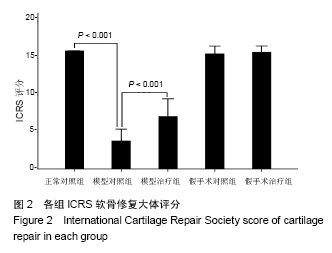
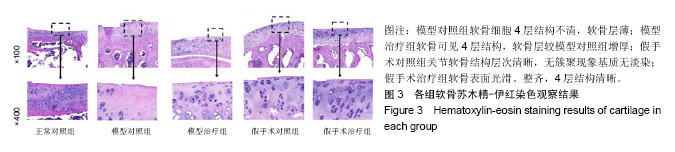
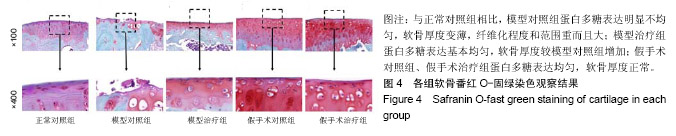
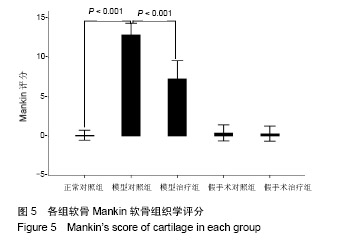
| [1] Yuan GH,Masukohongo K,Kato T,et al.Immunologic intervention in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010; 48(3):602-611. [2] 韩廷成,周临东,董松林.中医外治法治疗膝骨关节炎的现状与分析[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2012,21(5):566-568. [3] Gaudin-Audrain C,Irwin N,Mansur S,et al.Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor deficiency leads to modifications of trabecular bone volume and quality in mice. Bone. 2013;53(1):221-230. [4] Shimazu-Kuwahara S,Kanemaru Y,Harada N,et al. Glucose- dependent insulinotropic polypeptide deficiency reduced fat accumulation and insulin resistance, but deteriorated bone loss in ovariectomized mice.J Diabetes Investig.2018. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12978. [Epub ahead of print] [5] Kieffer TJ,McIntosh CH,Pederson RA.Degradation of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and truncated glucagon-like peptide 1 in vitro and in vivo by dipeptidyl peptidase iv. Endocrinology. 1995;136(8):3585-3596. [6] Usdin TB,Mezey E,Button DC,et al.Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor, a member of the secretin-vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor family, is widely distributed in peripheral organs and the brain.Endocrinology.1993;133(6):2861-2870. [7] Joo E,Harada N,Yamane S,et al.Inhibition of gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor signaling in adipose tissue reduces insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in high-fat diet-fed mice. Diabetes. 2017;66(4):868-879. [8] Nasteska D,Harada N,Suzuki K,et al.Chronic reduction of gip secretion alleviates obesity and insulin resistance under high-fat diet conditions.Diabetes.2014;63(7):2332-2343. [9] Torekov SS,Harsløf T,Rejnmark L,et al. A functional amino acid substitution in the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) gene is associated with lower bone mineral density and increased fracture risk.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(4):E729-733. [10] Holst JJ,Windelov JA,Boer GA,et al.Searching for the physiological role of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide.J Diabetes Investig.2016;7 Suppl 1:8-12. [11] Mieczkowska A,Irwin N,Flatt PR,et al.Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (gip) receptor deletion leads to reduced bone strength and quality.Bone.2013;56(2):337-342. [12] Mai X,Lu Z,Lei Z,et al.Phosphorylation of osteopontin in osteoarthritis degenerative cartilage and its effect on matrix metalloprotease 13.Rheumatol Int.2013;33(5):1313-1319. [13] Wayne JS,Mcdowell CL,Shields KJ,et al.In vivo response of polylactic acid-alginate scaffolds and bone marrow-derived cells for cartilage tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part A. 2005; 11(5-6):953-963. [14] Mankin HJ,Dorfman H,Lippiello L,et al.Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. Ii. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data.B J Bone Joint Surg Am.1971; 53(3):523-537. [15] 姜旭,吴成爱,王莹,等.膝关节骨性关节炎中wisp-1调控机制的研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(5):537-540. [16] Xu M,Zhang L,Zhao L,et al. Phosphorylation of osteopontin in osteoarthritis degenerative cartilage and its effect on matrix metalloprotease 13.Rheumatol Int.2013;33(5):1313-1319. [17] Li Y,Lin T,Duan Y,et al.Upregulation of mmp-13 and timp-1 expression in response to mechanical strain in mc3t3-e1 osteoblastic cells.Bmc Res Notes.2010;3(1):309. [18] Mieczkowska A,Bouvard B,Chappard D,et al.Glucose- dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (gip) directly affects collagen fibril diameter and collagen cross-linking in osteoblast cultures. Bone. 2015;74:29-36. [19] Mabilleau G,Mieczkowska A,Irwin N,et al.Beneficial effects of a n-terminally modified gip agonist on tissue-level bone material properties.Bone.2014;63:61-68. [20] 余洁,许岭翎.肠促胰素与骨代谢[J].中华糖尿病杂志, 2017,9(3): 200-202. [21] 吴松,石俊俊,卫定禄,等.Dala2gip对淀粉样前体蛋白/早老素1转基因小鼠膝关节软骨损伤保护效应的研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2017,34(11):1861-1864. [22] 邓莉,王海波.膝骨性关节炎动物模型的研究进展[J].广东医学, 2018,56(12):1895-1897 [23] Duffy AM,Hölscher C.The incretin analogue d-ala 2 gip reduces plaque load, astrogliosis and oxidative stress in an app/ps1 mouse model of alzheimer’s disease.Neuroscience.2013; 228: 294-300. [24] 李保驰,王维山,董金波,等. MMP3、MMP13在骨性关节炎患者滑膜中的表达及意义[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2014,20(6):593-596. [25] 包刚,刘永,刘亚丽,等.MMP-13在骨性关节炎滑膜组织中的表达分析[J].中国实验诊断学, 2016,20(9):1548-1549. [26] Hughes A,Oxford AE,Tawara K,et al.Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in cartilage pathophysiology; contributing factors to apoptosis and osteoarthriti. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3).pii: E665.doi:10.3390/ijms18030665. [27] Li NG,Shi ZH,Tang YP,et al. New hope for the treatment of osteoarthritis through selective inhibition of MMP-13.Curr Med Chem.2011;18(7):977-1001. [28] Phull AR,Eo SH,Abbas Q,et al. Applications of chondrocyte- based cartilage engineering: An overview. BioMed Res Int. 2016;2016(2):1879837. [29] Bollag R,Zhong Q, Ding K, et al. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide is an integrative hormone with osteotropic effects. Mol Cell Endocrinol.2001;177(1-2):35-41. [30] Zhong Q,Ding KH,Mulloy AL,et al.Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide stimulates proliferation and tgf-beta release from mg-63 cells.Peptides.2003;24(4):611-616. [31] Howard S,Anastassiades T.Differential effects of bone associated factors on newly synthesized anionic glycoconjugates by articular chondrocyte cultures from adult and immature bovines.J Rheumatol. 1993;20(12):2083-2094. |
.jpg)

.jpg)
.jpg)