| [1] Barkauskas CE, Cronce MJ, Rackley CR, et al. Type 2 alveolar cells are stem cells in adult lung. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(7): 3025-3036.[2] Volckaert T, De Langhe S. Lung epithelial stem cells and their niches: Fgf10 takes center stage. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2014;7: 1-15.[3] Avellino R, Delwel R. Expression and regulation of C /EBPα in normal myelopoiesis and in malignant transformation. Blood. 2017;129(15):2083 -2091.[4] Xue M, Li X, Chen W. Hypoxia regulates the expression and localization of CCAAT / enhancer binding protein α by hypoxia inducible factor-1α in bladder transitional carcinoma cells . Mol Med Rep. 2015;12(2):2121-2127.[5] Zhong F,Wang W,Lee K,et al. Role of C/EBP-α in Adriamycin-induced podocyte injury. Sci Rep. 2016;6:33520.[6] Roos AB, Berg T, Barton JL, et al. Airway epithelial cell differentiation during lung organogenesis requires C/EBPα and C/EBPβ.Dev Dyn.2012;241(5):911-923.[7] Berg T, Didon L, Nord M.Ectopic expression of C/EBPalpha in the lung epithelium disrupts late lung development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2006; 291(4): L683-L693.[8] Siebel C, Lendahl U.Notch Signaling in Development, Tissue Homeostasis, and Disease. Physiol Rev. 2017; 97(4):1235-1294.[9] Tsao PN, Matsuoka C, Wei SC, et al. Epithelial Notch signaling regulates lung alveolar morphogenesis and airway epithelial integrity. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2016;113(29):8242-8247. [10] Kageyama R, Ohtsuka T, Kobayashi T, et al. The Hes gene family: repressors and oscillators that orchestrate embryogenesis. Development. 2007;134(7):1243-1251. [11] De Obaldia ME, Bell JJ, Wang X, et al. T cell development requires constraint of the myeloid regulator C/EBPα by the Notch target and transcriptional repressor Hes1. Nat Immunol. 2013; 14(12):1277-1284.[12] 卢衍敏,卢红艳,刘姜艳,等. 高氧调节早产大鼠肺泡Ⅱ型上皮细胞CCAAT增强子结合蛋白α和肺泡表面活性蛋白的表达[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2017,33(6):767-771.[13] Muguruma Y, Yahata T, Warita T,et al. Jagged1-induced Notch activation contributes to the acquisition of bortezomib resistance in myeloma cells.Blood Cancer. 2017;15;7(12):650.[14] 江超,郅淑引,刘谈珍,等.mi R-25抑制剂对肺腺癌细胞A549/DDP作用的初步研究[J].中华临床医师杂志, 2016,10(11):1574-1579.[15] 范伟明,姚志成,徐见亮,等.STEAP3对肝癌细胞增殖能力的抑制作用及机制[J].中华肝脏外科手术学电子杂志, 2017,6(2):134-138.[16] 黄团结,宋及时,马珊珊,等.重组人MG53蛋白对人脐带间充质干细胞氧化损伤的保护作用[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志,2017,7(1):35-44.[17] Raina S, Preston GM, Guggino WB, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of an aquaporin cDNA from salivary, lacrimal, and respiratory tissues. J Biol Chem.1995; 270(4):1908-1912.[18] O'Reilly MA. Giving new identities to alveolar epithelial type I cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.2017;56(3):277-278. [19] Desai TJ, Brownfield DG, Krasnow MA. Alveolar progenitor and stem cells in lung development, renewal and cancer. Nature. 2014;507:190-194.[20] Hou A, Fu J, Yang H, et al. Hyperoxia stimulates the transdifferentiation of type Ⅱ alveolar epithelial cells in newborn rats . Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2015; 308(9):L861-L872.[21] Zhang QY,Fu JH, Xue XD.Expression and function of aquaporin-1 in hyperoxia-exposed alveolar epithelial type II cell.Exp Ther Med.2014;8:493-498.[22] McGrath-Morrow SA, Stahl J. Apoptosis in neonatal murine lung exposed to hyperoxia. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.2001;25: 150-155.[23] O’Reilly MA, Staversky RJ, Finkelstein JN, et al. Activation of the G2 cell cycle checkpoint enhances survival of epithelial cells exposed to hyperoxia. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2003; 284:L368-L375.[24] 刘春梅,常立文,李文斌,等.Notch2、Notch4在大鼠肺发育中的动态表达[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2006,21(2):71-73.[25] Taichman DB,Loomes KM,Schachtner SK,et al.Notch1 and Jagged1 expression by the developing pulmonary vasculature. Dev Dyn.2002;225:166-175.[26] Hussain M, Xu C, Ahmad M, et al. Notch signaling; linking embryonic lung development and asthmatic airway remodeling. Mol Pharmacol.2017;92(6):676-693.[27] Xu J, Chi F, Guo T,et al.NOTCH reprograms mitochondrial metabolism for proinflammatory macrophage activation. J Clin Invest.2015;125:1579-1590.[28] Xu K, Moghal N,Egan S. E. Notch signaling in lung development and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol.2012;727:89-98.[29] 张谦慎,常立文,刘汉楚,等. Notch信号在新生鼠高氧肺损伤中的表达[J].中华围产医学杂志,2004,7(5):305-307.[30] 汪鸿,常立文,李文斌,等.Notch受体在早产鼠高氧肺损伤中的动态表达[J].实用儿科临床杂志,2006,21(6):328-330.[31] 汪鸿,常立文,卢红艳,等.高氧对胎鼠肺泡II型上皮细胞Notch 受体的影响[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2008,17(11):1158-62.[32] Sang L, Roberts JM, Coller HA. Hijacking HES1: How tumors co-opt the anti-differentiation strategies of quiescent cells.Trends Mol Med. 2010;16(1):17-26. [33] Cassel TN, Nord M. C/EBP transcription factors in the lung epithelium. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2003;285(4): L773- L781.[34] Didon L, Roos AB, Elmberger GP, et al.Lung-specific inactivation of CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha causes a pathological pattern characteristic of COPD. Eur Respir J.2010;35:186-197.[35] Miglino N, Roth M, Tamm M,et al. Asthma and COPD-The C/EBP connection. Open Respir Med J.2012;6:1-13.[36] Timchenko NA, Harris TE, Wilde M, et al. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-α regulates p21 protein and hepatocyte proliferation in newborn mice.Mol Cell Biol.1997;17:7353-7361. [37] Wang H, Iakova P, Wilde M,et al. C/EBPα arrests cell proliferation through direct inhibition of Cdk2 and Cdk4. Mol Cell.2001;8: 817-828. [38] Sato A, Yamada N, Ogawa Y, et al. