中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (32): 5215-5221.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0853
• 组织构建基础实验 basic experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
耐力运动者白细胞介素6基因多态性与血清白细胞介素6水平的关联
陈俊飞1,2,严 翊1,郭建军3,孙明晓4,汤 强2,谢敏豪5
- 1北京体育大学运动人体科学学院,北京市 100084;2江苏省体育科学研究所,江苏省南京市 210033;3国家体育总局体育科学研究所,北京市 100061;4北京医院,北京市 100005;5国家体育总局运动医学研究所,北京市 100061
Association of interleukin-6 polymorphism with serum level of interleukin-6 in endurance athletes
Chen Jun-fei1, 2, Yan Yi1, Guo Jian-jun3, Sun Ming-xiao4, Tang Qiang2, Xie Min-hao5
- 1Sport Science College, Beijing Sport University,Beijing 100084, China; 2Jiangsu Research Institute of Sports Science, Nanjing 210033, Jiangsu Province, China; 3China Institute of Sport Science, Beijing 100061, China; 4Beijing Hospital, Beijing 100005, China; 5National Institute of Sports Medicine, Beijing 100061, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
耐力性运动:又称有氧运动,是运动处方最主要和最基本的运动手段。在治疗性运动处方和预防性运动处方中,主要用于心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的慢性疾病的康复和预防,以改善和提高心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的功能。在健身、健美运动处方中,耐力性(有氧)运动是保持全面身心健康、保持理想体质量的有效运动方式。
H-W平衡:即:Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium,是指对于一个大且随机交配的种群,基因频率和基因型频率在没有迁移、突变和选择的条件下会保持不变。该检验的意义在于对抽样调查的结果进行检验,评估所研究的对象群体是否符合H-W平衡,从而评估抽样调查资料的可靠性。
文题释义:
耐力性运动:又称有氧运动,是运动处方最主要和最基本的运动手段。在治疗性运动处方和预防性运动处方中,主要用于心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的慢性疾病的康复和预防,以改善和提高心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的功能。在健身、健美运动处方中,耐力性(有氧)运动是保持全面身心健康、保持理想体质量的有效运动方式。
H-W平衡:即:Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium,是指对于一个大且随机交配的种群,基因频率和基因型频率在没有迁移、突变和选择的条件下会保持不变。该检验的意义在于对抽样调查的结果进行检验,评估所研究的对象群体是否符合H-W平衡,从而评估抽样调查资料的可靠性。
.jpg) 文题释义:
耐力性运动:又称有氧运动,是运动处方最主要和最基本的运动手段。在治疗性运动处方和预防性运动处方中,主要用于心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的慢性疾病的康复和预防,以改善和提高心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的功能。在健身、健美运动处方中,耐力性(有氧)运动是保持全面身心健康、保持理想体质量的有效运动方式。
H-W平衡:即:Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium,是指对于一个大且随机交配的种群,基因频率和基因型频率在没有迁移、突变和选择的条件下会保持不变。该检验的意义在于对抽样调查的结果进行检验,评估所研究的对象群体是否符合H-W平衡,从而评估抽样调查资料的可靠性。
文题释义:
耐力性运动:又称有氧运动,是运动处方最主要和最基本的运动手段。在治疗性运动处方和预防性运动处方中,主要用于心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的慢性疾病的康复和预防,以改善和提高心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的功能。在健身、健美运动处方中,耐力性(有氧)运动是保持全面身心健康、保持理想体质量的有效运动方式。
H-W平衡:即:Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium,是指对于一个大且随机交配的种群,基因频率和基因型频率在没有迁移、突变和选择的条件下会保持不变。该检验的意义在于对抽样调查的结果进行检验,评估所研究的对象群体是否符合H-W平衡,从而评估抽样调查资料的可靠性。摘要
背景:人的有氧耐力具有很高的遗传度,随着分子生物技术的发展,通过分子遗传标记的筛选,对基因诊断和预测有氧耐力具有重要的价值。
目的:分析耐力运动者白细胞介素6基因单核苷酸多态性位点的分布特征,探讨其是否可以作为分子遗传标记?以及白细胞介素6基因多态性是否与血清白细胞介素6水平存在关联?
