中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (9): 1390-1396.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1612
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
大黄游离蒽醌对脂肪干细胞移植治疗大鼠急性胰腺炎的影响
郑俊杰1,田伟军2,王金峰3,叶 奎4
- 天津市第四中心医院,1肝胆胃肠外科,4血管外科,天津市 300140;2天津医科大学总医院普外科,天津市 300052;3辽宁电力中心医院外二科,辽宁省沈阳市 110000
Effect of rhubarb-free anthraquinone in the treatment of acute pancreatitis with adipose-derived stem cell transplantation in rats
Zheng Junjie1, Tian Weijun2, Wang Jinfeng3, Ye Kui4
- 1Department of Hepatobiliary and Gastrointestinal Surgery, 4Department of Vascular Surgery, Tianjin 4th Central Hospital, Tianjin 300140, China; 2Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300052, China; 3Second Department of Surgery, Liaoning Electric Power Center Hospital, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义: 大黄游离蒽醌:是提取自中药大黄的一种羟基蒽醌类化合物,研究表明其在治疗急性胰腺炎方面效果显著。 脂肪干细胞移植:移植的脂肪干细胞可归巢到损伤的胰腺组织,并表达胰腺组织表面的标记物,发挥胰腺组织功能,起到治疗急性胰腺炎的作用。
摘要
背景:研究表明大黄游离蒽醌能够保护肠黏膜细胞结构和功能的稳定,但尚未有将其与脂肪干细胞联合治疗大鼠急性胰腺炎的报道。
目的:观察并探讨大黄游离蒽对脂肪干细胞移植治疗大鼠急性胰腺炎的影响及其机制。
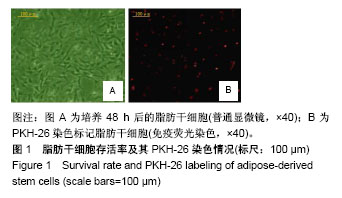
方法:体外快速复苏并培养购自中国医学科学院的冻存鼠脂肪干细胞,随后采用MTT比色法测定脂肪干细胞的细胞存活率并行PKH-26标记。将北京维通利华动物实验技术有限公司提供的SD大鼠随机平均分为4组,病理模型组大鼠采用肠壁穿刺逆行胰胆管注射体积分数5%牛黄胆酸钠建立急性胰腺炎病理模型,然后尾静脉注射0.5 mL的L-DMEM完全培养液;大黄游离蒽组建模后给予大黄游离蒽醌200 mg/kg灌胃;脂肪干细胞组建模后尾静脉注射0.5 mL细胞浓度1×107 L-1脂肪干细胞;联合治疗组建模后同时给予以上2种干预。各个实验组中所有干预治疗措施每日进行1次且连续治疗3 d。
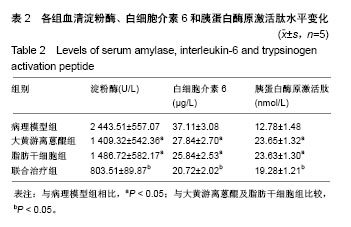
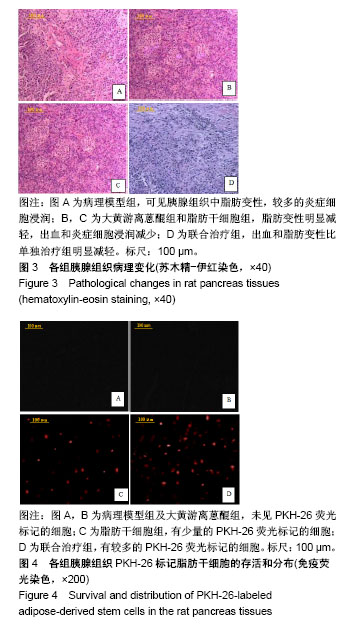
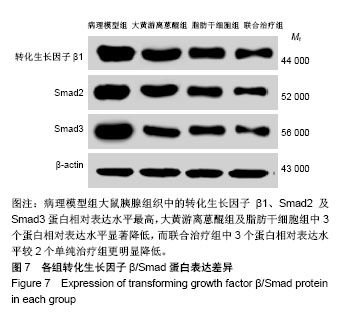
结果与结论:①与理模型组的大鼠相比,大黄游离蒽醌组和脂肪干细胞组大鼠血清淀粉酶活性以及白细胞介素6水平显著降低(P < 0.05),胰蛋白酶原激活肽水平显著升高(P < 0.05);经过脂肪干细胞移植和大黄游离蒽醌灌胃处理联合治疗,上述3指标水平较大黄游离蒽醌组和脂肪干细胞组进一步降低(P < 0.05);②苏木精-伊红染色结果显示,此2个单独治疗组大鼠胰腺组织中脂肪变性、出血、细胞坏死及炎症细胞浸润等病理变化程度均有明显减轻,联合治疗组中大鼠的病理变化的缓解程度则更为明显;③荧光显微镜下观察可见,PKH-26标记的阳性细胞数联合治疗组最多,脂肪干细胞组次之,而在大黄游离蒽组及病理模型组则未见(P < 0.05);④TUNEL法检测可见,与病理模型组比较,2个单独治疗组中胰腺组织中的细胞凋亡数明显降低,联合治疗组进一步降低(P < 0.01);⑤RT-PCR和Western blot法检测显示,病理模型组大鼠胰腺组织转化生长因子β1及Smad2/3基因和蛋白表达最高,联合治疗组最低(P < 0.01),而2个单独干预组均较病理模型组显著较低(P < 0.05);⑥结果证实,大黄游离蒽干预联合脂肪干细胞移植治疗大鼠急性胰腺炎可以有效改善模型大鼠急性胰腺炎的血液生化指标水平;并可明显地缓解急性胰腺炎模型大鼠炎症反应程度和胰腺组织形态学病变以及胰腺细胞的凋亡,这可能与降低转化生长因子β/Smad信号通路有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0003-1683-6067(郑俊杰)
中图分类号:

.jpg)
.jpg)