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-α suppresses lung tumor development in mice through the p38α MAP kinase pathway. PLoS One.2013;8 (2):e57013.[39] Martis PC, Whitsett JA, Xu Y, et al. C/EBP {alpha} is required for lung maturation at birth. Development.2006;133(6):1155-1164.[40] Chen YD,Liu JY,Lu YM,et al.Functional roles of C/EBPα and SUMO-modification in lung development.Int J Mol Med.2017; 40(4):1037-1046.[41] Yang G, Hinson MD, Bordner JE, et al.Silencing hyperoxia-induced C/EBPα in neonatal mice improves lung architecture via enhanced proliferation of alveolar epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2011;301(2):L187-L196.[42] Xu Y, Saegusa C, Schehr A, et al.C/EBPα is required for pulmonary cytoprotection during hyperoxia.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2009;297(2):L286-L298.[43] Cook BD, Evans T. BMP signaling balances murine myeloid potential through SMAD-independent p38MAPK and NOTCH pathways.Blood.2014;124(3):393-402.[44] Bai YX, Fang F, Jiang JL,et al.Extrinsic Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Inhibits Hyperoxia-Induced Alveolar Epithelial Type II Cells Apoptosis, Oxidative Stress, and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) Production by Enhancing Notch 1 and Homocysteine-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Protein (HERP) Expression.Med Sci Monit.2017;23:5774-5782.[45] Wang H, Chang L, Li W. Temporal expression of Notch in preterm rat lungs exposed to hyperoxia. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.2005;25:159-161. [46] Yee M, Vitiello PF, Roper JM, et al. Type II epithelial cells are critical target for hyperoxia-mediated impairment of postnatal lung development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.2006;291: L1101–L1111.[47] Tshori S, Nechushtan H.Mast cell transcription factors--regulators of cell fate and phenotype. Biochim Biophys Acta.2012;1822(1): 42-48.[48] Liu H, Xiong Y, Zhu X,et al.Icariin improves osteoporosis, inhibits the expression of PPARγ, C/EBPα, FABP4 mRNA, N1ICD and jagged1 proteins, and increases Notch2 mRNA in ovariectomized rats.Exp Ther Med.2017;13(4):1360-1368. [49] Lai PY, Tsai CB, Tseng MJ, et al. Active form Notch4 promotes the proliferation differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commum.2013;430(3):1132-1139. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
C/EBPα:CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白α(CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha,C/EBPα)是亮氨酸拉链转录因子家族成员之一,在细胞增殖、分化、信号传导、肿瘤发生以及机体的免疫、应激反应、能量代谢、血液生成等方面发挥重要作用。在肺泡上皮细胞中,C/EBPα可调节其增殖与分化,并促进肺表面活性物质生成,从而促进肺发育。
