95%CI(1.074,239.267),P=0.044;OR=2.310,95%CI(1.388,3.845),P=0.001];④结果表明,多孔钽棒植入治疗ARCOⅠ-Ⅱ期非创伤性股骨头坏死术后短期临床效果较好,激素性股骨头坏死、坏死范围、坏死位置及钽棒顶端距坏死中心距离是多孔钽棒治疗ARCOⅠ-Ⅱ期非创伤性股骨头坏死后塌陷的独立影响因素。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5235-0668 (苏敬阳)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: