中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (15): 2308-2313.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1175
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
静压力下牙周膜成纤维细胞分泌炎性因子与p38信号通路的关系
唐海芳1,2,3,4,彭娟敏1,2,3,4,康 娜1,2,3,4
- (1广西医科大学附属口腔医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;2广西口腔颌面修复与重建研究自治区级重点实验室,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;3广西颅颌面畸形临床医学研究中心,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021;4颌面外科疾病诊治研究重点实验室(广西高校重点实验室),广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021)
Relationship between p38 signaling pathway and periodontal ligament fibroblasts secreting inflammatory factors under static pressure
Tang Haifang1, 2, 3, 4, Peng Juanmin1, 2, 3, 4, Kang Na1, 2, 3, 4
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
细胞静压力:是一种细胞的体外力学,通过重力加载装置,于单层细胞上放置一片盖玻片,再在玻片上加载重物,通过玻片传递,使细胞承受均匀单一的压应力。该装置设计简单,操作方便,却能使单层细胞顶-底向单向受力,力值可靠,且细胞体外培养环境不受其影响,静压力加载时间不受限制。
p38 MAPK:属于应激性蛋白激酶,在G蛋白偶联受体、应力刺激、炎症因子等作用下可激活p38 MAPK,活化的p38 MAPK从胞质进入胞核内,为应激条件下的炎症反应、细胞免疫调节、细胞凋亡过程的做出应答。p38 MAPK通路信号通路与炎症反应及其分泌调控机制关系密切,是哺乳动物细胞信号通路中的经典途径,趋化因子、炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子、环氧合酶2等的产生都有赖于p38通路的调控。
.jpg)
文题释义:
细胞静压力:是一种细胞的体外力学,通过重力加载装置,于单层细胞上放置一片盖玻片,再在玻片上加载重物,通过玻片传递,使细胞承受均匀单一的压应力。该装置设计简单,操作方便,却能使单层细胞顶-底向单向受力,力值可靠,且细胞体外培养环境不受其影响,静压力加载时间不受限制。
p38 MAPK:属于应激性蛋白激酶,在G蛋白偶联受体、应力刺激、炎症因子等作用下可激活p38 MAPK,活化的p38 MAPK从胞质进入胞核内,为应激条件下的炎症反应、细胞免疫调节、细胞凋亡过程的做出应答。p38 MAPK通路信号通路与炎症反应及其分泌调控机制关系密切,是哺乳动物细胞信号通路中的经典途径,趋化因子、炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子、环氧合酶2等的产生都有赖于p38通路的调控。
摘要
背景:研究表明p38 MAPK通路在炎症因子的合成中起到重要作用,但对正畸牙移动过程牙周膜成纤维细胞中p38 MAPK信号通路与白细胞介素17、白细胞介素6等炎性因子关系的相关报道较少。
目的:分析人牙周膜成纤维细胞加载持续性静压力后在合成炎症因子白细胞介素6、白细胞介素17过程与p38 MAPK的关系,探讨p38 MAPK信号通路对白细胞介素17和白细胞介素6表达的影响。
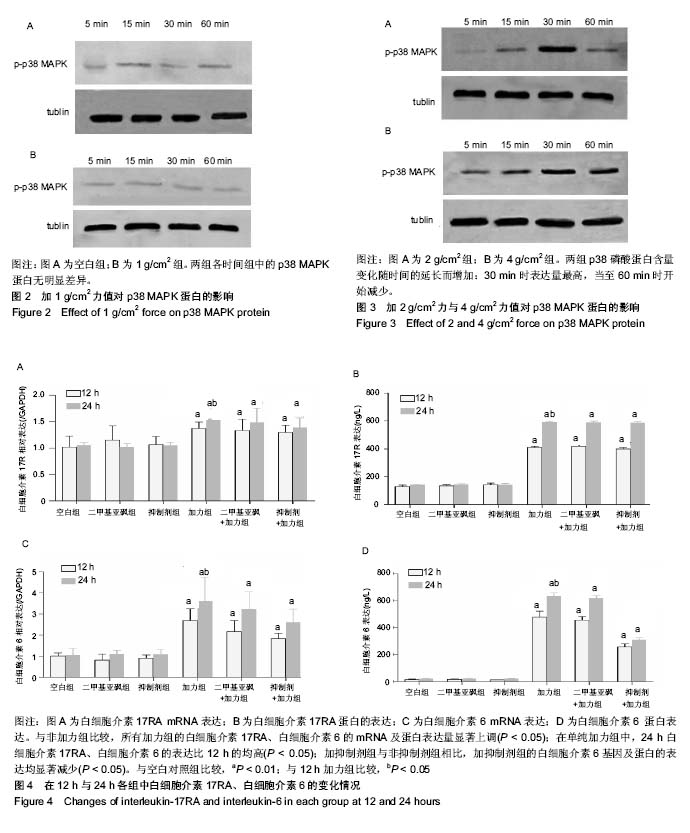
方法:①取年龄在11-15岁正畸者需要拔除的新鲜第一、二前磨牙的牙周组织(正畸者及其监护人均知情同意),体外培养牙周膜成纤维细胞,建立细胞重力加载模型;②细胞种板,分别加力0,1,2,4 g/cm2,每加力组分别加力5,15,30和60 min,检测p38 MAPK蛋白表达;③取第4代细胞接种后,随机分为6组:空白组、加二甲基亚砜组、加抑制剂组(p38 MAPK阻断剂SB203580)、加力组、加力+二甲基亚砜组、加力+抑制剂组,对细胞预处理60 min,通过定量RT-qPCR和酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测牙周膜成纤维细胞受4 g/cm2压力刺激后白细胞介素17和白细胞介素6的mRNA和蛋白水平。