Notch1/Hes1信号:Notch信号通路是一条进化上十分保守的信号转导系统,由受体、配体和DNA结合蛋白3部分组成。Notch配体与受体相互作用,Notch蛋白经过3次剪切,由胞内段释放入胞质,并进入细胞核与转录因子CSL结合, 形成NICD/CSL转录激活复合体,从而激活Hes1等碱性-螺旋-环-螺旋(basichelix-loop-helix,bHLH)转录因子家族的靶基因,发挥生物学作用。Notch受体通过与配体的相互作用传导细胞信号,在多种组织和器官的早期发育过程中以及细胞增殖、分化、凋亡中发挥重要调控作用。
文题释义:
C/EBPα:CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白α(CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha,C/EBPα)是亮氨酸拉链转录因子家族成员之一,在细胞增殖、分化、信号传导、肿瘤发生以及机体的免疫、应激反应、能量代谢、血液生成等方面发挥重要作用。在肺泡上皮细胞中,C/EBPα可调节其增殖与分化,并促进肺表面活性物质生成,从而促进肺发育。
Notch1/Hes1信号:Notch信号通路是一条进化上十分保守的信号转导系统,由受体、配体和DNA结合蛋白3部分组成。Notch配体与受体相互作用,Notch蛋白经过3次剪切,由胞内段释放入胞质,并进入细胞核与转录因子CSL结合, 形成NICD/CSL转录激活复合体,从而激活Hes1等碱性-螺旋-环-螺旋(basichelix-loop-helix,bHLH)转录因子家族的靶基因,发挥生物学作用。Notch受体通过与配体的相互作用传导细胞信号,在多种组织和器官的早期发育过程中以及细胞增殖、分化、凋亡中发挥重要调控作用。.jpg) 文题释义:
C/EBPα:CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白α(CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha,C/EBPα)是亮氨酸拉链转录因子家族成员之一,在细胞增殖、分化、信号传导、肿瘤发生以及机体的免疫、应激反应、能量代谢、血液生成等方面发挥重要作用。在肺泡上皮细胞中,C/EBPα可调节其增殖与分化,并促进肺表面活性物质生成,从而促进肺发育。
Notch1/Hes1信号:Notch信号通路是一条进化上十分保守的信号转导系统,由受体、配体和DNA结合蛋白3部分组成。Notch配体与受体相互作用,Notch蛋白经过3次剪切,由胞内段释放入胞质,并进入细胞核与转录因子CSL结合, 形成NICD/CSL转录激活复合体,从而激活Hes1等碱性-螺旋-环-螺旋(basichelix-loop-helix,bHLH)转录因子家族的靶基因,发挥生物学作用。Notch受体通过与配体的相互作用传导细胞信号,在多种组织和器官的早期发育过程中以及细胞增殖、分化、凋亡中发挥重要调控作用。
文题释义:
C/EBPα:CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白α(CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha,C/EBPα)是亮氨酸拉链转录因子家族成员之一,在细胞增殖、分化、信号传导、肿瘤发生以及机体的免疫、应激反应、能量代谢、血液生成等方面发挥重要作用。在肺泡上皮细胞中,C/EBPα可调节其增殖与分化,并促进肺表面活性物质生成,从而促进肺发育。
Notch1/Hes1信号:Notch信号通路是一条进化上十分保守的信号转导系统,由受体、配体和DNA结合蛋白3部分组成。Notch配体与受体相互作用,Notch蛋白经过3次剪切,由胞内段释放入胞质,并进入细胞核与转录因子CSL结合, 形成NICD/CSL转录激活复合体,从而激活Hes1等碱性-螺旋-环-螺旋(basichelix-loop-helix,bHLH)转录因子家族的靶基因,发挥生物学作用。Notch受体通过与配体的相互作用传导细胞信号,在多种组织和器官的早期发育过程中以及细胞增殖、分化、凋亡中发挥重要调控作用。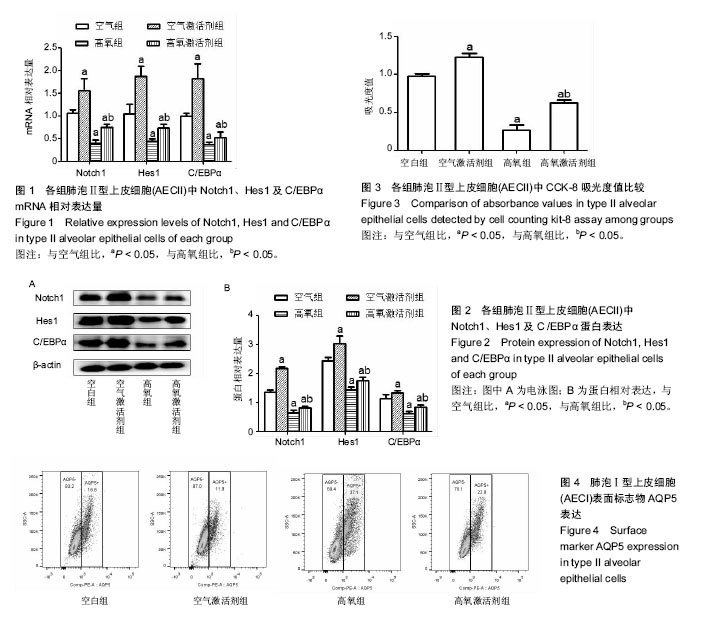
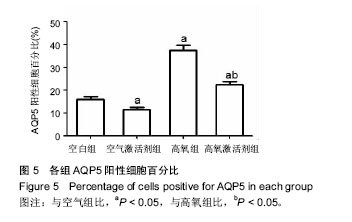
.jpg) 文题释义:
C/EBPα:CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白α(CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha,C/EBPα)是亮氨酸拉链转录因子家族成员之一,在细胞增殖、分化、信号传导、肿瘤发生以及机体的免疫、应激反应、能量代谢、血液生成等方面发挥重要作用。在肺泡上皮细胞中,C/EBPα可调节其增殖与分化,并促进肺表面活性物质生成,从而促进肺发育。
Notch1/Hes1信号:Notch信号通路是一条进化上十分保守的信号转导系统,由受体、配体和DNA结合蛋白3部分组成。Notch配体与受体相互作用,Notch蛋白经过3次剪切,由胞内段释放入胞质,并进入细胞核与转录因子CSL结合, 形成NICD/CSL转录激活复合体,从而激活Hes1等碱性-螺旋-环-螺旋(basichelix-loop-helix,bHLH)转录因子家族的靶基因,发挥生物学作用。Notch受体通过与配体的相互作用传导细胞信号,在多种组织和器官的早期发育过程中以及细胞增殖、分化、凋亡中发挥重要调控作用。
文题释义:
C/EBPα:CCAAT/增强子结合蛋白α(CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha,C/EBPα)是亮氨酸拉链转录因子家族成员之一,在细胞增殖、分化、信号传导、肿瘤发生以及机体的免疫、应激反应、能量代谢、血液生成等方面发挥重要作用。在肺泡上皮细胞中,C/EBPα可调节其增殖与分化,并促进肺表面活性物质生成,从而促进肺发育。
Notch1/Hes1信号:Notch信号通路是一条进化上十分保守的信号转导系统,由受体、配体和DNA结合蛋白3部分组成。Notch配体与受体相互作用,Notch蛋白经过3次剪切,由胞内段释放入胞质,并进入细胞核与转录因子CSL结合, 形成NICD/CSL转录激活复合体,从而激活Hes1等碱性-螺旋-环-螺旋(basichelix-loop-helix,bHLH)转录因子家族的靶基因,发挥生物学作用。Notch受体通过与配体的相互作用传导细胞信号,在多种组织和器官的早期发育过程中以及细胞增殖、分化、凋亡中发挥重要调控作用。