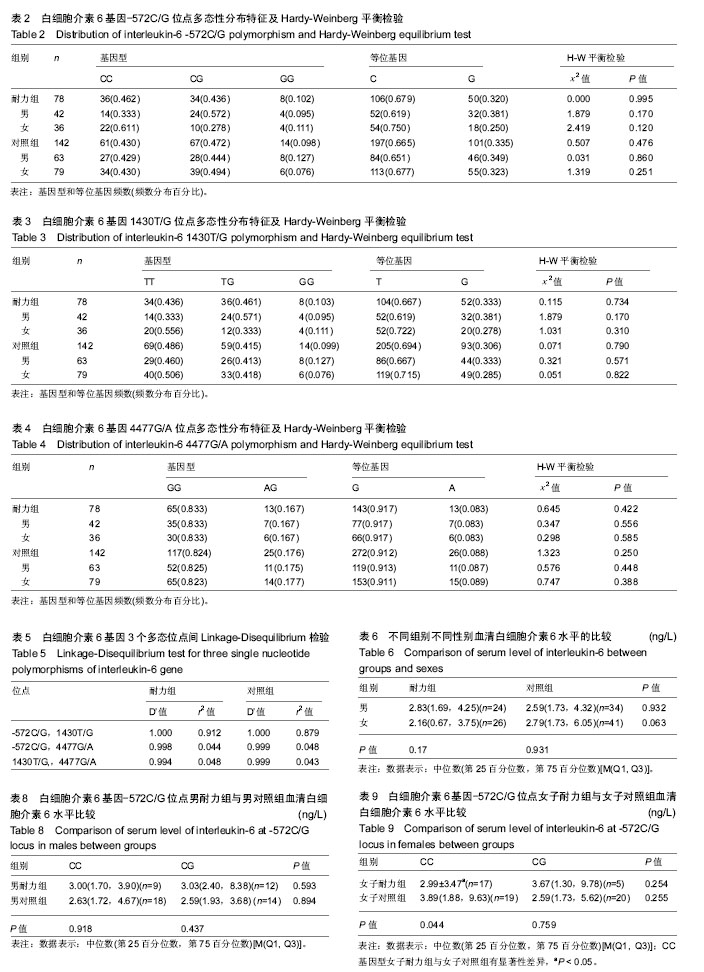
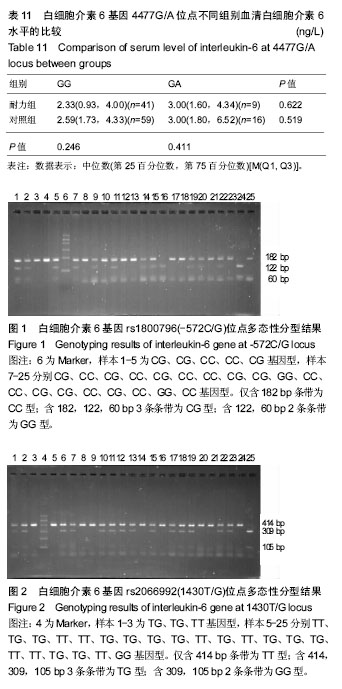
方法:选取两组研究对象:①耐力组:从事耐力性项目(中、长跑,马拉松,竞走等)至少2年,且运动等级至少二级的北方平原汉族运动员,共78人;②对照组:北京市城区某中学学生(非肥胖或低体质量,12-15岁),共142人,父母及其本人均为北方平原汉族人。运用PCR-RFLP方法对白细胞介素6基因rs1800796 (-572C/G)、rs2066992(1430T/G)、rs13306436(4477G/A)3个单核苷酸多态性位点进行等位基因分型;用ELISA法检测血清白细胞介素6水平。
结果与结论:①耐力组-572C/G位点基因型分布存在性别差异(P < 0.05),但女子耐力组与女子对照组基因型分布相比,P=0.095。其中,女子耐力组CC基因型占61.1%,CG+GG基因型占38.9%;女子对照组CC基因型占43.0%,CG+GG基因型占57.0%;②女子耐力组-572C/G位点CC基因型运动员血清白细胞介素6水平低于女子对照组(P < 0.05)。另外,耐力组-572C/G位点CC基因型运动员血清白细胞介素6水平有低于对照组的趋势,P=0.070;③结果说明,白细胞介素6基因rs1800796多态性位点是女子耐力运动员的分子遗传标记。白细胞介素6基因rs1800796多态性位点CC基因型女子运动员血清白细胞介素6水平低于女子对照组。白细胞介素6基因rs1800796、 rs2066992、rs13306436位点不能作为男性运动员的遗传分子标记,可能与样本量不够大有关,尚需进一步的研究。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-6854-3859(陈俊飞)
中图分类号:

.jpg) 文题释义:
耐力性运动:又称有氧运动,是运动处方最主要和最基本的运动手段。在治疗性运动处方和预防性运动处方中,主要用于心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的慢性疾病的康复和预防,以改善和提高心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的功能。在健身、健美运动处方中,耐力性(有氧)运动是保持全面身心健康、保持理想体质量的有效运动方式。
H-W平衡:即:Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium,是指对于一个大且随机交配的种群,基因频率和基因型频率在没有迁移、突变和选择的条件下会保持不变。该检验的意义在于对抽样调查的结果进行检验,评估所研究的对象群体是否符合H-W平衡,从而评估抽样调查资料的可靠性。
文题释义:
耐力性运动:又称有氧运动,是运动处方最主要和最基本的运动手段。在治疗性运动处方和预防性运动处方中,主要用于心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的慢性疾病的康复和预防,以改善和提高心血管、呼吸、内分泌等系统的功能。在健身、健美运动处方中,耐力性(有氧)运动是保持全面身心健康、保持理想体质量的有效运动方式。
H-W平衡:即:Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium,是指对于一个大且随机交配的种群,基因频率和基因型频率在没有迁移、突变和选择的条件下会保持不变。该检验的意义在于对抽样调查的结果进行检验,评估所研究的对象群体是否符合H-W平衡,从而评估抽样调查资料的可靠性。