结果与结论:①2 g/cm2组、4 g/cm2组p38 MAPK磷酸化蛋白表达变化随时间的延长而增加:30 min时表达量最高,60 min时开始减少;②与未加力的3组相比,加力组的白细胞介素17和白细胞介素6表达量上调,加抑制剂组的白细胞介素6表达量下降,白细胞介素17表达量无明显差异;③结果提示,静压力可促使牙周膜成纤维细胞分泌白细胞介素17和白细胞介素6,且白细胞介素6的分泌可能与p38 MAPK信号通路有关,但不足以证明该通路参与静压力对牙周膜成纤维细胞诱导白细胞介素17的表达。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-3542-7146(唐海芳)
背景:研究表明p38 MAPK通路在炎症因子的合成中起到重要作用,但对正畸牙移动过程牙周膜成纤维细胞中p38 MAPK信号通路与白细胞介素17、白细胞介素6等炎性因子关系的相关报道较少。
目的:分析人牙周膜成纤维细胞加载持续性静压力后在合成炎症因子白细胞介素6、白细胞介素17过程与p38 MAPK的关系,探讨p38 MAPK信号通路对白细胞介素17和白细胞介素6表达的影响。
方法:①取年龄在11-15岁正畸者需要拔除的新鲜第一、二前磨牙的牙周组织(正畸者及其监护人均知情同意),体外培养牙周膜成纤维细胞,建立细胞重力加载模型;②细胞种板,分别加力0,1,2,4 g/cm2,每加力组分别加力5,15,30和60 min,检测p38 MAPK蛋白表达;③取第4代细胞接种后,随机分为6组:空白组、加二甲基亚砜组、加抑制剂组(p38 MAPK阻断剂SB203580)、加力组、加力+二甲基亚砜组、加力+抑制剂组,对细胞预处理60 min,通过定量RT-qPCR和酶联免疫吸附法(ELISA)检测牙周膜成纤维细胞受4 g/cm2压力刺激后白细胞介素17和白细胞介素6的mRNA和蛋白水平。
结果与结论:①2 g/cm2组、4 g/cm2组p38 MAPK磷酸化蛋白表达变化随时间的延长而增加:30 min时表达量最高,60 min时开始减少;②与未加力的3组相比,加力组的白细胞介素17和白细胞介素6表达量上调,加抑制剂组的白细胞介素6表达量下降,白细胞介素17表达量无明显差异;③结果提示,静压力可促使牙周膜成纤维细胞分泌白细胞介素17和白细胞介素6,且白细胞介素6的分泌可能与p38 MAPK信号通路有关,但不足以证明该通路参与静压力对牙周膜成纤维细胞诱导白细胞介素17的表达。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-3542-7146(唐海芳)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg) #br#
文题释义:#br#
细胞静压力:是一种细胞的体外力学,通过重力加载装置,于单层细胞上放置一片盖玻片,再在玻片上加载重物,通过玻片传递,使细胞承受均匀单一的压应力。该装置设计简单,操作方便,却能使单层细胞顶-底向单向受力,力值可靠,且细胞体外培养环境不受其影响,静压力加载时间不受限制。#br#
p38 MAPK:属于应激性蛋白激酶,在G蛋白偶联受体、应力刺激、炎症因子等作用下可激活p38 MAPK,活化的p38 MAPK从胞质进入胞核内,为应激条件下的炎症反应、细胞免疫调节、细胞凋亡过程的做出应答。p38 MAPK通路信号通路与炎症反应及其分泌调控机制关系密切,是哺乳动物细胞信号通路中的经典途径,趋化因子、炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子、环氧合酶2等的产生都有赖于p38通路的调控。#br#
#br#
#br#
文题释义:#br#
细胞静压力:是一种细胞的体外力学,通过重力加载装置,于单层细胞上放置一片盖玻片,再在玻片上加载重物,通过玻片传递,使细胞承受均匀单一的压应力。该装置设计简单,操作方便,却能使单层细胞顶-底向单向受力,力值可靠,且细胞体外培养环境不受其影响,静压力加载时间不受限制。#br#
p38 MAPK:属于应激性蛋白激酶,在G蛋白偶联受体、应力刺激、炎症因子等作用下可激活p38 MAPK,活化的p38 MAPK从胞质进入胞核内,为应激条件下的炎症反应、细胞免疫调节、细胞凋亡过程的做出应答。p38 MAPK通路信号通路与炎症反应及其分泌调控机制关系密切,是哺乳动物细胞信号通路中的经典途径,趋化因子、炎症因子如肿瘤坏死因子、环氧合酶2等的产生都有赖于p38通路的调控。#br#
#br#